Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have an increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) events and CV mortality. Carotid subclinical atherosclerosis is independently associated with incident CV event rates amongst patients with RA. The complement system has been linked to the both the etiopathogenesis of RA and CV disease. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the association between a comprehensive assessment of the complement system and carotid intima media thickness and carotid plaque in RA patients.
Methods: 430 patients with RA were recruited. Functional assays of the three pathways of the complement system, utilizing new-generation techniques, were assessed. Additionally, serum levels of individual components of the complement system belonging to the three pathways were measured: C1q (classical), lectin (lectin), C2, C4, and C4b (classical and lectin), factor D and properdin (alternative), C3 and C3a (common), C5, C5a, and C9 (terminal), as well as regulators factor I and C1-inhibitor. Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis by ultrasonography was evaluated. Multivariable linear regression analysis was conducted to investigate the association between the complement system and carotid intima media thickness and plaque.
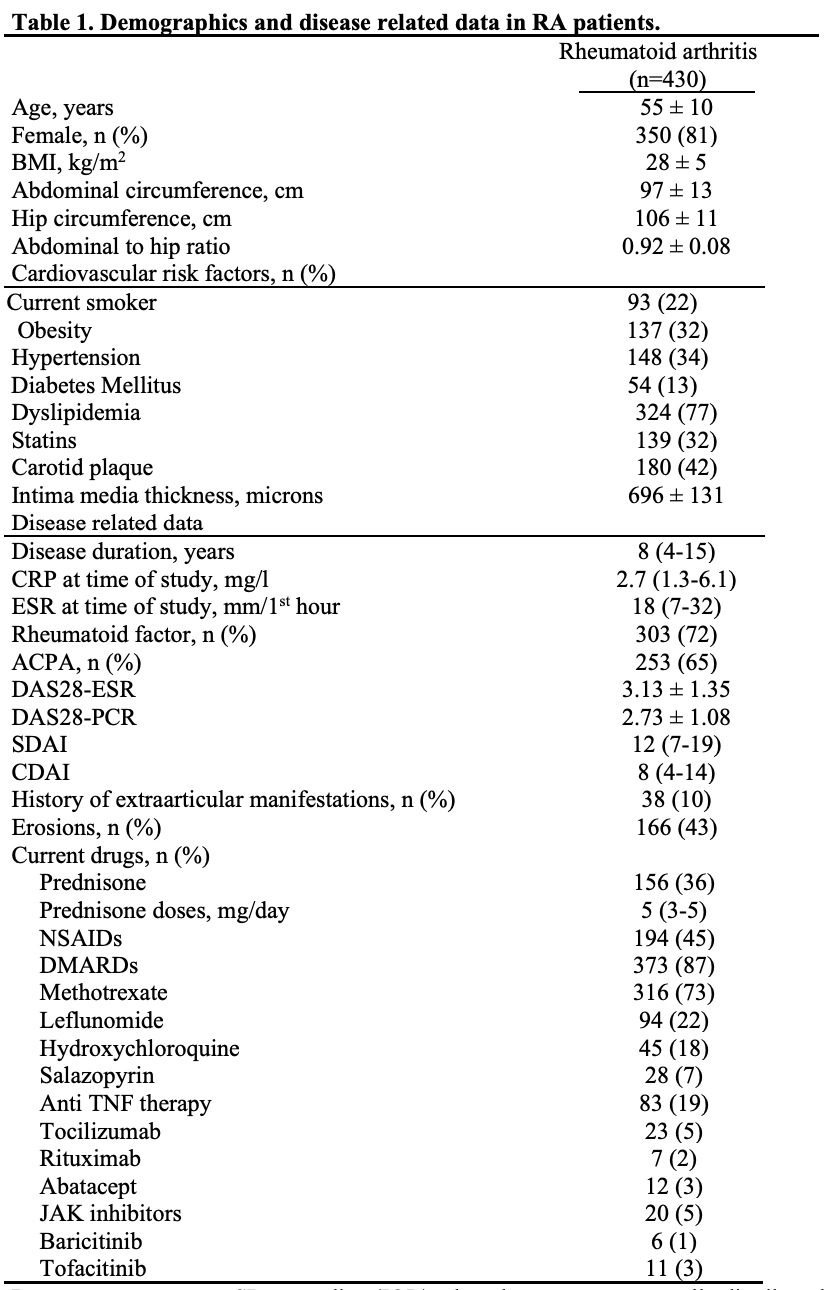
Results: The study population had a mean age of 55 ± 10 years (81% women). Demographic and disease-related characteristics of the participants, frequency of treatment usage, and historical disease-related data are shown in Table 1
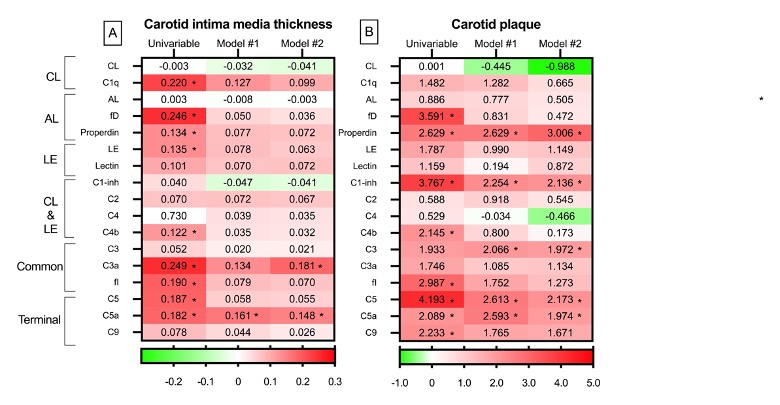
The relation of the complement system to carotid ultrasound evaluation is expressed in Figure 1. Regarding cIMT, many positive associations (red in the heatmap) disclosed statistical significance in the univariable analysis. After multivariable analysis that included demographics and traditional CV factors (Model #1 in Figure 1-A), many significant associations were lost (red color decreased in the heatmap). Only C5a maintained a significant and positive relation to cIMT. Due to potential influences from disease activity, medications, and various other factors related to the disease, we conducted an additional multivariable analysis (Model #2 in Figure 1-A). Remarkably, C3a and C5a continued to exhibit a positive and significant relation to cIMT after this full adjustment.
The analysis of the relation between complement system and carotid plaque yielded similar results to the ones of cIMT in the univariable analysis (Figure 1-B). However, after adjustment for age, sex, abdominal circumference, hypertension, diabetes, the use of statins (Model #1 in Figure 1-B), and disease duration, ESR, ACPA positivity and the utilization of NSAIDs and hydroxychloroquine (Model #2 in Figure 1-B), a higher frequency of significant relations between them were found. In this regard, properdin of the alternative route, C1-inhibitor of the classical and lectin cascades, C3 of the common pathway, and C5 and C5a of the terminal, maintained a significant and positive association with the presence of plaque ( Figure 1-B).
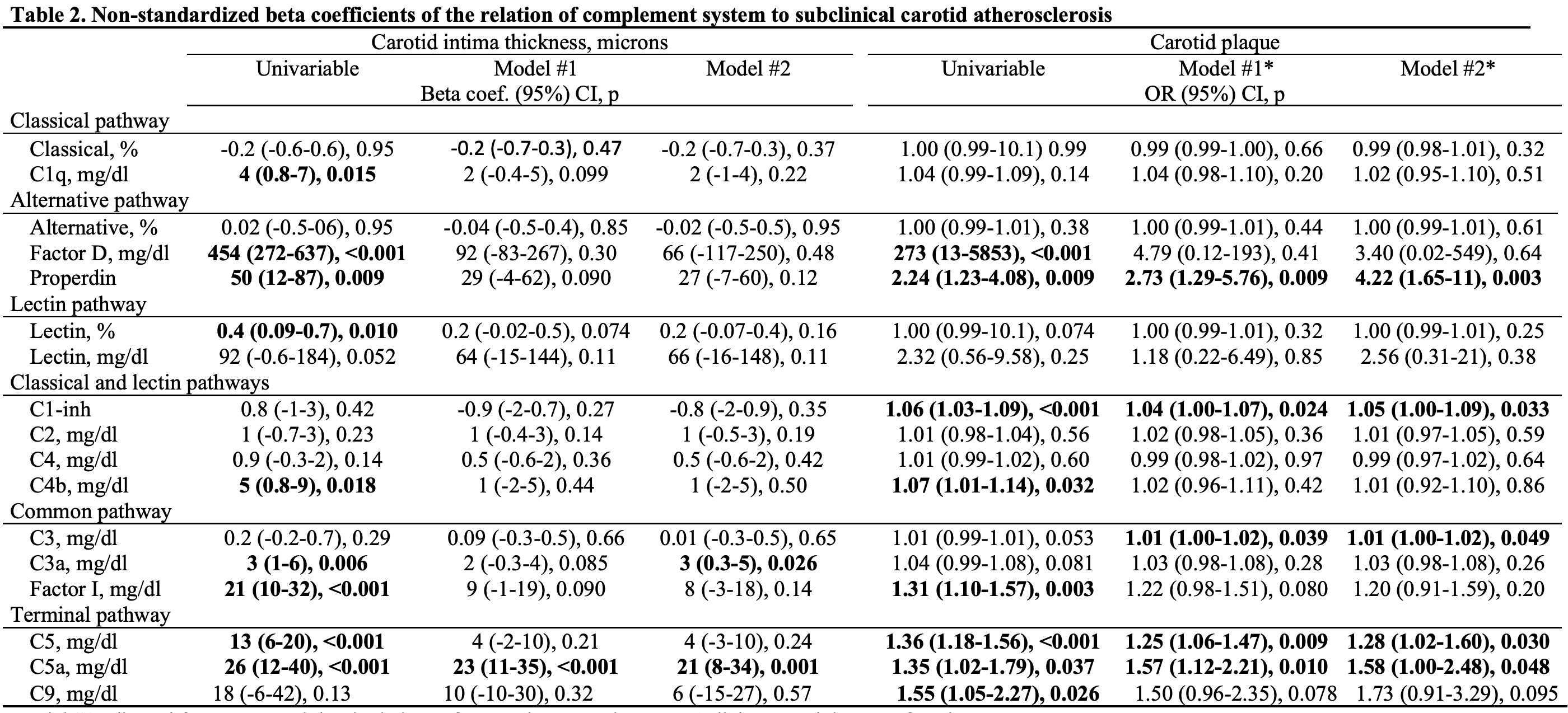
Additionally, non-standardized beta coefficients and odds ratios of the relation of complement system to cIMT and carotid plaque are presented in Table 2.
Conclusion: Complement system and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis are linked in patients with RA.
CRP: C reactive protein; ACPA: Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. NSAID: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; DMARD: disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. TNF: tumor necrosis factor, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; BMI: body mass index; DAS28: Disease Activity Score in 28 joints; CDAI: Clinical Disease Activity Index; SDAI: Simple Disease Activity Index. Dyslipidemia was defined if one of the following was present: total cholesterol > 200 mg/dL, triglycerides > 150 mg/dL, HDL cholesterol < 40 in men or <50 mg/dL in women, or LDL cholesterol > 130 mg/dL.
Model #2 adjusted for Model #1 + rheumatoid factor and the use of NSAIDs, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine and anti-TNF alpha therapies.
Model #1* adjusted for age, sex, abdominal circumference, hypertension, type 2 diabetes and the use of statins.
Model #2* adjusted for Model #1* + disease duration, ESR, ACPA positivity and the utilization of NSAIDs and hydroxychloroquine.
In this analysis complement system is the independent variable and carotid intima media thickness and carotid plaque are the dependent variable.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Quevedo-Rodríguez A, Hernández-Díaz M, Rodríguez-González2 D, Gomez-Bernal F, Quevedo-Abeledo J, González-Rivero A, González López E, Ocejo-Viñals g, Gonzalez-Gay M, Ferraz-Amaro i. Relationship Between the Complement System and Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-the-complement-system-and-subclinical-carotid-atherosclerosis-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-the-complement-system-and-subclinical-carotid-atherosclerosis-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/