Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic fibroinflammatory disorder characterized by elevated serum IgG4 levels and tissue infiltration by IgG4-positive plasma cells. Despite advances in understanding this entity, there is a lack of reliable biomarkers for assessing disease activity and improving follow-up.The aim is to evaluate the role of novel biomarkers, including plasmablasts and the cytokines IL-1β, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, IL-21, and IFN-gamma as well as their respective ratios, in monitoring disease activity. Additionally, to compare them with classical biomarkers used to date.
Methods: An ambispective cohort of patients with IgG4-RD was recruited at a single tertiary care hospital. Inclusion required fulfilling at least one of the established diagnostic criteria: Umehara, Okazaki, or the 2019 ACR/EULAR classification criteria. Clinical variables were collected, including demographic data and initial disease manifestations. Disease activity was assessed using the IgG4-RD Responder Index, blood tests, and physician-determined activity, all evaluated at the same time point upon study inclusion. In patients with an available PET-CT at that time, this was also included as an additional variable.Biomarkers used to assess activity included classical parameters: CRP, ESR, serum IgG4 and total IgG levels (and their ratio), C3, C4, hemoglobin, and eosinophil count. Novel biomarkers included plasmablasts and the cytokines IL-1β (proinflammatory), IL-10 (anti-inflammatory), IL-13 (profibrotic), IFN-gamma (Th1 phenotype), IL-5 (Th2), IL-4 and IL-21 (follicular Th phenotype), as well as their respective ratios.
Results: The study included 35 patients with IgG4-RD, predominantly male (77.14%), with a mean Responder Index of 6.09 (CI 4.63–7.55) (Tabla 1). PET-CT evaluation showed statistically significant correlations with eosinophil count (p=0.03) and the ratios IL-13/IFN-γ (p=0.04), IL-21/IFN-γ (p=0.02), and IFN-γ/IL-4 (p=0.00), highlighting the role of these interleukins in inflammatory processes. Physician-based activity assessment showed a statistically significant correlation only with IgG levels (p=0.01).The Responder Index correlated significantly with IgG (p=0.02), IgG4 (p=0.01), and IL-5 levels (p=0.03), as well as with the IL-10/IL-5 (p=0.05) and IL-21/IL-5 (p=0.05) ratios. Neither CRP nor ESR showed statistically significant associations (Table 2)
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the utility of novel biomarkers in monitoring IgG4-RD activity. The correlation between PET-CT findings and cytokine ratios (IL-13/IFN-γ, IL-21/IFN-γ, IFN-γ/IL-4) supports their role in inflammatory assessment. IgG and IgG4 remain relevant markers correlated with the Responder Index, whereas CRP and ESR showed limited utility. IL-5 stands out as key, especially through its ratios with IL-10 and IL-21, showing significant correlations with disease activity. These findings support an integrative approach combining classical and novel biomarkers (particularly cytokine ratios) to improve disease activity monitoring in IgG4-RD.
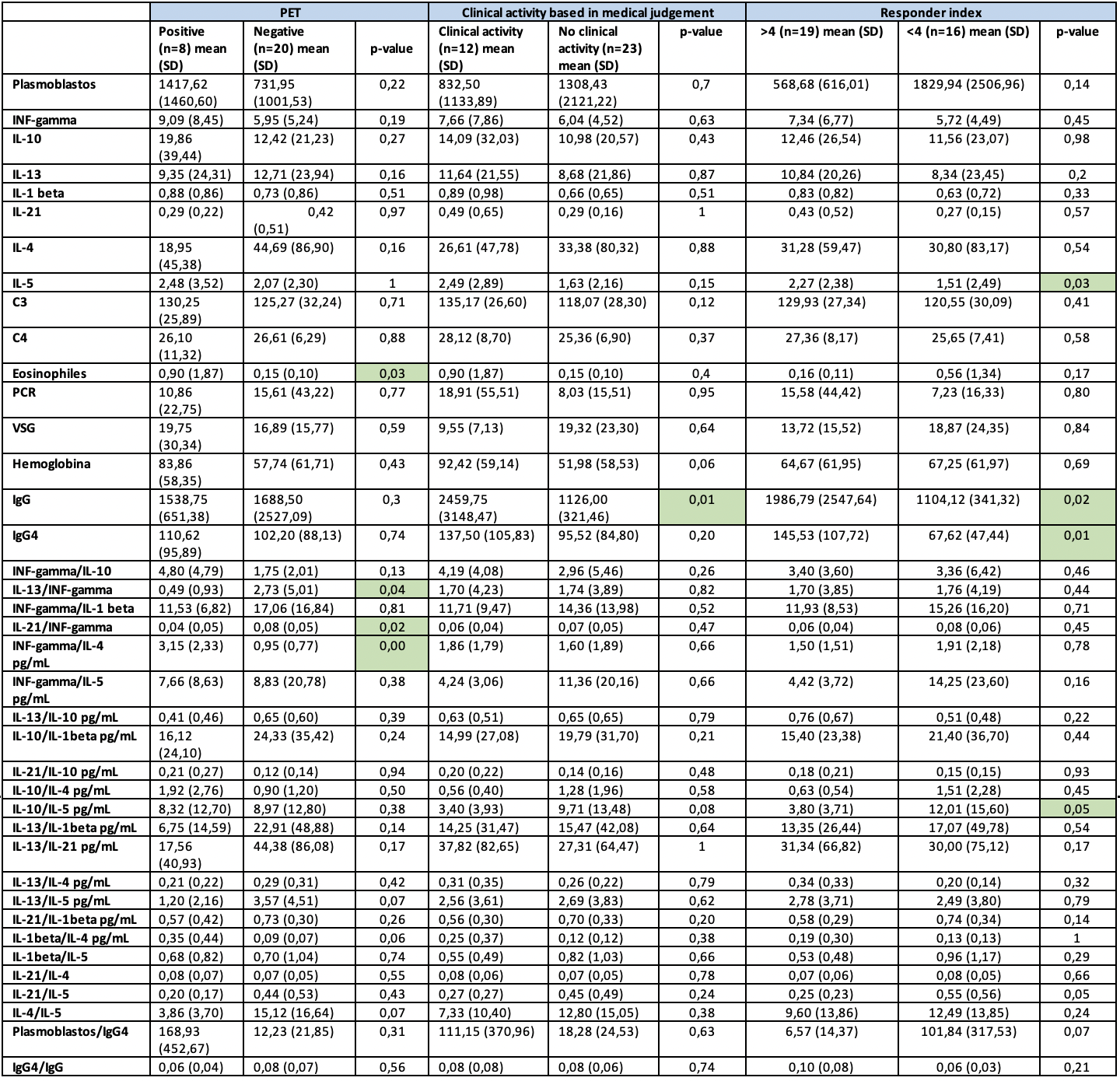 Table 1. Baseline demographic characteristics
Table 1. Baseline demographic characteristics
.jpg) Table 2. Comparative Analysis of Classical and Novel Biomarkers According to PET Findings, Clinical Assessment, and IgG4-RD Responder Index
Table 2. Comparative Analysis of Classical and Novel Biomarkers According to PET Findings, Clinical Assessment, and IgG4-RD Responder Index
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López M, Benito-Melero r, Martinez-Martinez L, Sang-Park H, Calleja s, Codes Mendez H, Martín M, Magallares B, Castellví I, Laiz A, Diaz C, Corominas H. Redefining disease activity assessment in IgG4-Related Disease: The role of classical and novel biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/redefining-disease-activity-assessment-in-igg4-related-disease-the-role-of-classical-and-novel-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/redefining-disease-activity-assessment-in-igg4-related-disease-the-role-of-classical-and-novel-biomarkers/
