Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Cardiopulmonary Aspects
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been shown to be associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality. Red cell distribution width (RDW) represents the variability of red blood cell size. RDW correlates with CVD in the general population as well as in those with spondyloarthritis including psoriatic arthritis. RDW also correlates with RA disease activity as measured by acute phase reactants. We explored the relationship between RDW, CVD and the composite of traditional cardiovascular risk factors, the Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) risk score, in patients with seropositive RA.
Methods: A retrospective chart review study was conducted at the Cleveland VA Medical Center. Medical records were reviewed for RA ICD10 diagnosis in 2017 in patients being treated with MTX monotherapy for seropositive RA (rheumatoid factor (RF) and/or cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody positive (CCP)). Charts were reviewed for demographic information, concomitant diagnoses of diabetes, hypertension, CVD diagnosis and ASCVD risk factors as calculated by the ASCVD 10-Year Risk Score. RDW, C-Reactive Protein (CRP), hemoglobin, platelet count, and albumin were collected prior to the start of MTX, 6 and 12 months into therapy, and at the last time point available. ASCVD Risk Score was calculated both prior to treatment with MTX and at the last available time point. When calculating ASCVD Risk Score, if age or lipid levels were above or below the limitations of the calculator, either the upper or lower limit values were used, respectively. Correlations were analyzed by Spearman’s and differences among groups by Mann-Whitney U (spss v24).
Results: Clinical characteristics of the 95 patients at the start of therapy and at the last available time point are shown in Table 1.
Prior to therapy with MTX: RDW positively correlated with CRP (r=0.3, p=0.007) and negatively correlated with albumin (r= -0.4, p< 0.0001), and hemoglobin (r= -0.4, p< 0.0001), but did not correlate with the ASCVD 10-Year Risk Score (r=0.2, p=0.07) or CVD at any time point (p=0.6).
At the last available time point: RA therapy at this time point is shown in Table 2. RA patients with CVD diagnosis had a higher ASCVD Risk Score (p=0.02). Positive correlations were found between RDW and age (r=0.3, p=0.002), and RDW and ASCVD 10-Year Risk Score (r=0.2, p=0.02) (Figure 1). Those RA patients diagnosed with CVD had higher RDW levels at the last endpoint (p=0.01) compared to RA patients without known CVD.
Conclusion: RDW correlates with ASCVD risk score and CVD in other arthropathies. Here we extend this observation to seropositive RA patients during the first year after the introduction of MTX. RDW prior to initiation of MTX associated with parameters of inflammation, including higher CRP, and lower albumin, but not ASCVD risk score or CVD, perhaps making it limited for pre-screening for CVD at the pre-treatment time point. However, at the last available time point post introduction of therapy, RDW correlated with ASCVD Risk Score and was associated with CVD. Further study of RDW as a biomarker of CVD in seropositive RA is warranted to help identify those patients who need more CVD risk abatement.
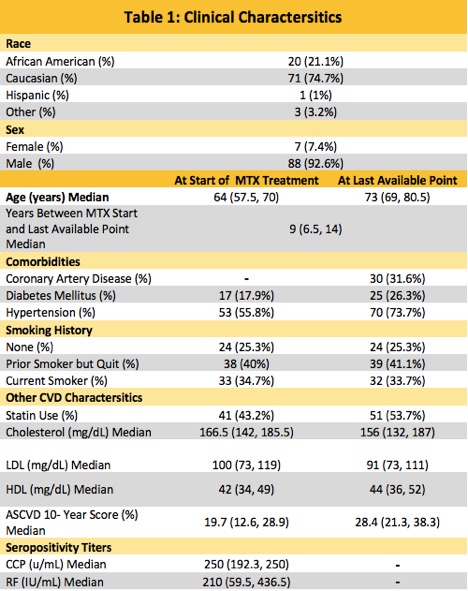 Table 1 lists the clinical characteristics of the 95 patients at the start of therapy and at the last available time point.
Table 1 lists the clinical characteristics of the 95 patients at the start of therapy and at the last available time point.
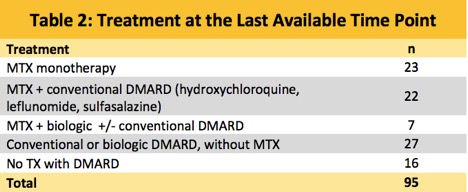 Table 2 depicts the RA therapy of patients at the last available time point.
Table 2 depicts the RA therapy of patients at the last available time point.
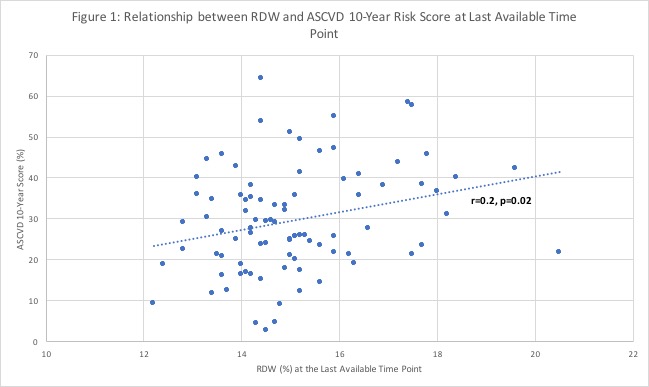 Figure 1 illustrates the linear relationship between RDW and ASCVD 10-Year Risk Score (r=0.2, p=0.02) at the last available time point.
Figure 1 illustrates the linear relationship between RDW and ASCVD 10-Year Risk Score (r=0.2, p=0.02) at the last available time point.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gad I, Damjanovska S, Kostadinova L, Lange A, Burant C, Wilson B, Bej T, Singer N, Mattar M, Zidar D, Anthony D. Red Cell Distribution Width Is Associated with ASCVD Risk Score and CVD in RA After Initiation of Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/red-cell-distribution-width-is-associated-with-ascvd-risk-score-and-cvd-in-ra-after-initiation-of-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/red-cell-distribution-width-is-associated-with-ascvd-risk-score-and-cvd-in-ra-after-initiation-of-methotrexate/
