Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Collagen‐induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model is one of the best recognized animal model for autoimmune diseases. In this model clinical methods of evaluating inflammation and its severity are flawed due to observer bias; for histological studies mice need to be sacrificed so longitudinal studies in the same mouse cannot be performed. The hypothesis of our study was that as by PET imaging the degree of inflammation can be quantified so in a CIA mouse model by total body PET (TB-PET) imaging (i) we should be able to quantify the total inflammatory burden (SUVmax) to determine the kinetics of the degree of changes in inflammation with the progress of the disease (ii) this will allow to perform longitudinal studies to determine the efficacy of novel drugs within days.
Methods: Arthritis was induced using bovine type II collagen in DBA/1J mice (n=40) as per the standard protocol; mice developed arthritis around Day 28. The mice (n=10) had weekly PET imaging that is on day 28, day 35, day 42, and day 56. The maximum18F-FDG uptake (SUV score) was determined for the most severe joint in each mouse to generate a comprehensivePET score (PS). To further evaluate about applications of this model for quantitative longitudinal studies for therapeutic response 15 mice were treated with mouse anti-IL-23 mab; these mice received anti-IL23 mab weekly injections of 100ug/mouse for 4 weeks (Day35, Day42, Day49and Day56). Mice were scored clinically and scanned on these days and on day 63 one week after completion of the 4th dose. Mice (n=5) were additionally scanned on “day 5” and on “day 10” to determine early clinical response of IL-23p19 antibody.
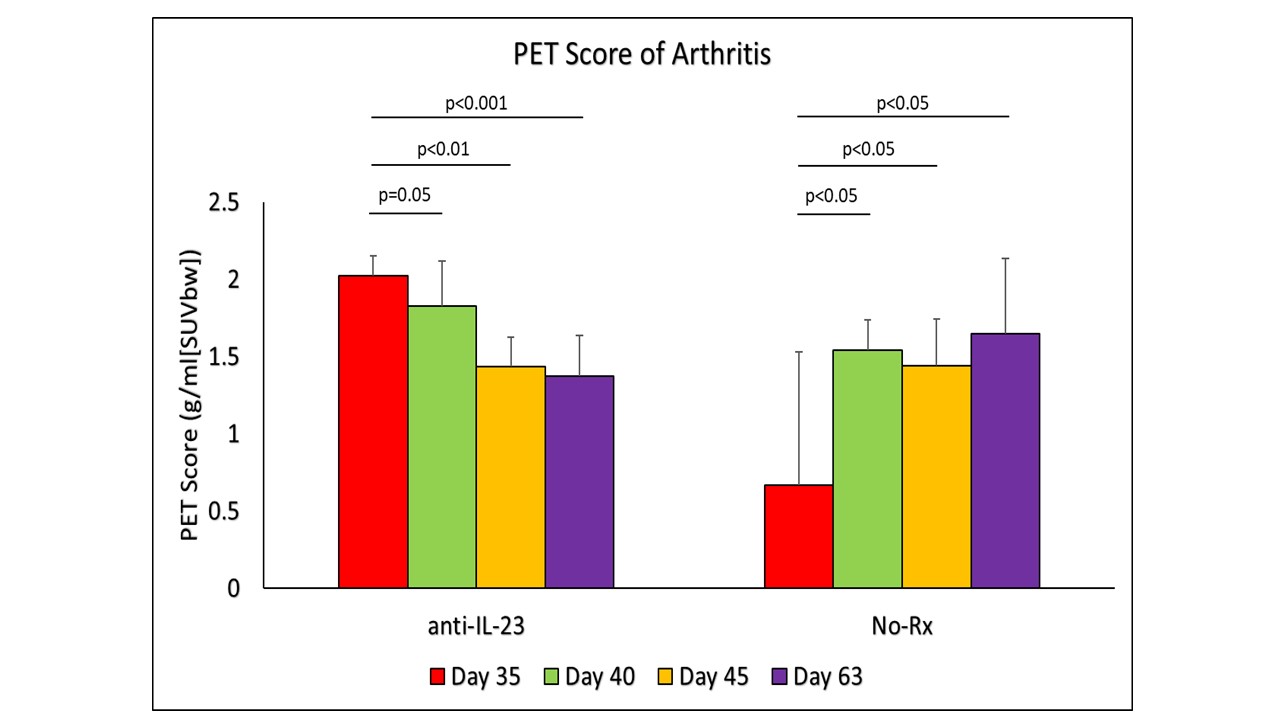
Results: The clinical scores (CS) as well the PET scores (PS) for arthritis in the untreated mice gradually increased with time. The median clinical score(CS)increased with time to 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5 and 3 respectively on day 28, 35, 42 and 56. The PS SUV score (SUVmax) on Day 0 was 1.02. PS median values compared to the Day “0” increased to 1.52 on day 28 (p< 0.05), 3.5 on day 35 (p< 0.05),4.5 on day 42 (p< 0.05) and 3.5 on day 56 (p< 0.05). Our results confirm that the kinetics of the total inflammatory load can be quantified at different time points. The murine anti-IL-23 mAb treatment provided expected results, with time CS reduced from 7.3±1.8 (n=12) on day 35 to 2.8±1.1 (n=12) on day 63 (p< 0.001). Quantified in vivo PS median values as well showed improvement, PS (SUVmax) median values compared to the day 35 (before treatment) in this longitudinal study decreased with time: 2.0 on day 35 (before treatment), 1.8 on Day 40, 1.5 on Day 45 (p< 0.05), and 1.3 on day 63 (p< 0.05) (Figure 1,2,3). These results demonstrated the unique quantifiable measures of therapeutic efficacy of anti-IL-23 mAb.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate the quantification of the kinetics of degree of change in inflammation provided by the PET-CIA model; while the mice treated with mAb showed therapeutic efficacy as early as on the Day 5 (Figure 2,3). Thus, this model will be a novel tool for monitoring inflammatory load and a unique tool to evaluate efficacy or resistance to therapies during early stages of treatment. With time we are transferring these observations to quantify the degree of inflammation in human with RA and PsA.
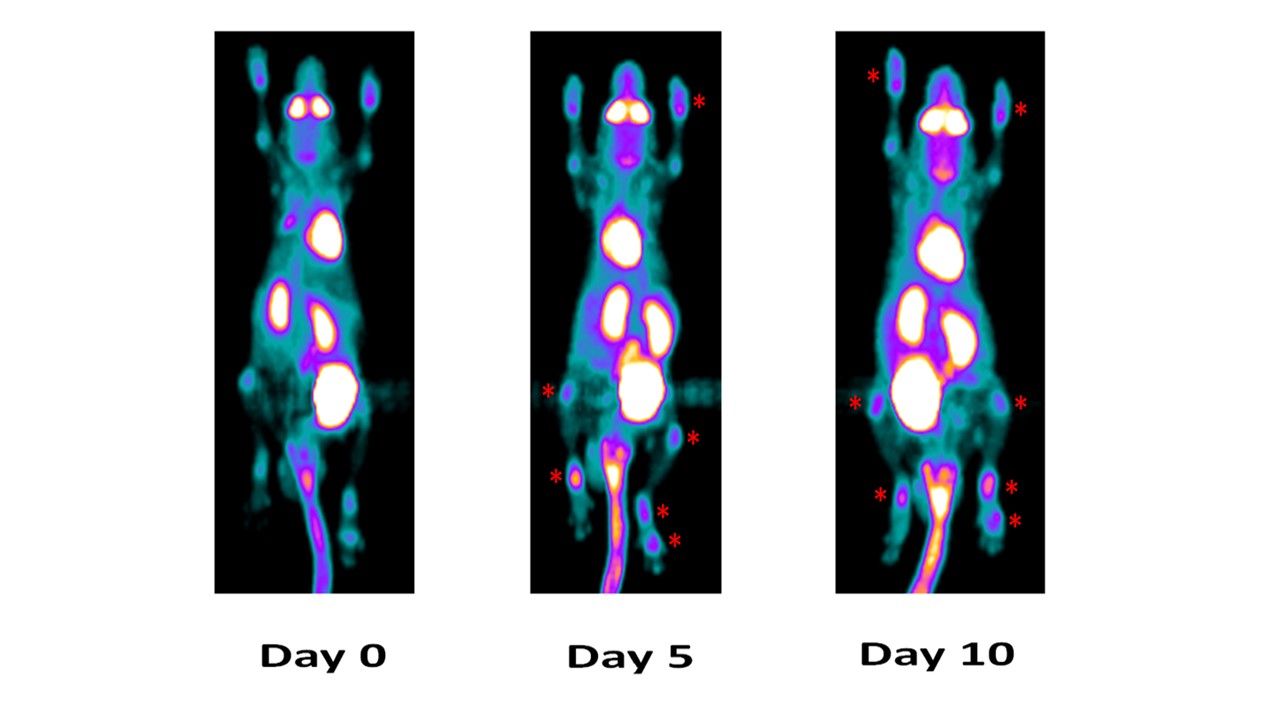
This mouse not treated with anti-IL_23p19 mAb in longitudinal study by PET imaging demonstrated a progressive increase of PET signaling that is higher degree of inflammation on both fore and hind limb joints on Day 5 and Day 10.
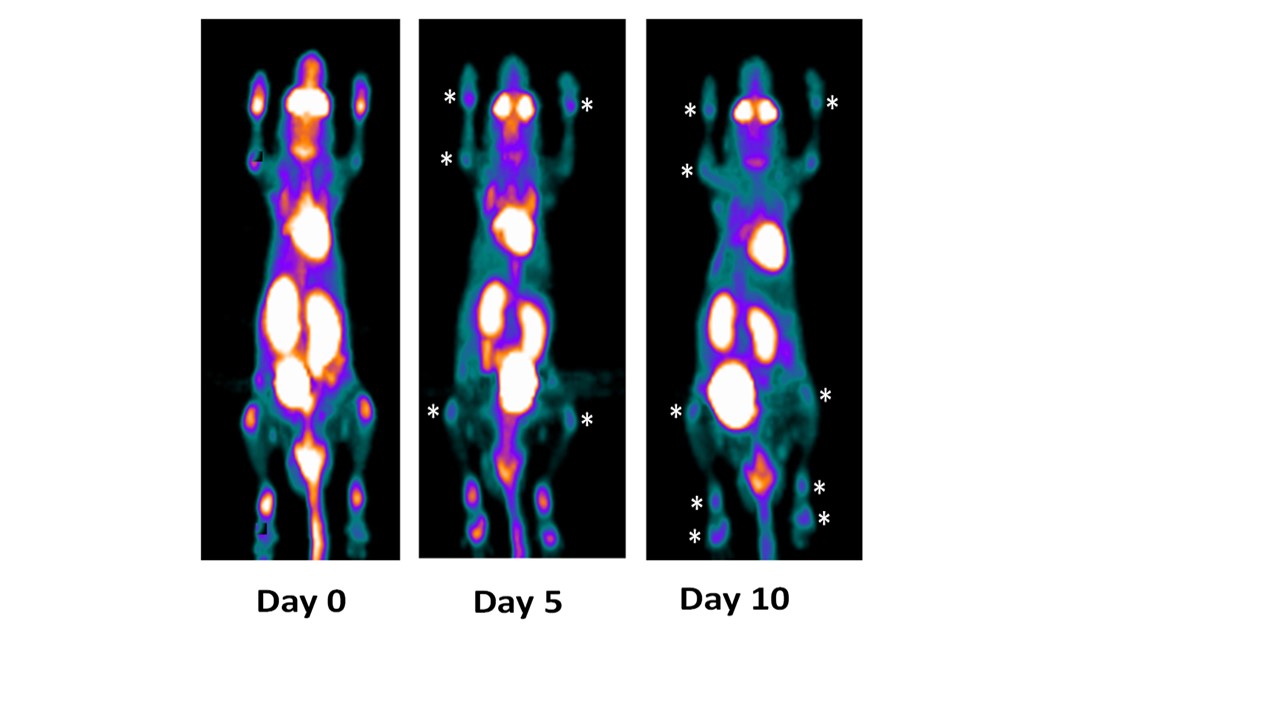
This mouse treated with anti-IL_23 mAb in longitudinal study by PET imaging demonstrated progressive reduction of PET signaling that is the degree of inflammation on both fore and hind limb joints on Day 5 and Day 10.
Change in PET Score (SUVmax) over the study to demonstrate the change in inflammation in treatment against the control group. Day 35 was the beginning of anti-IL23 antibody treatment and imaging, with further imaging on days 40, 45, and 63. Mice without any treatment showed significant increase in inflammation, while mice with anti-IL_23 antibody treatment demonstrated significant decrease of inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri S, Raychaudhuri S, Chandrasekar N, Abria C, Banerjee S, Raychaudhuri S, Chaudhari A. Quantifying Inflammation: A Novel In-Vivo Total Body PET Imaging Tool to Determine the Kinetics of the Degree of Changes in Inflammation in Different Time Points [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantifying-inflammation-a-novel-in-vivo-total-body-pet-imaging-tool-to-determine-the-kinetics-of-the-degree-of-changes-in-inflammation-in-different-time-points/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantifying-inflammation-a-novel-in-vivo-total-body-pet-imaging-tool-to-determine-the-kinetics-of-the-degree-of-changes-in-inflammation-in-different-time-points/