Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The Accelerating Medicines Project (AMP) has enabled significant increases in understanding of SLE nephritis pathology, providing a profile of dozens of leukocyte subsets within affected kidneys by single-cell RNA sequencing of nephritis biopsies. While these results suggest a complex network of interactions between cell populations during nephritis, the spatial positioning of these cells is lost during the sequencing process. Inferred interactions between the diverse identified cell types would be greatly strengthened by detailed spatial information, placing these cells in context with each other and with the surrounding structures of the kidney.
Methods: In consultation with AMP, we have used CODEX, a multicycle imaging technology allowing for staining of up to 40 targets on a single tissue sample without tissue degradation, to capture preliminary images of the AMP tissue biopsies available at New York University. Extensive antibody screening, sample preparation, optimization of antigen retrieval, and imaging steps are required, which remain under active optimization to allow for imaging the entirety of the AMP biopsy cohort available at the Grossman School of Medicine, which has been fully processed for future staining.
Results: At present we are able to image sixteen targets capturing dense interstitial T and B cell infiltrates, intratubular and interstitial myeloid populations, and sparser glomerular infiltrating cells in our demonstration cohort, with clear imaging of the glomeruli, tubules, and interstitial spaces. Further targets will be added as they are optimized, further allowing subsetting of T, B, and myeloid populations, with the goal of capturing the populations identified previously in single-cell sequencing.
Conclusion: CODEX imaging of renal biopsy samples provides spatial context for prior observations across a range of SLE nephritis samples, with complex interstitial populations found around glomeruli and tubules in active disease. Deeper profiling with expanded antigen targets to enable further sub-population phenotyping and activation states and imaging of the full cohort of biopsies available at NYU will provide a spatial atlas to SLE nephritis and further reveal underlying mechanisms of disease.
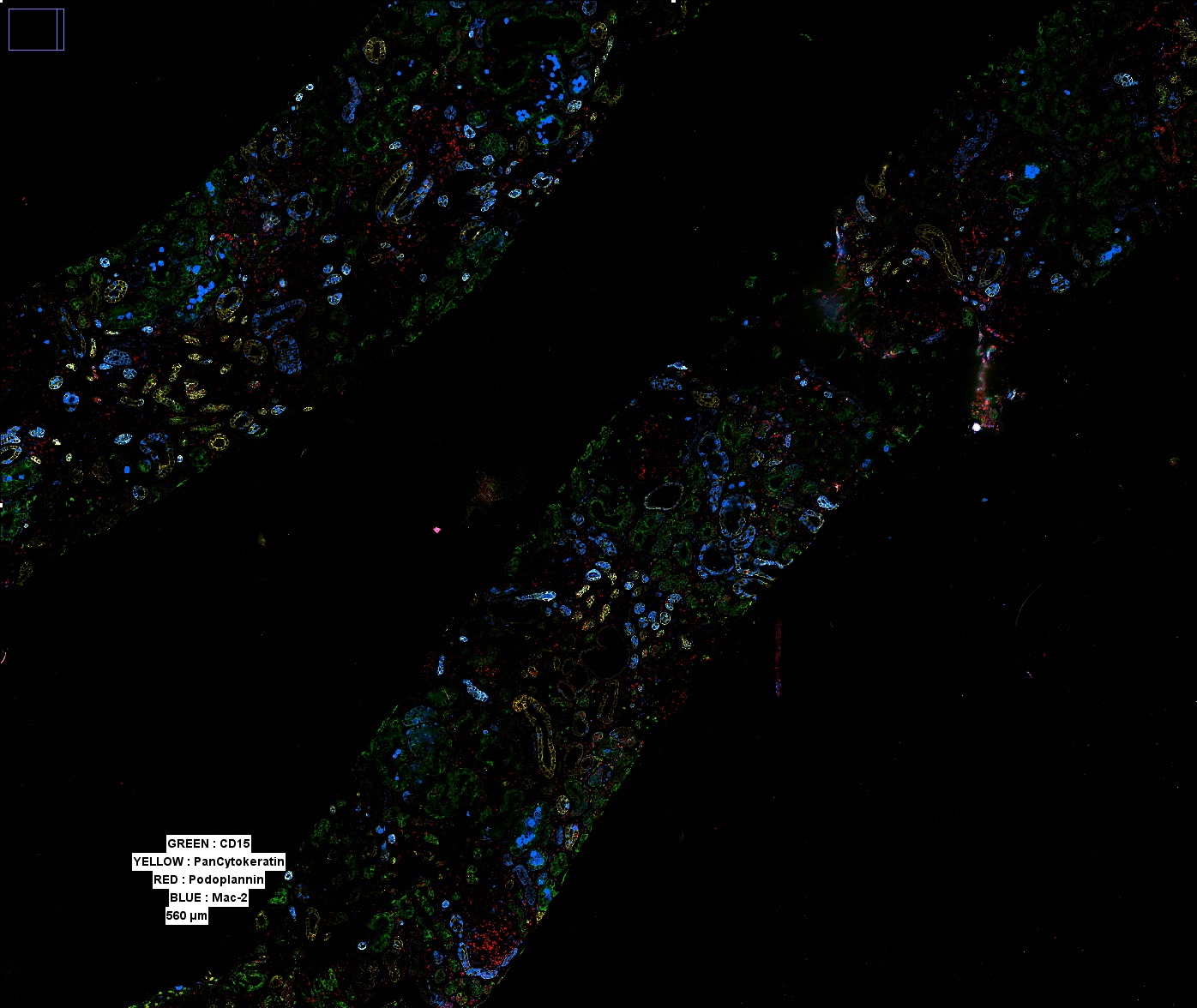 A wide view of a selected biopsy demonstrates ultrastructure via multiple structural markers. Multiple such regions can be captured, allowing for the entirety of a biopsy sample to be imaged. All images shown display only a subset of the overall stained markers due to visual limitations.
A wide view of a selected biopsy demonstrates ultrastructure via multiple structural markers. Multiple such regions can be captured, allowing for the entirety of a biopsy sample to be imaged. All images shown display only a subset of the overall stained markers due to visual limitations.
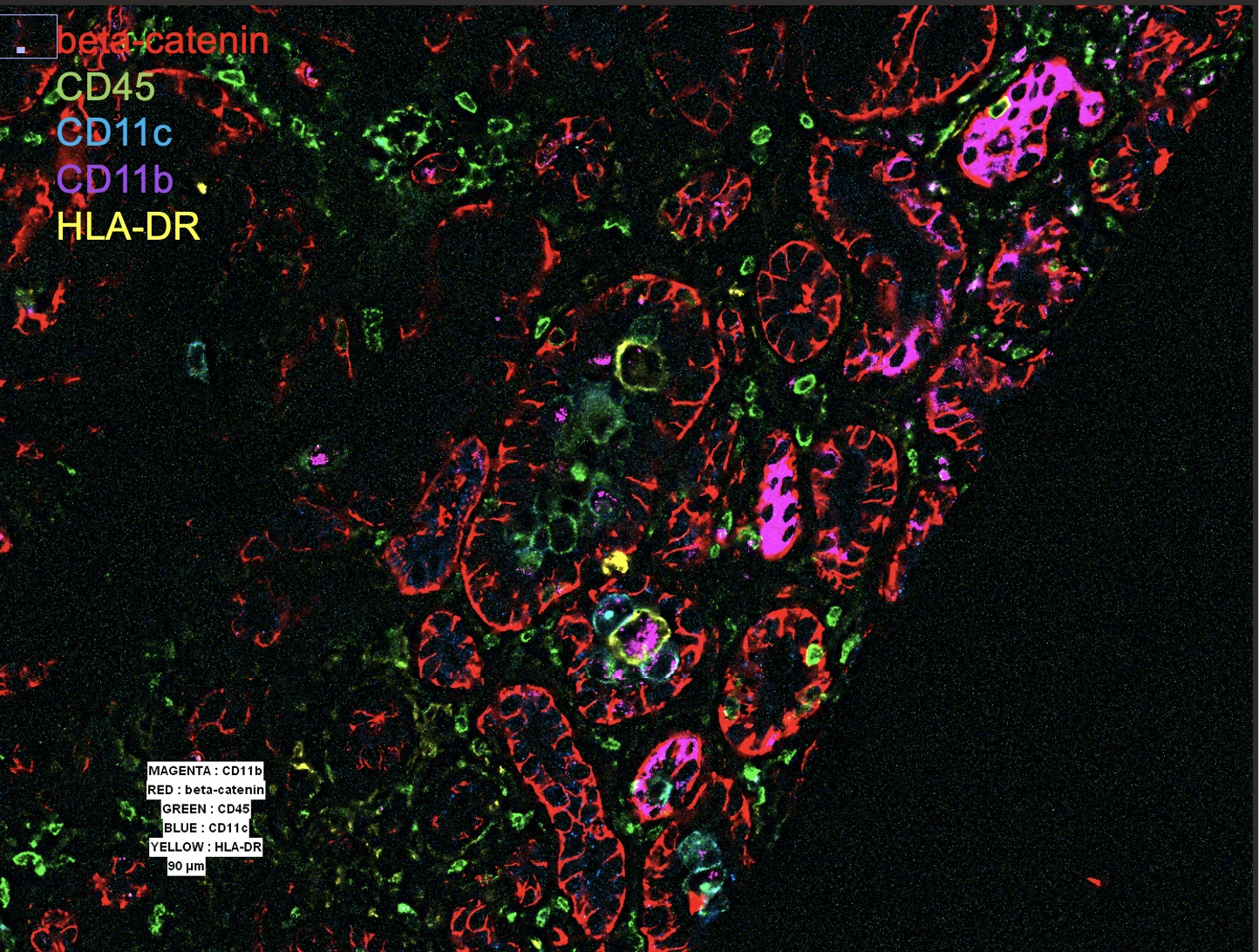 Close examination of a tubule reveals diverse infiltrating cells, including CD11c+, CD11b/c+, and sparse CD11b/c+ HLA-DR+ cells. Surrounding interstitial lymphocytes can be seen, which correspond to CD3+ CD4+ T cells (stains not shown).
Close examination of a tubule reveals diverse infiltrating cells, including CD11c+, CD11b/c+, and sparse CD11b/c+ HLA-DR+ cells. Surrounding interstitial lymphocytes can be seen, which correspond to CD3+ CD4+ T cells (stains not shown).
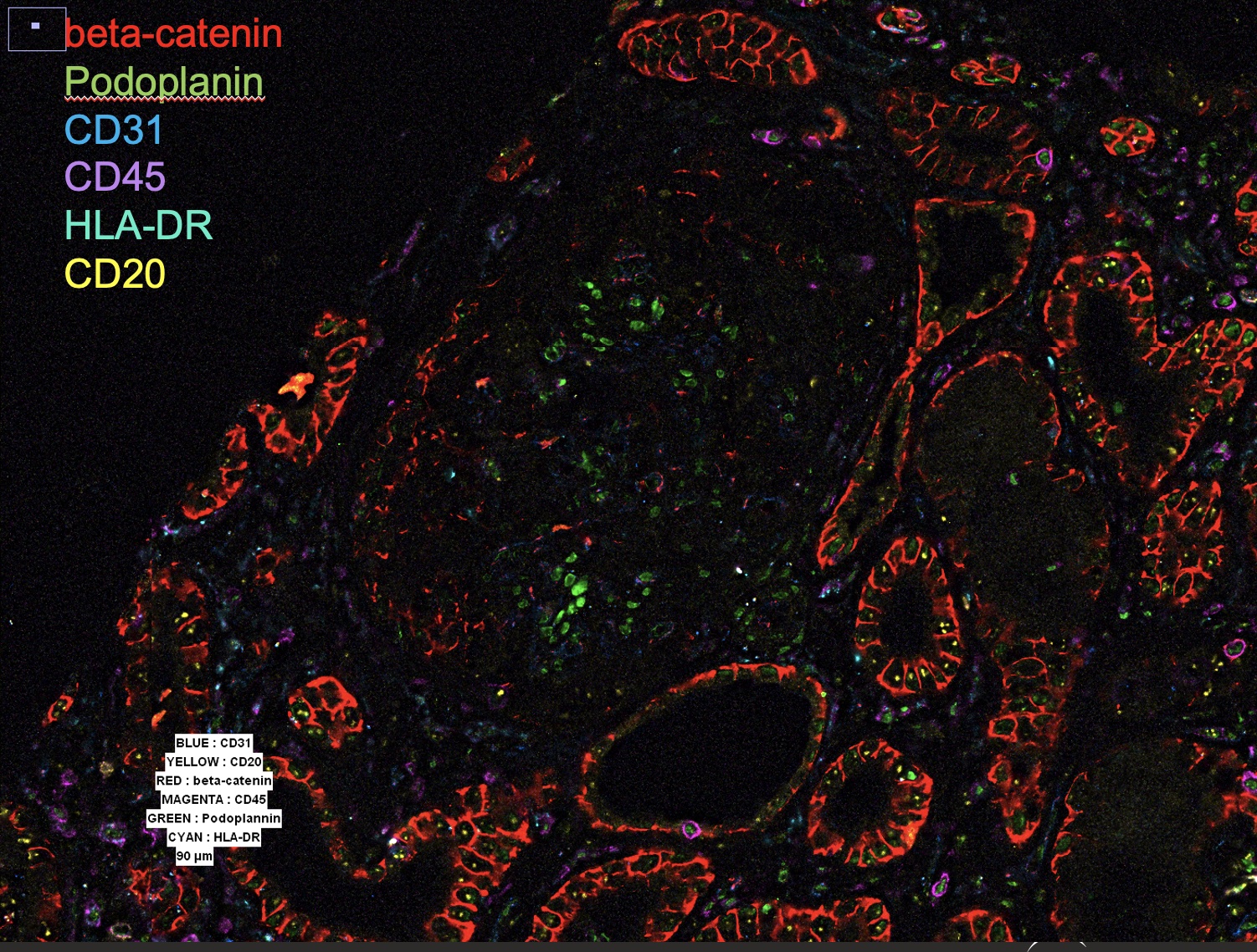 Periglomerular infiltration, without significant glomerular cellular involvement, is seen in this image. CD20+ B cells and HLA-DR+ cells can be seen in the lower left.
Periglomerular infiltration, without significant glomerular cellular involvement, is seen in this image. CD20+ B cells and HLA-DR+ cells can be seen in the lower left.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smuda C, Eichinger A, Clancy R, Buyon J, Reizis B. Putting the Pieces on the Board: Mapping SLE Nephritis Biopsies from the Accelerating Medicines Project Using High-Density Immunofluorescence Imaging [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/putting-the-pieces-on-the-board-mapping-sle-nephritis-biopsies-from-the-accelerating-medicines-project-using-high-density-immunofluorescence-imaging/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/putting-the-pieces-on-the-board-mapping-sle-nephritis-biopsies-from-the-accelerating-medicines-project-using-high-density-immunofluorescence-imaging/
