Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common and complex inflammatory polyarthritis. Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) have shown superior efficacy compared to traditional treatments, but predictors for therapeutic response are yet to discover. Our aim is to utilize the proteomics OLINK analysis method to identify biomarkers associated with the effectiveness of JAKi in patients with RA, thereby providing treatment strategy for precision medicine.
Methods: This study enrolled RA patients from Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan. Therapeutic effectiveness was classified according to EULAR response criteria. Plasma proteins were collected before JAKi treatment, and a proteomic analysis using the OLINK inflammation platform examined differences in plasma protein levels between groups.
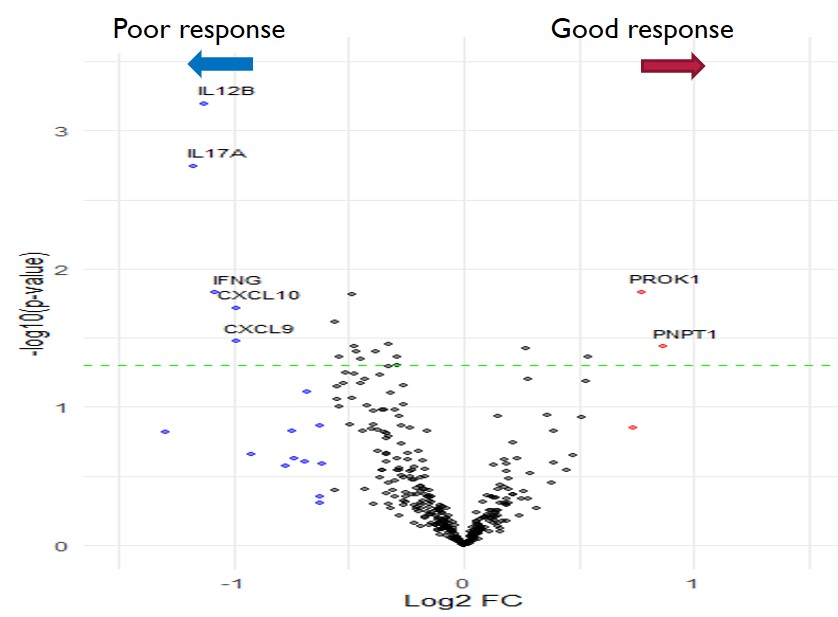
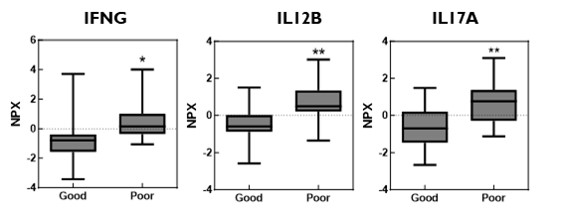
Results: The overall good response rate to JAKi was 54.76% (58.33% in patients treated with baricitinib, 35.71% with tofacitinib, and 68.75% with upadacitinib). Elevated pre-treatment plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-12B, IL-17A, and interferon (IFN)-γ were associated with poor responses to JAK inhibitors. High IFN-γ and IL-12B levels were linked to poor responses to baricitinib, while high IL-17A levels were associated with poor responses to tofacitinib. No protein markers were found related to poor responses to upadacitinib. Pathway analysis using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) provided insights into the signaling pathways regulated by JAK inhibitors after treatment.
Conclusion: IFN-γ, IL-12B, and IL-17A may serve as biomarkers for JAKi treatment responsiveness in RA patients, aiding rheumatologists in making more accurate drug choices and improving patient outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu T, Chen Y. Proteomic Insights into JAK Inhibitor Therapeutic Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-insights-into-jak-inhibitor-therapeutic-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-insights-into-jak-inhibitor-therapeutic-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/