Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Immunological Complications of Therapy (0437–0440)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:30AM-9:45AM
Background/Purpose: Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are a frequent and serious complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment for cancer, which can resemble primary rheumatic diseases. Predictors associated with development of rheumatic irAEs have not been well characterized in previous studies due to lack of a comparator group and sample size limitations. The aim of this study was to identify predictors at time of ICI initiation associated with rheumatic irAEs as well as de novo inflammatory arthritis, the most common type of rheumatic irAE.
Methods: We performed a case-control study of all cancer patients initiating an ICI at a large tertiary academic health care system and cancer center (2011-2020). We screened for rheumatic irAEs through a comprehensive medical record review of all patients evaluated by a rheumatologist or prescribed an immunomodulator (IM) after initial ICI prescription (baseline), using electronic query. IMs are one of 55 medications used to treat irAEs based on published guidelines. Two board-certified rheumatologists confirmed the presence and type of rheumatic irAE case by independent medical record review. Controls had no pre-existing rheumatic disease, did not receive glucocorticoids, had no IM or rheumatologic evaluation after ICI, and survived at least 6 months after initial ICI (since patients with early demise may not have an opportunity to develop a rheumatic irAE). We found no patients with rheumatic irAEs on medical record review of 100 random controls (negative predictive value 100%). Predictors at the initiation of ICI included: cancer type (the most prevalent cancer, lung cancer was the reference group), ICI regimen, pre-existing autoimmune disease, and glucocorticoid use. Multivariable logistic regression estimated odds ratios (ORs) for rheumatic irAE case status. A similar analysis was performed to find predictors of de novo inflammatory arthritis.
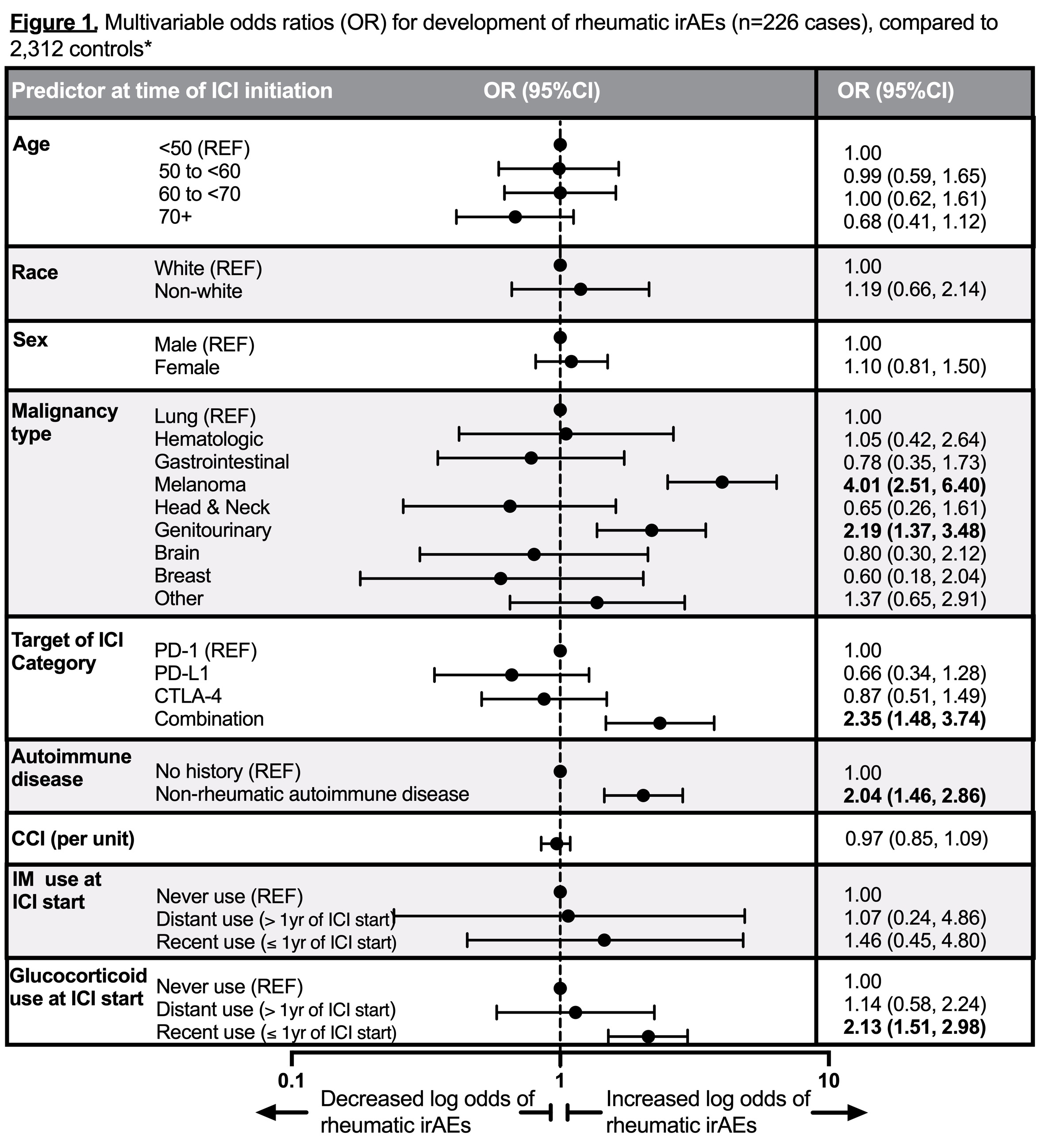
Results: We found 8,028 ICI recipients (mean age 65.5 years, 43.1% female, and 31.8% with lung cancer). We identified 226 (2.8%) confirmed rheumatic irAE cases and 118 (1.5%) with de novo inflammatory arthritis. There were 2,312 controls without rheumatic irAEs included in analyses. Baseline predictors of rheumatic irAE case status were: melanoma (OR 4.01, 2.51-6.40) or genitourinary (GU) cancer (OR 2.19, 1.37-3.48, ref=lung cancer), combination ICI (OR 2.35, 1.48-3.74, ref=PD-1), pre-existing autoimmune disease (OR 2.04, 1.46-2.86), and glucocorticoid use within one year prior to ICI (OR 2.13, 1.51-2.98, ref=non-use) (Figure 1). Baseline predictors of de novo inflammatory arthritis were similar: melanoma (OR 2.95, 1.60-5.43) or GU cancer (OR 2.39, 1.34-4.26, ref=lung cancer), combination ICI (OR 2.31, 1.26-4.26, ref=PD-1), pre-existing autoimmune disease (OR 2.74, 1.79-4.19), and glucocorticoid use one year prior to ICI (OR 1.96, 1.26-3.06, ref=non-use) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In this large study of patients who received an ICI, we found melanoma, GU cancer, pre-existing autoimmune disease, and glucocorticoid use within 1 year of ICI may be novel predictors of rheumatic irAEs. The possible biologic basis of these associations should be the subject of future research.
*Controls were patients without rheumatic disease at baseline, used no glucocorticoid or immunomodulator after baseline, and had no rheumatologic evaluation after baseline. Multivariable models were mutually adjusted for all covariates listed in the column.
CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; CI, confidence interval; CTLA_4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitors; IM, immunomodulator; irAE, immune-related adverse event; OR, odds ratio; PD_1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; REF, Reference.
*Controls were patients without rheumatic disease at baseline, used no glucocorticoid or immunomodulator after baseline, and had no rheumatologic evaluation after baseline. Multivariable models were mutually adjusted for all covariates listed in the column.
CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; CI, confidence interval; CTLA_4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitors; IM, immunomodulator; irAE, immune-related adverse event; OR, odds ratio; PD_1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; REF, Reference.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cunningham-Bussel A, Wang J, Prisco L, Martin L, Vanni K, Zaccardelli A, Nasrallah M, Gedmintas L, MacFarlane L, Shadick N, Awad M, Rahma O, LeBoeuf N, Gravallese E, Sparks J. Predictors of Rheumatic Immune-related Adverse Events and de Novo Inflammatory Arthritis After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-treatment for Cancer [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-rheumatic-immune-related-adverse-events-and-de-novo-inflammatory-arthritis-after-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-treatment-for-cancer/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-rheumatic-immune-related-adverse-events-and-de-novo-inflammatory-arthritis-after-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-treatment-for-cancer/