Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0066–0095) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is the major type II PRMT that catalyzes the formation of symmetrical dimethyl arginine (SDMA) on protein substrates and is involved in the regulation of key inflammatory genes. In particular, PRMT5 plays an essential role in T cell homeostasis and activation-induced expansion by maintaining cytokine signaling. It has been shown to promote inflammatory T-cell responses, particularly those driven by Th1 and Th17 cells. Therefore, targeting PRMT5 with selective inhibitors offers a novel therapeutic approach to target T-cell mediated autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. We have previously reported that treatment with selective small-molecule inhibitors of PRMT5 leads to potent suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in preclinical models of acute graft-vs-host disease and myeloproliferative neoplasms. We therefore evaluated the effects of novel, selective and orally bioavailable PRMT5 inhibitors in rodent models of T-cell-driven autoimmunity and inflammation.
Methods: Orally administered PRMT5 inhibitors (PRMT5i) were evaluated in vivo in several rodent models including an MRL/lpr model of systemic lupus erythematosus, an imiquimod (IMQ)-induced model of psoriasis, a CIA mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis, an experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN) rat model, and a human artery/NSG mouse chimera model of giant cell arteritis (GCA). In vitro, proliferation (Ki67), IFNγ and IL-17 production was measured in healthy human CD4+ T cells following stimulation and treatment with PRMT5i.
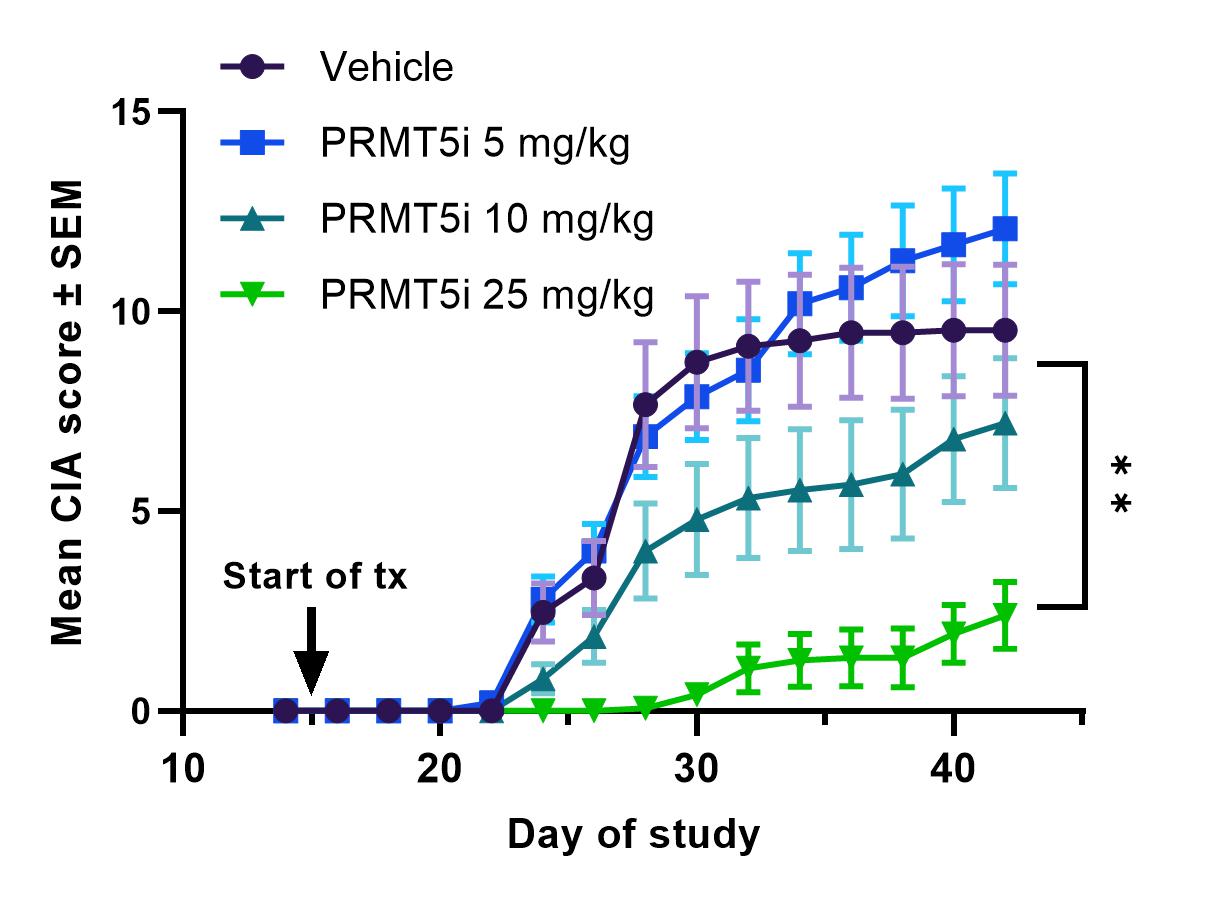
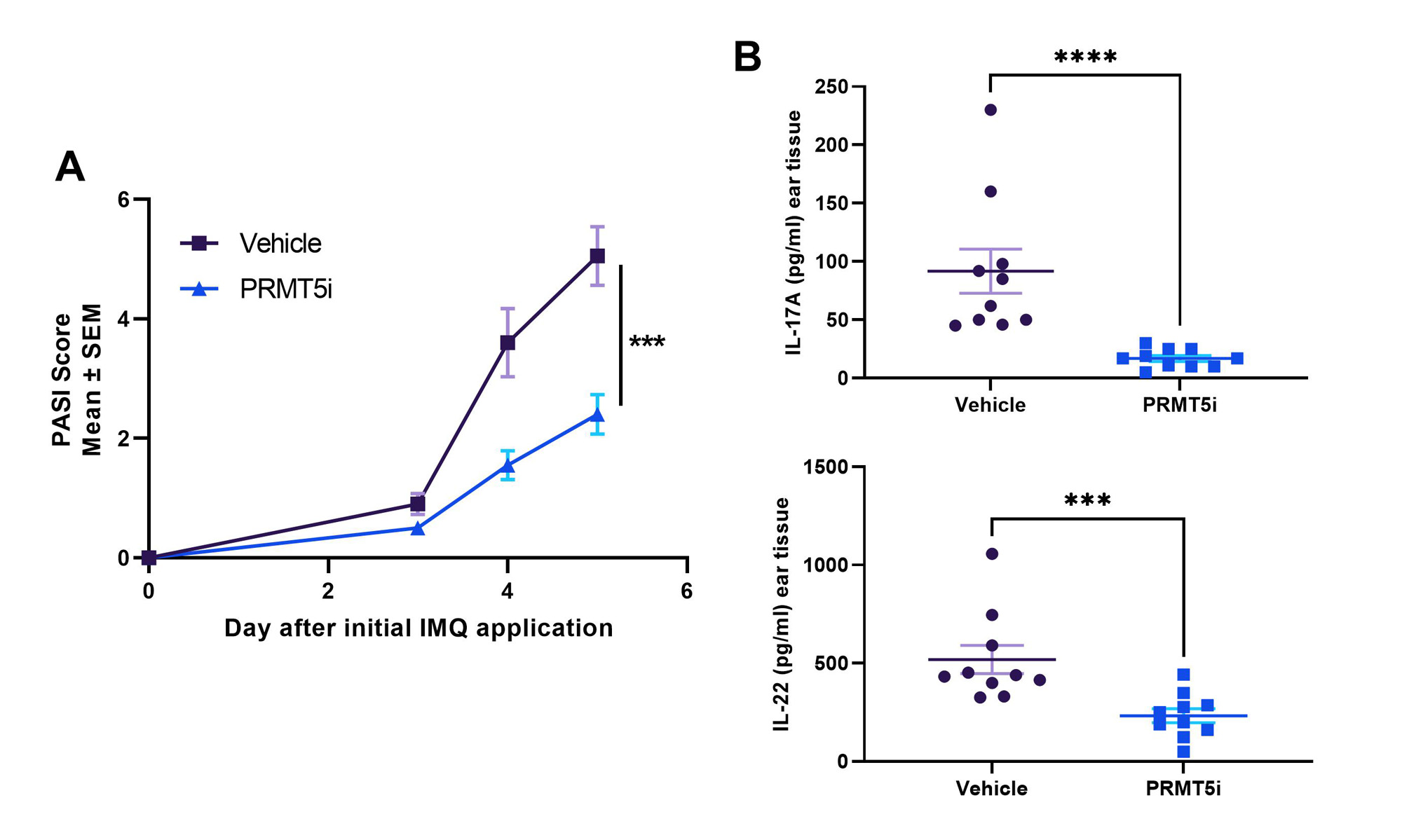
Results: In vitro, PRMT5i treatment significantly inhibited T-cell proliferation and differentiation of Th1 and Th17 cells. Consistent with these effects, PRMT5i treatment of MRL/lpr mice led to significant, dose-dependent reduction of disease severity including reduction in proteinuria, anti-dsDNA antibodies in serum, kidney pathology and key serum cytokines such as TNF, IFNγ and BAFF. Treated animals showed decreased pro-inflammatory CD4+ cells and increased Tregs in kidneys and spleens compared to vehicle controls. In addition, PRMT5i were efficacious at reducing disease severity (PASI score) in the IMQ-induced psoriasis model. Inhibitor treated animals had significantly lower IL-17A and IL-22 serum concentrations compared to vehicle controls. In the CIA model, PRMT5i administration reduced disease incidence and severity in a dose-dependent manner. PRMT5i treatment in a rat model of EAN also resulted in significant reduction of disease severity as evidenced by reduced inflammatory infiltration and higher myelination of peripheral neuronal tissue. Finally, in a humanized mouse model of GCA, treatment with PRMT5i reduced inflammatory mononuclear cell infiltration in the blood vessel wall and reduced levels of IFNγ and IL-21 compared to either vehicle or prednisolone treated animals.
Conclusion: PRMT5 inhibitors were highly effective in suppressing Th1, Th17 and IFNγ-mediated immune responses in a number of preclinical models of human autoimmune diseases at well-tolerated doses. These data support the potential development of PRMT5i as a therapy for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bhagwat N, Penmetsa K, Devalaraja M, Marusic S, Weyand C, Ohtsuki S, Scherle P, Vaddi K. Pharmacological Inhibition of PRMT5 Demonstrates Broad Efficacy in Multiple Preclinical Models of Autoimmunity and Inflammation by Suppressing Th1, Th17 and TNF-Mediated Inflammatory Responses [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacological-inhibition-of-prmt5-demonstrates-broad-efficacy-in-multiple-preclinical-models-of-autoimmunity-and-inflammation-by-suppressing-th1-th17-and-tnf-mediated-inflammatory-responses/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacological-inhibition-of-prmt5-demonstrates-broad-efficacy-in-multiple-preclinical-models-of-autoimmunity-and-inflammation-by-suppressing-th1-th17-and-tnf-mediated-inflammatory-responses/