Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: It is still unclear whether Natural Killer (NK) and Natural Killer T (NKT) cells play a pathogenic or protective role in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). There is no data on the effect of methotrexate (MTX), which is the first line of therapy for RA, on NK and NKT cells and their immunophenotypic subsets.
Methods: Two groups of RA patients (2010 ACR/EULAR criteria) aged 18-60 years – Treatment naïve RA with active disease (SJC≥2, TJC≥4) and MTX-treated RA (≥15 mg/week MTX for ≥6 months)- were included, along with age-and-sex-matched healthy controls (HC). Peripheral blood (PB) (and synovial fluid (SF), where available) mononuclear cells (MCs) were isolated through Ficoll Histopaque density gradient centrifugation, and the proportion of NK cells (CD56+CD3–), their subsets (CD56dimCD3–, CD56briCD3–, CD56+CD16+CD3–) and NKT cells (CD56+CD3+) were quantified through flow cytometry and compared between groups.
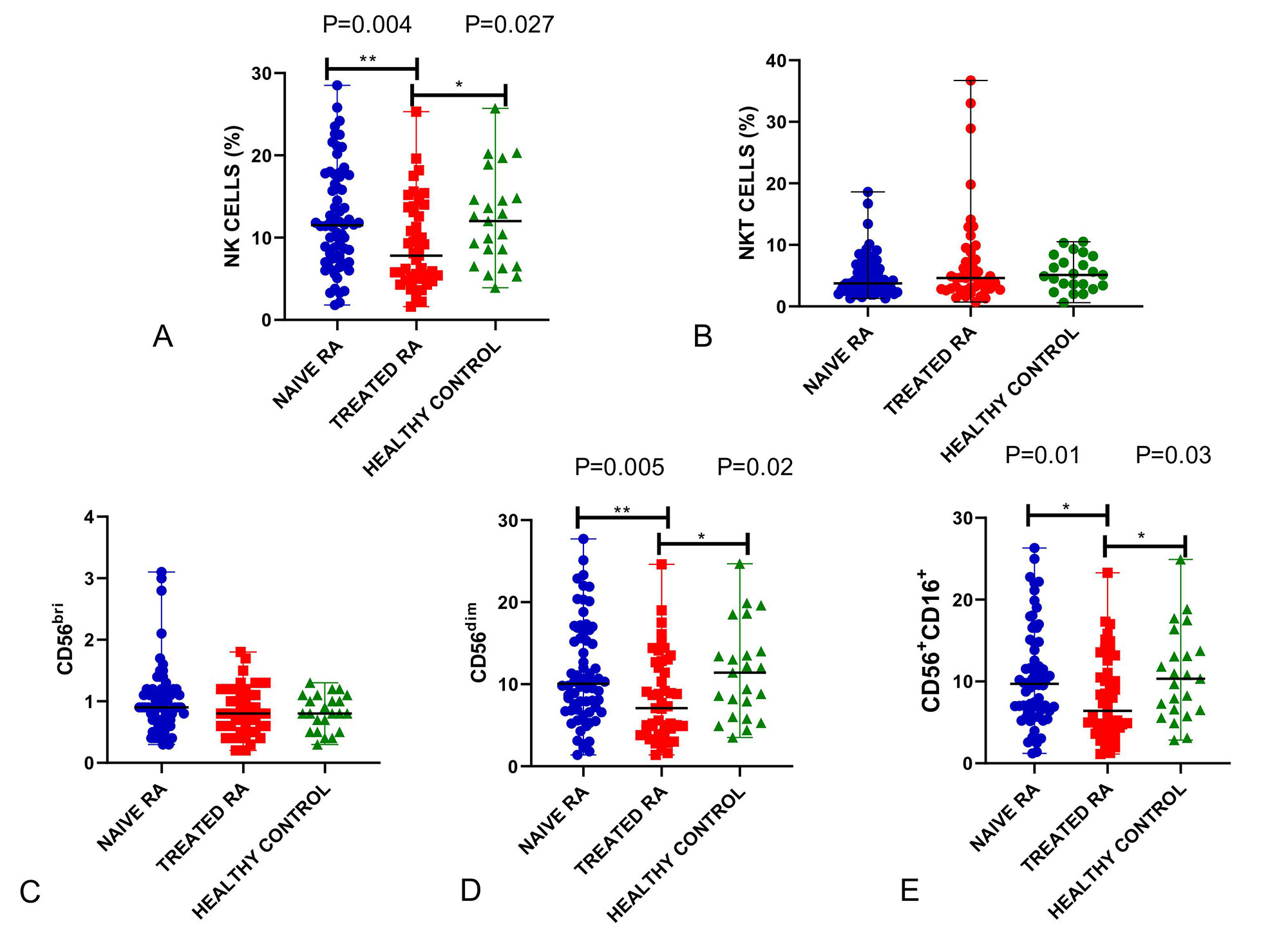
Results: A total of 138 subjects [68 naïve RA, 47 MTX-treated RA, and 23 HC; mean age 42 (10) years, 118 (85%) females] were included. Mean DAS28-ESR in naïve RA and MTX-treated RA was 6.2 (1.0) and 4.8 (1.0), respectively. The proportion of PB NK cells was found to be lower (p=0.009) in MTX-treated RA (7.8%) compared to naïve RA (11.5%) and HC (12%) (Figure 1A), while the proportion of NKT cells was similar in the three groups (3.75%, 4.6% and 5.1%) (Figure 1B). On NK cell subset analysis, CD56dimCD3– and CD16+CD56+CD3– cells were lower in MTX-treated RA (7.1%, p=0.01 and 6.4%, p=0.02 respectively) compared to naïve RA (10% and 9.7%) and healthy controls (11.4% and 10.3%), while the CD56briCD3– population was similar across all three groups (Figure 1C-E). SFMCs were available for 9 RA patients. Comparison of PB and SF NK and NKT cells showed that SFNK had a significantly lower proportion of dual positive (CD16+CD56+CD3–) NK cells (33%) compared to PB (91%, p=0.01), suggesting a predominant secretory rather than a cytotoxic phenotype of SFNK cells.
Conclusion: Peripheral blood and synovial fluid have contrasting NK cell immunophenotypes. Treatment with MTX reduces the proportion of peripheral blood NK cells, particularly the CD56dimCD3– and CD16+CD56+CD3– (dual positive) subsets, in patients with active RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jain S, Laishangtham B, Khullar A, Saikia B, Dhir V. Peripheral Blood and Synovial Fluid Natural Killer (NK) and Natural Killer T (NKT) Cell Immunophenotypes in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Role as Biomarkers of Methotrexate Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-and-synovial-fluid-natural-killer-nk-and-natural-killer-t-nkt-cell-immunophenotypes-in-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-their-role-as-biomarkers-of-methotrexate-response/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-and-synovial-fluid-natural-killer-nk-and-natural-killer-t-nkt-cell-immunophenotypes-in-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-their-role-as-biomarkers-of-methotrexate-response/