Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Detection of autoantibodies is key for the identification and prognosis of patients with connective tissue diseases (CTD); however, some current testing methods are manual, time-consuming, and fragmented, highlighting the need for the development of new fully automated diagnostic tools. We report the performance characteristics of MosaiQ Aiplex CTD prototype, (Quotient Suisse, Eysins, CH), a new planar microarray (MA) immunoassay designed for use with the fully automated, continuous random access, high throughput MosaiQ system for qualitative serological detection of eleven IgG autoantibodies commonly found in CTD (dsDNA, SS-A 60, TRIM21, SS-B, Sm, Sm/RNP, U1RNP, Jo-1, Scl-70, Centromere B, Ribosomal P).
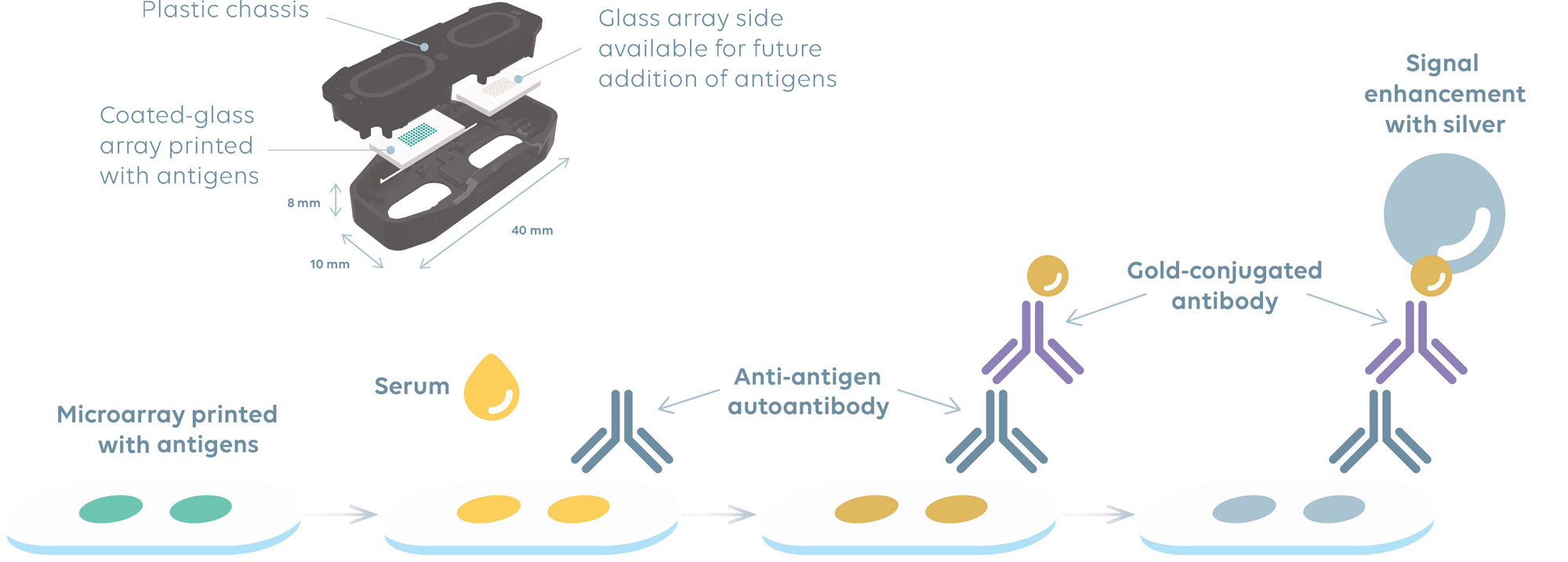
Methods: Each MA consists of two wells, each enclosing an epoxy-silane functionalized glass chip, framed in a plastic chassis (Figure 1). Antigens probes were printed in duplicate, except in triplicate for dsDNA. One side of the MA was printed, leaving the other side available for future addition of antigens. MA were assembled into magazines and loaded in the MosaiQ 125 instrument and read by the on-board Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) antenna. Key information (i.e., number of MA, lot number, expiry date) is transmitted to the instrument which evaluates the adequacy of resources to execute the selected test order and alerts user when any replacement of reagents is required. MAs are released from the magazine and automatically processed in the system where they undergo sample/buffer/reagent addition and removal to generate a final spot signal for interpretation by the instrument.
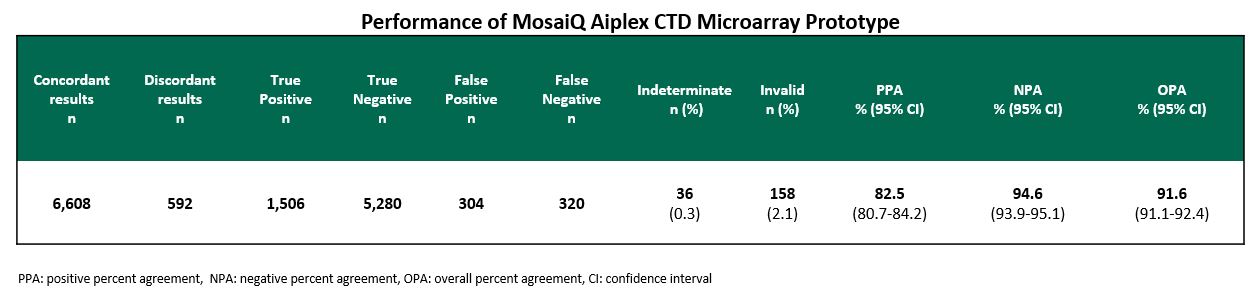
Results: A cohort of 123 individual serum samples, of which 20 were obtained from blood donations and the rest from a CTD sample bank, were tested in 6-8 replicates with the investigational device, across 3 instruments and 3 MA lots (except for U1RNP which was tested on two lots) and compared with the results obtained with a CE-marked device. Table 1 shows that across analytes the total positive, negative, and overall percent agreement (PPA, NPA and OPA) respectively, were 82.5% (95% CI 80.7-84.2), 94.6% (95% CI 93.9-95.1), and 91.6% (95% CI 91.1-92.4). Rates of indeterminate and invalid results were 0.3% and 2.1%, respectively.
Conclusion: These preliminary results support the performance of the MosaiQ MA technology platform and Aiplex CTD prototype device for the serological qualitative detection of IgG autoantibodies commonly found in CTD. Clinical studies to further evaluate the performance of the investigational device are ongoing. Future versions of the MA are planned to expand the number of analytes included. The MosaiQ System has the potential to advance CTD testing by increasing laboratory efficiency and productivity by automatically analyzing multiple autoantibodies simultaneously and processing large number of samples per day.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bijlsma D, Lukasik E, Hausmann M, Gomez G, Ginocchio C, Moreau E. Performance Characteristics of a Novel, Fully Automated Multiplexed Immunoassay Microarray Prototype for the Serological Detection of Eleven IgG Autoantibodies Commonly Found in Connective Tissue Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-characteristics-of-a-novel-fully-automated-multiplexed-immunoassay-microarray-prototype-for-the-serological-detection-of-eleven-igg-autoantibodies-commonly-found-in-connective-tissue-dise/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-characteristics-of-a-novel-fully-automated-multiplexed-immunoassay-microarray-prototype-for-the-serological-detection-of-eleven-igg-autoantibodies-commonly-found-in-connective-tissue-dise/