Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There is no consensus on the frequency of monitoring of patients with autoimmune disease-related interstitial lung diseases (ILDs), but a frequency of 1 year is often used in clinical practice. We used data from clinical trials to evaluate ILD progression at time-points up to 1 year in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated ILD (SSc-ILD) and rheumatoid arthritis-associated ILD (RA-ILD).
Methods: We analyzed data from patients with fibrosing SSc-ILD who received placebo in the SENSCIS trial and patients with progressive fibrosing RA-ILD who received placebo in the INBUILD trial. We assessed the proportions of patients with ILD progression (absolute decline in FVC % predicted ≥5% or death) at weeks 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 36 and 52. A worst observation carried forward approach was used to impute missing FVC values in the evaluation of a patient’s progression status at each time point. Time to ILD progression over 52 weeks was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
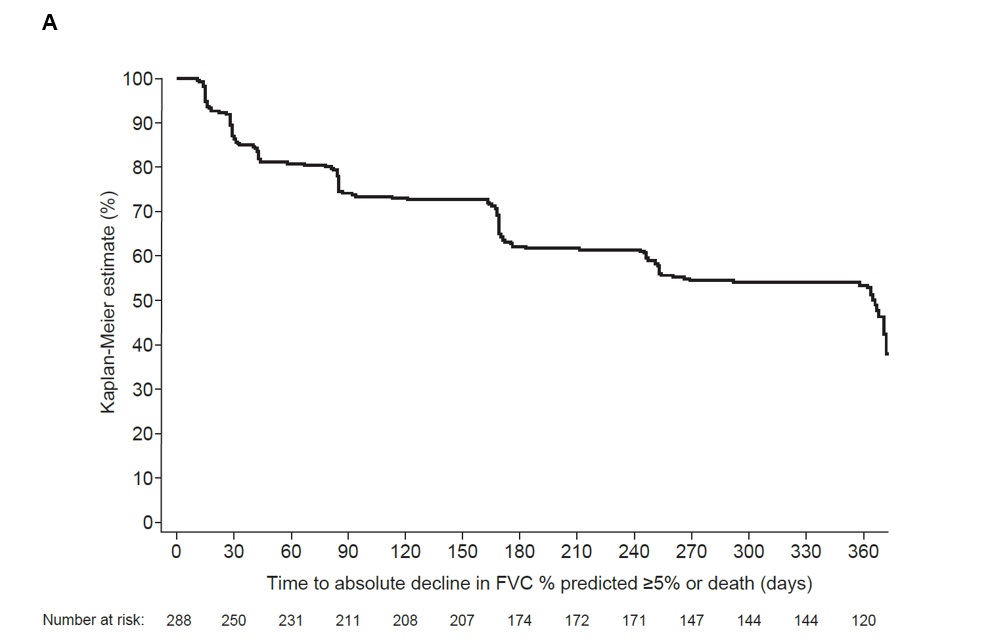
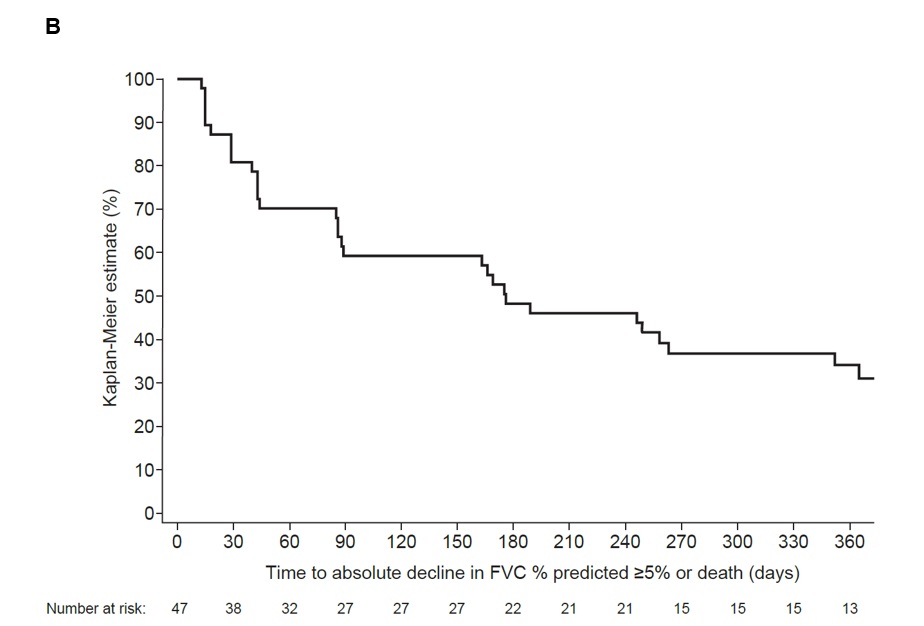
Results: Among patients with SSc-ILD in the SENSCIS trial (n=288), mean (SD) time since SSc-ILD diagnosis was 2.6 (1.8) years and mean (SD) FVC at baseline was 72.7 (16.6) % predicted. The proportions of patients with SSc-ILD progression at weeks 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 36 and 52 were 7.6%, 11.1%, 11.1%, 16.3%, 25.0%, 30.9% and 36.5%. Among patients with RA-ILD in the INBUILD trial (n=47), mean (SD) time since RA-ILD diagnosis was 3.7 (3.5) years and mean (SD) FVC at baseline was 72.0 (14.9) % predicted. The proportions of patients with RA-ILD progression at weeks 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 36 and 52 were 12.8%, 12.8%, 25.5%, 23.4%, 40.4%, 51.1% and 55.3%. Kaplan-Meier estimates of time to ILD progression are shown in the Figure.
Conclusion: In clinical trials in patients with SSc-ILD and RA-ILD, a substantial proportion of patients showed ILD progression over as little as three months. Patients with SSc-ILD and RA-ILD should be monitored more frequently than annually, including patients more than 1-2 years after diagnosis, to enable early detection of ILD progression and timely decision-making about treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Distler O, Alves M, Toenges G, Hoffmann-Vold A. Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease Due to Systemic Sclerosis or Rheumatoid Arthritis Need Monitoring More Frequently Than Annually [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-with-interstitial-lung-disease-due-to-systemic-sclerosis-or-rheumatoid-arthritis-need-monitoring-more-frequently-than-annually/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-with-interstitial-lung-disease-due-to-systemic-sclerosis-or-rheumatoid-arthritis-need-monitoring-more-frequently-than-annually/