Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Composite measures (e.g. SDAI) to assess Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) disease activity incorporate patient (PGA) and evaluator (EGA) global assessments. EGA and PGA are often discordant, reflecting divergent perspectives on evaluation of disease impact and potentially towards therapeutic goals. We evaluated the stability of PGA minus EGA (PGA-EGA) concordance or discordance from baseline to up to 5 years, and across all levels of disease activity in 822 patients (≥ 90% confirmed RA) from the prospective longitudinal Early Undifferentiated PolyArthritis (EUPA) cohort.
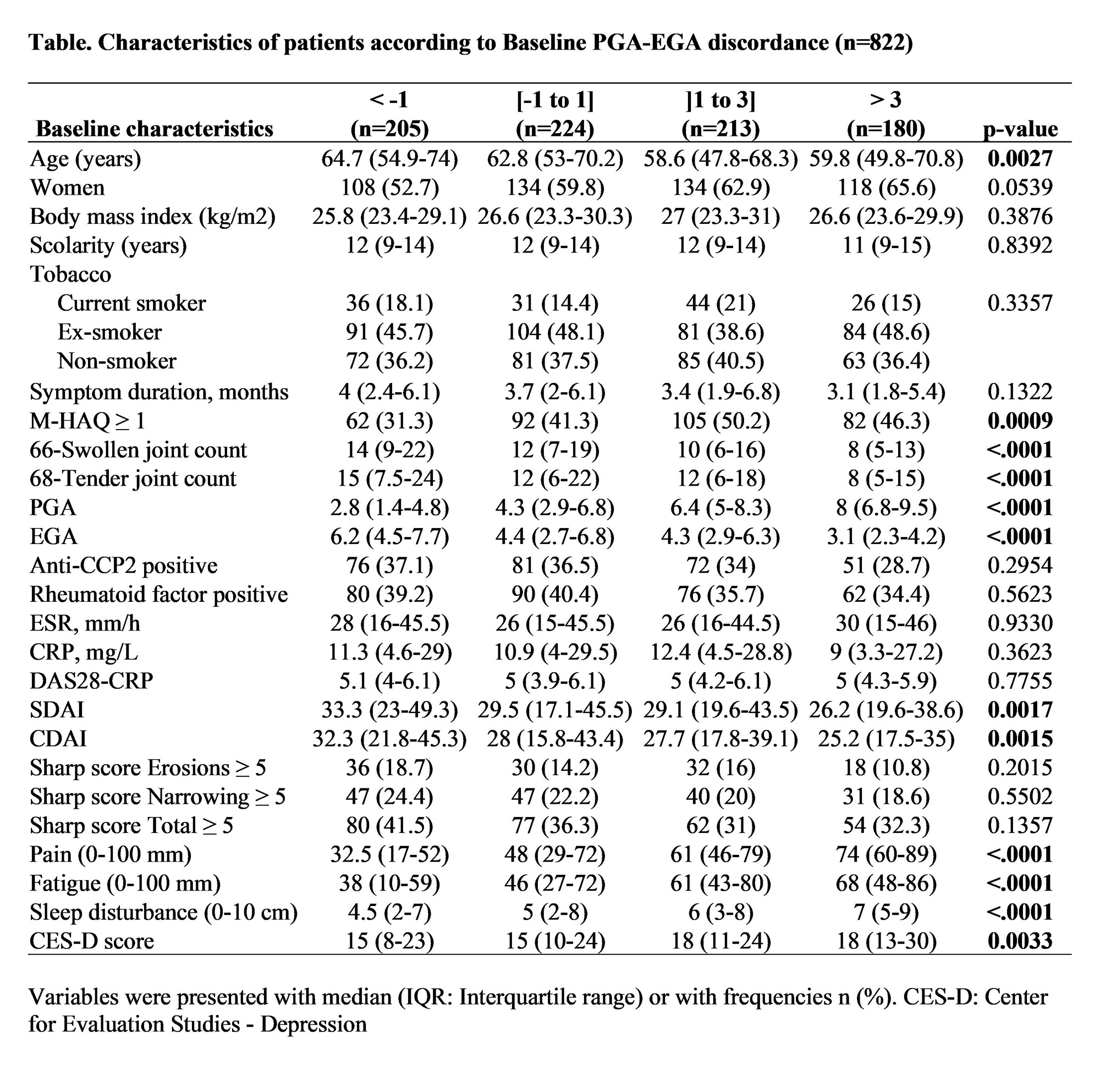
Methods: Demographics, clinical and serological variables, radiographic damage (Sharp van der Heijde scores), treatments, comorbidities, and Patient-Reported Outcomes (pain, function, depression, sleep quality) were collected at baseline (median symptom duration 3.7 months) and at 12, 18, 30, 42 and 60 months from symptom onset. PGA and EGA were reported using a 0-10 cm visual analog scale (VAS). PGA-EGA discordance was divided in four subgroups: negative discordance group (< -1 cm), concordance group (≥-1cm and ≤+1 cm), positive discordance group I ( >1 cm and ≤3 cm) and group II ( >3 cm).
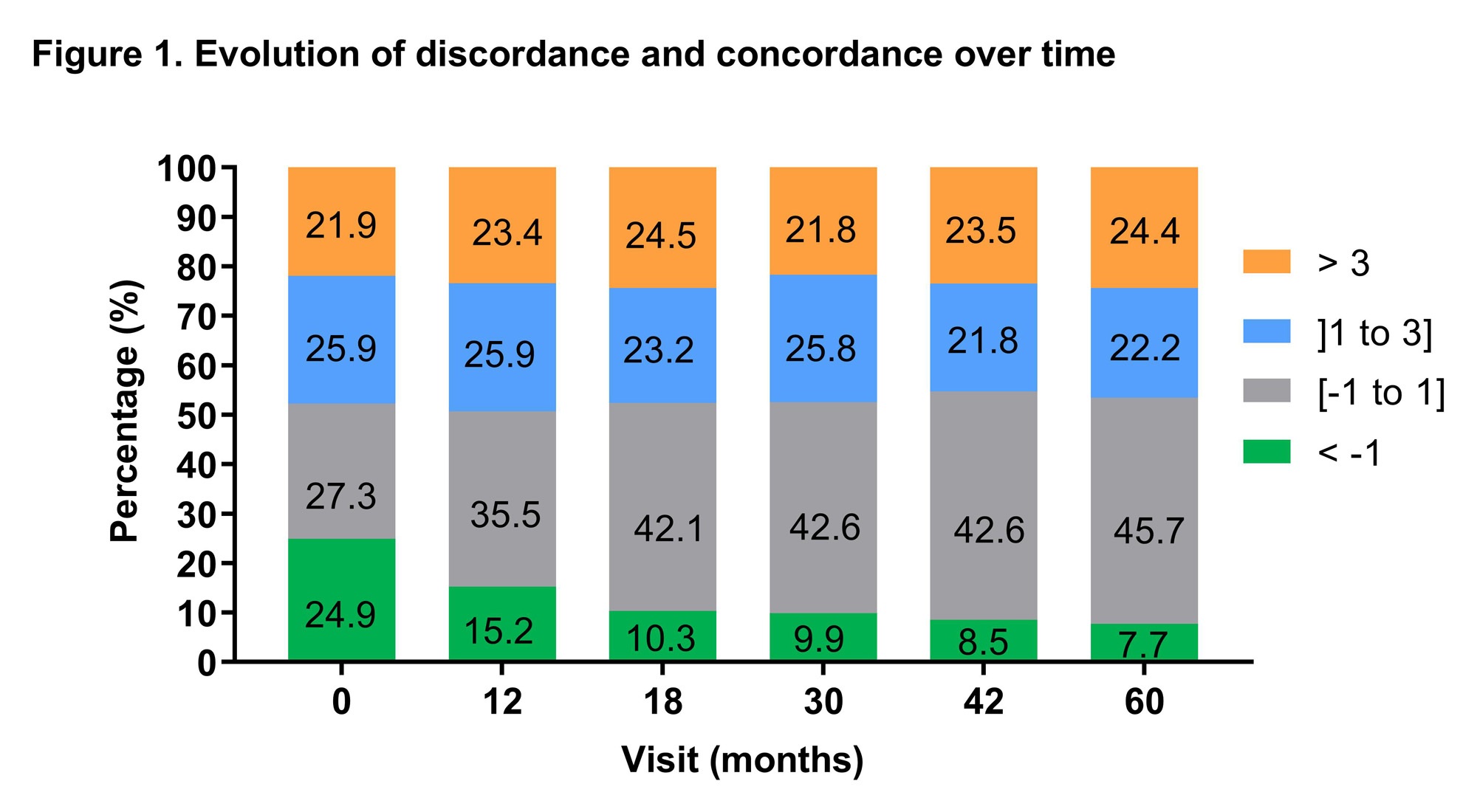
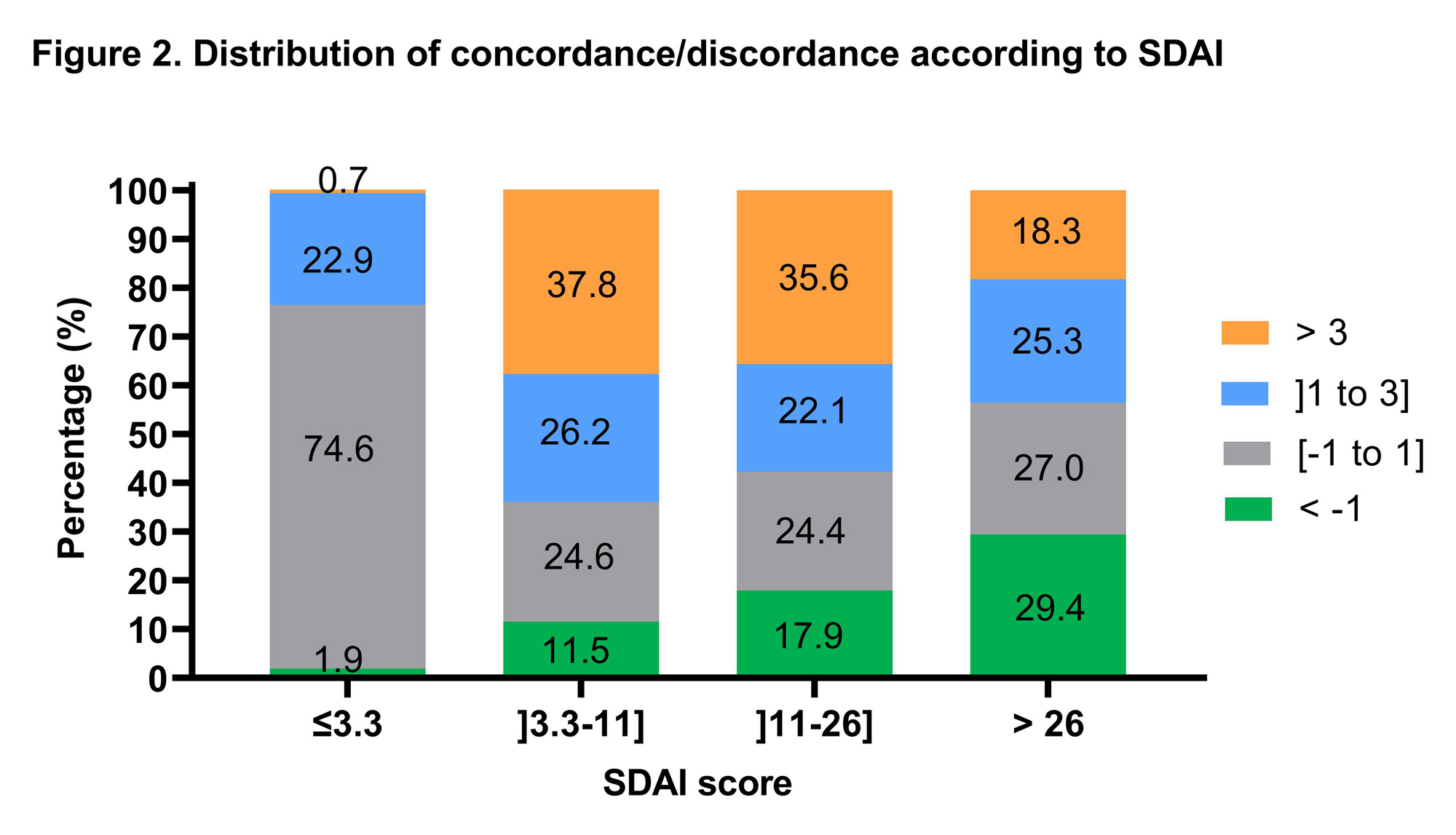
Results: At baseline, concordance was present in 27.3%, negative discordance in 24.9% while 47.8% expressed positive discordance (25.9 % group I and 21.9% group II). Over 60 months, concordance increased to 45.7%, negative discordance decreased to 7.7%, while positive discordant groups remained stable (still 46.4 % at 5 years). In positive discordant groups at baseline, patients were younger (median 58.6 years group I and 59.8 years group II, p < 0.003), had higher functional impact (M-HAQ ≥1, 46.3 % to 50.2 % p < 0.001), fewer tender and swollen joints (p < 0.0001), but rated higher for pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances (p < 0.0001) and depression (CES-D, median score 18 for both groups, p < 0.005). Only 20% (117/583) remained in the same subgroups between 18 and 60 months. The majority of those who remained stable were patients with concordance (79/117) and with positive discordance group II (25/117). Concordance was most frequent in remission, negative discordance in high disease activity, while group I positive discordance appeared independent of disease activity. Group II positive discordance was highest (35-38%) with low or moderate disease activity.
Conclusion: In this study of patients with early arthritis, almost half evaluated their global disease activity worse than the evaluator (positive discordance) and this proportion remained stable over the first 60 months of disease. Patients in positive discordant group were younger and reported higher functional impact, pain, fatigue, poor sleep and more symptoms of depression but had lower tender and swollen joint counts. Concordance was best when the patients were in SDAI remission. Negative discordance increased with disease activity. Over time, the relative proportions of each group remained similar, but only a small number of individual patients remained in the same group, most frequently in the concordance group but also among those who invariably rated their disease markedly more active than their physicians (group II), a subgroup important to identify early on to improve their management.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Couture A, Carrier N, Allard-Chamard H, ROUX S, Liang P, Boire G. Patient’s and Physician’s Evaluation of Global Assessment of Disease Activity over Follow up and Across Disease Activity Levels in Recent-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-and-physicians-evaluation-of-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-over-follow-up-and-across-disease-activity-levels-in-recent-onset-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-and-physicians-evaluation-of-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-over-follow-up-and-across-disease-activity-levels-in-recent-onset-rheumatoid-arthritis/