Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0325–0344) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic immune-mediated disease that commonly involves the pancreas in the form of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). Despite being one of the most common manifestations of the disease, the burden of abdominal symptomatology experienced by patients with IgG4-related AIP is not well-described.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional study of patient-reported data using our large, prospective, single-center cohort of patients with IgG4-RD. Subjects were included if they met 2019 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria. Subjects were excluded if the presence of AIP was unclear from chart review. All eligible subjects were sent surveys that contained questions regarding demographics, disease characteristics, comorbidities, treatment history, and detailed abdominal symptomatology. We compared characteristics between survey responders and non-responders as well as survey responses between patients with and without AIP using Chi-square tests for categorical and unpaired T tests for continuous variables.
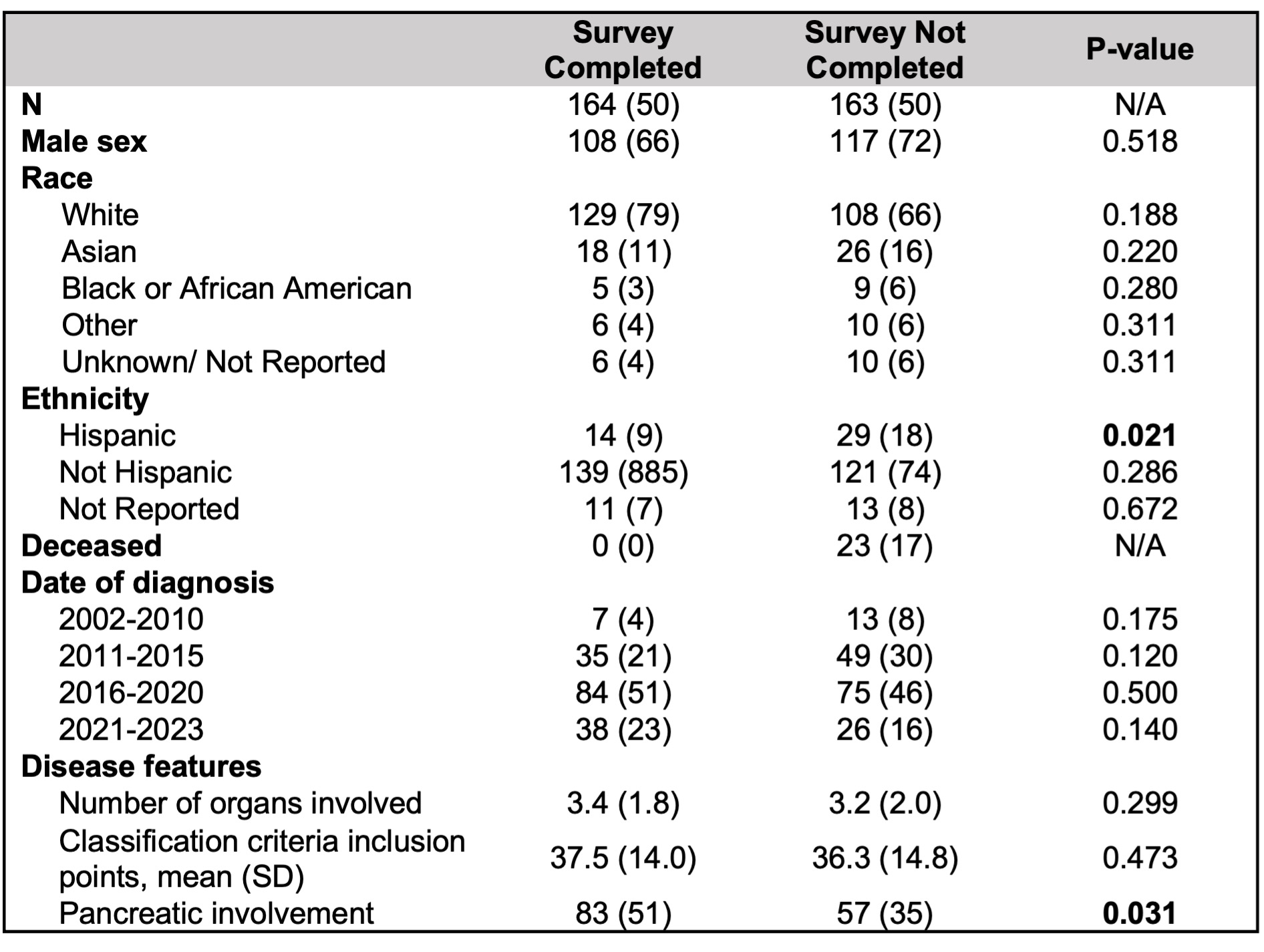
Results: Of 327 eligible subjects, 164 (50%) completed surveys; the remainder did not respond to survey invitations, were deceased, or did not have accurate contact information available. Hispanic subjects were less likely to respond to the survey, while subjects with AIP were more likely to respond to the survey than those without; otherwise, demographics were similar between responders and non-responders (Table 1).
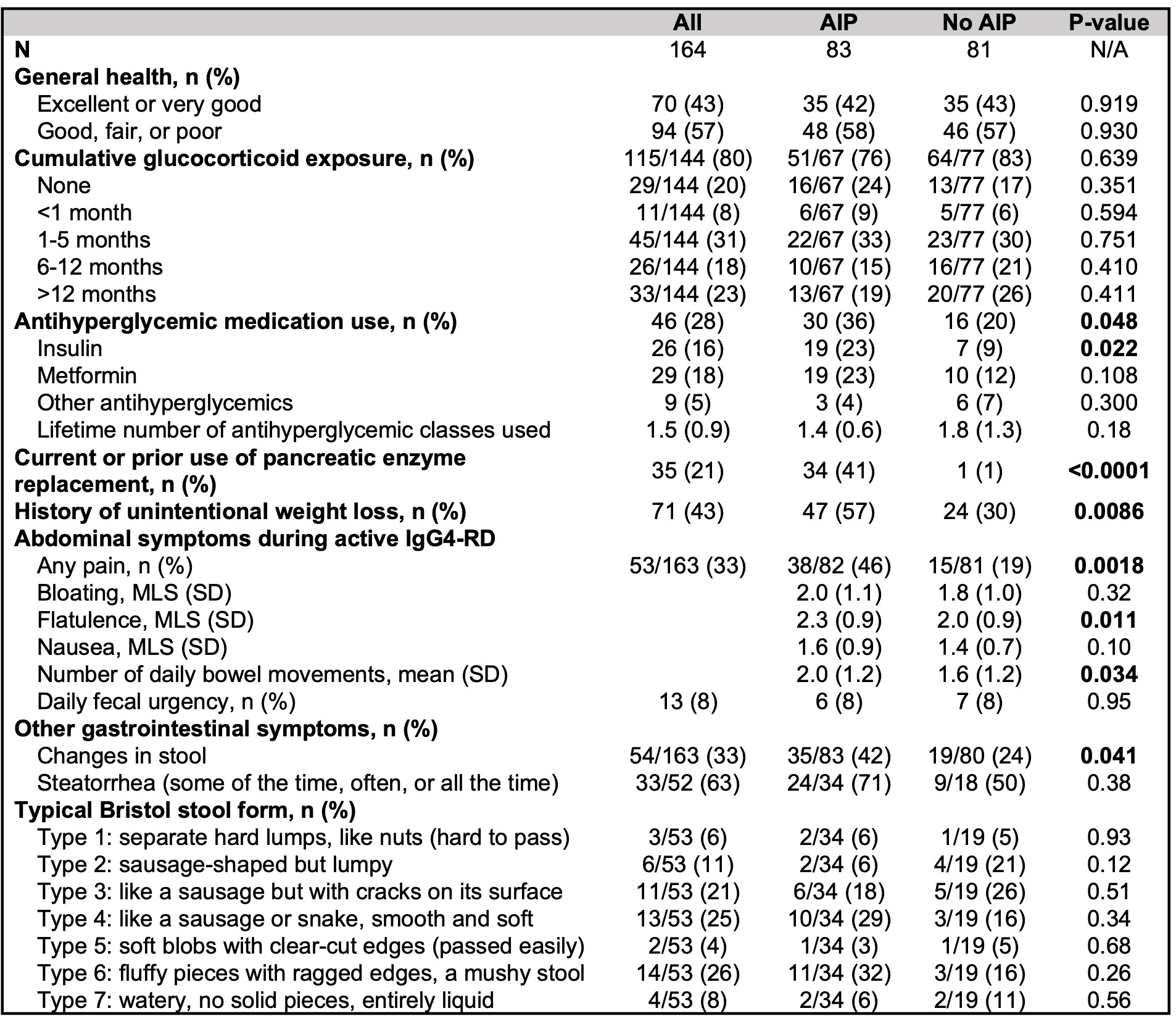
Disease features and abdominal symptoms in subjects with and without AIP are shown in Table 2. Overall, 43% of subjects characterized their general health as either “excellent” or “very good,” and 23% reported a cumulative glucocorticoid exposure duration of >1 year. Subjects with AIP more commonly reported having been prescribed insulin, any antihyperglycemic medication, and pancreatic enzyme replacement than those without AIP. Subjects with AIP more frequently experienced unintentional weight loss, abdominal pain, flatulence, and changes in stool consistency or frequency than those without AIP.
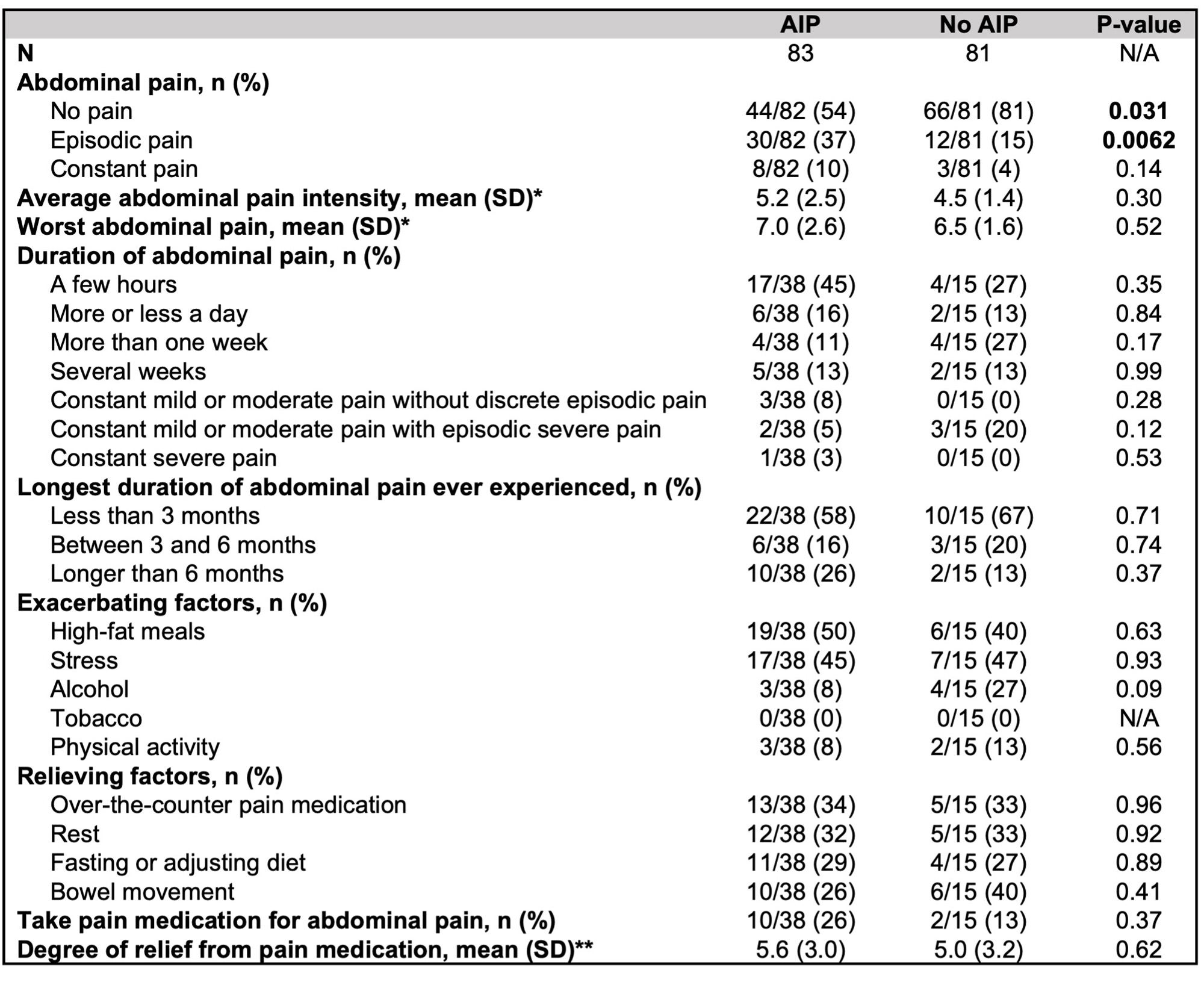
Patient-reported characteristics of abdominal pain are shown in Table 3. 38/83 (46%) subjects with AIP reported abdominal pain, and among these subjects, episodic pain was most common (30/38, 79%). 10/38 (26%) reported having experienced episodes of abdominal pain lasting over 6 months, compared with 2/15 (13%) of subjects without AIP who reported abdominal pain (p=0.37). High fat meals and stress were common exacerbating factors in both groups. Numerically more subjects with AIP reported taking pain medication for abdominal pain (26% vs. 13%, p=0.37).
Conclusion: In this large study using patient-reported measures, there was a high burden of symptomatology and comorbidities attributable to IgG4-RD in patients with and without AIP. Patients with AIP experience symptoms and complications attributable to both active pancreatitis (e.g., abdominal pain) and pancreatic insufficiency (e.g., insulin-dependent diabetes, weight loss requiring pancreatic enzyme replacement). These symptoms can have a significant impact on quality of life and should be assessed for and addressed by treating clinicians.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harvey L, Katz G, Hernandez-Barco Y, Fernandes A, McMahon A, McMahon G, Jha I, Wallace Z, Perugino C, Stone J. Patient-Reported Experiences and Comorbidities in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease with and Without Pancreatic Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-experiences-and-comorbidities-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-with-and-without-pancreatic-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-experiences-and-comorbidities-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-with-and-without-pancreatic-involvement/