Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
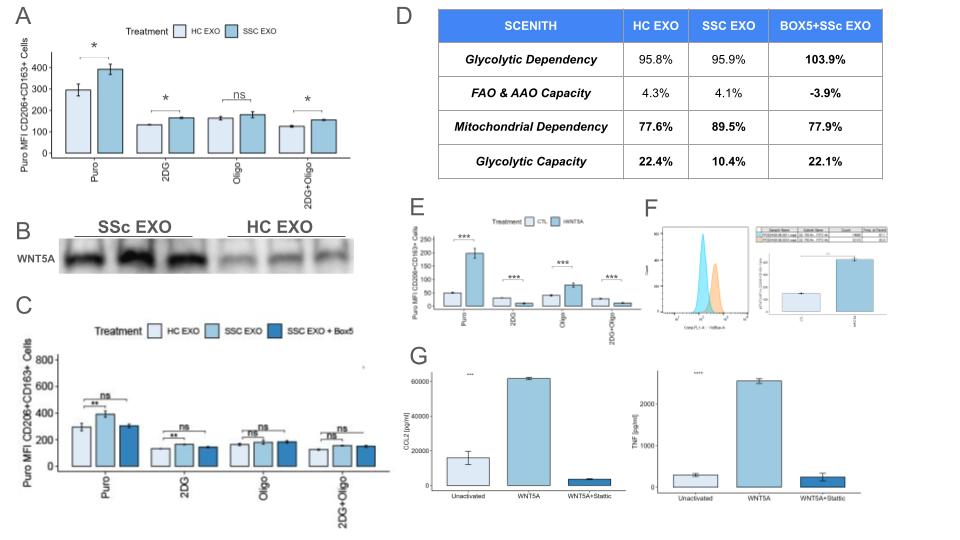
Background/Purpose: While we have shown that systemic sclerosis (SSc) dermal fibroblasts and macrophages (MØs) engage in reciprocal activation mediated by exosomes via paracrine signaling, the molecular mechanism underlying this mutual activation is unknown. Because MØ metabolic activity has recently emerged as a critical factor in the regulation of fibrotic disease, we hypothesized that SSc fibroblast-derived exosomes may modulate pro-fibrotic activation of MØs through metabolic reprogramming.
Methods: Primary human monocyte-derived MØs (hMDMs) were activated with SSc or control fibroblast-derived exosomes and metabolically phenotyped. The ability of SSc exosomes to activate MØs after treatment with metabolic inhibitors was assessed by flow cytometry, ELISA, and qRT-PCR. Exosome protein content was interrogated to identify candidate regulators of metabolic activity.
Results: SSc fibroblast-derived exosomes increased the basal metabolic rate of hMDMs, upregulated mitochondrial dependency, decreased glycolytic capacity, and increased lipid uptake relative to healthy controls. OXPHOS blockade abrogated the ability of SSc fibroblast exosomes to induce pro-fibrotic activation of hMDMs, and prevented reciprocal activation of SSc fibroblasts by SSc exosome-activated hMDMs in co-culture. SSc fibroblast exosomes upregulated expression of WNT5A, and pretreatment with Wnt pathway inhibitors abrogated SSc exosome-mediated activation. Treatment of hMDMs with rWNT5A partially recapitulated the MØ activation profile conferred by SSc fibroblast exosomes via a pSTAT3-dependent mechanism.
Conclusion: Here we provide evidence for the emerging role of immunometabolic dysfunction in SSc. Our data suggest that paracrine WNT-signaling induces metabolic shift in MØs in SSc that are mediate pro-fibrotic activation. These results provide foundational support for further investigation of the therapeutic utility of targeting MØ metabolism and noncanonical WNT-signaling for the treatment of SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Morris E, Jarnagin H, Yang H, Turnquist A, Whitfield M, Pioli P. Paracrine WNT Signaling Drives Pro-fibrotic Metabolic Activation of Systemic Sclerosis Macrophages [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/paracrine-wnt-signaling-drives-pro-fibrotic-metabolic-activation-of-systemic-sclerosis-macrophages/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/paracrine-wnt-signaling-drives-pro-fibrotic-metabolic-activation-of-systemic-sclerosis-macrophages/