Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is characterized by kidney inflammation. B cells play a central role in LN pathogenesis and type I interferon (IFN-I) pathway activation amplifies inflammation. Obinutuzumab, a glycoengineered, type II CD20 antibody demonstrated efficacy in patients (pts) with LN when added to standard therapy in the Phase II NOBILITY (NCT02550652) and Phase III REGENCY (NCT04221477) trials.This study explored the efficacy of obinutuzumab vs placebo (plus standard therapy) in various serological biomarker subgroups of pts with LN from the NOBILITY trial.
Methods: Pts received obinutuzumab or placebo at Weeks 0, 2, 24 and 26, plus standard therapy of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus glucocorticoids. All pts met ACR SLE classification criteria and had biopsy-proven proliferative LN. Whole blood from participants (88/126 pts) was used for bulk RNA sequencing. Baseline IFN-I status (high [hi] vs low [lo]) was determined in samples from healthy volunteers, using previously published gene signatures from the ROSE (NCT00962832) and TULIP (NCT02446912) trials. Cut-off for IFN-I status was determined using the median +2x median absolute deviation of age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Anti-dsDNA, anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA; SSA, SSB, RNP and Sm) and complement C3/C4 levels were assessed. Subgroup analyses were performed on baseline biomarker categories using the endpoint of Week 52 complete renal response (CRR). Odds ratios (OR) relative to placebo or MMF were estimated by logistic regression, with a significance level of α=0.2.
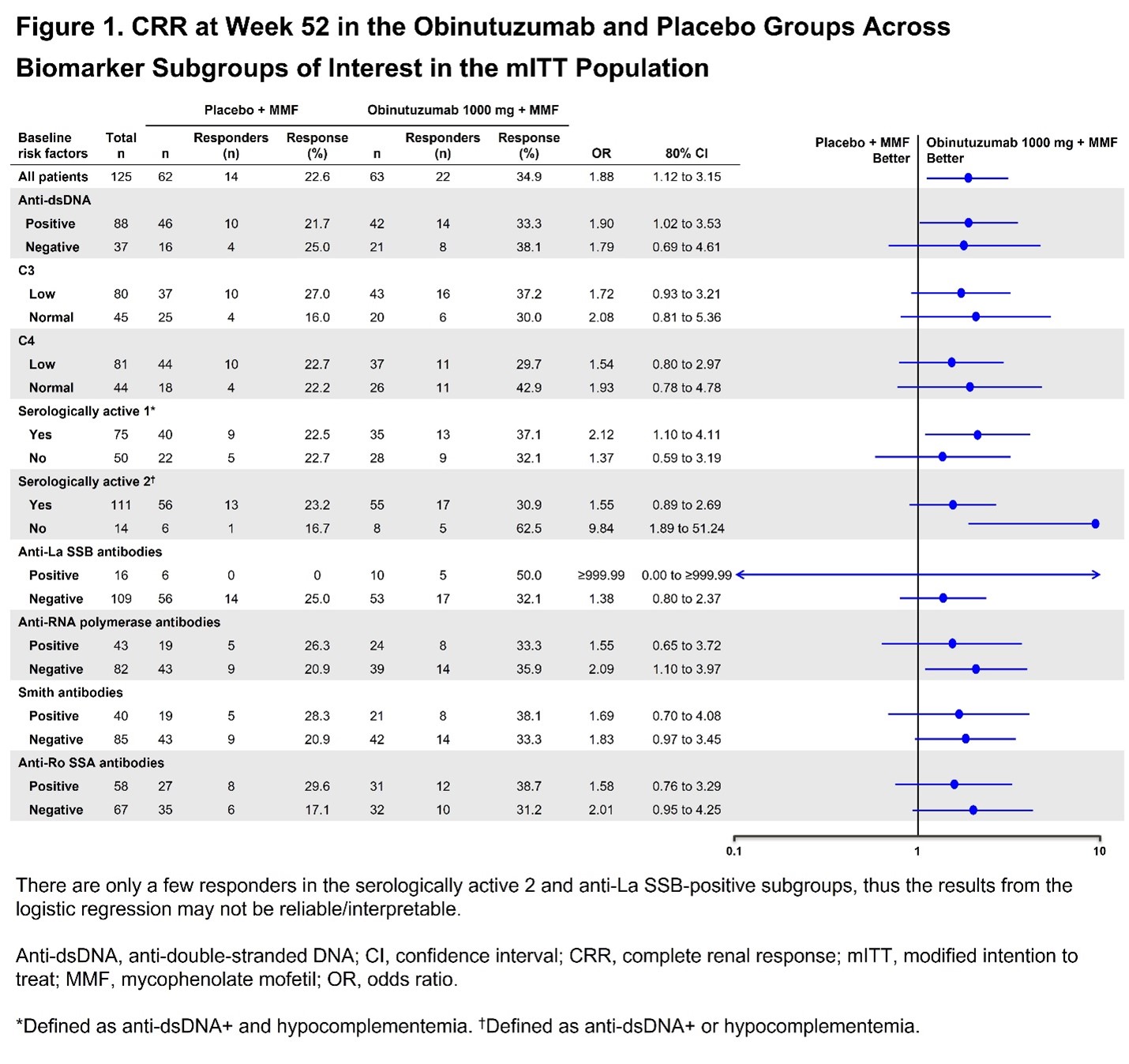
Results: Of 88 pts, 75 (85.2%) were categorized as IFNhi and 13 (14.8%) as IFNlo using the ROSE IFN-I gene signature. Baseline IFN-I status did not reliably predict the likelihood of achieving CRR at Week 52. At Week 52, in the IFNhi subgroup, 41% (16/39) of pts receiving obinutuzumab achieved CRR vs 19.4% (7/36) of pts receiving placebo (P< 0.2; OR [80% CI], 2.9 [1.5 to 6], Table 1). A statistically significant trend favoring obinutuzumab was observed in the IFNlo subgroup (33.3% [2/6] vs 14.2% (1/7); P >0.2; OR [80% CI], 3.0 [0.9 to 9.6], Table 1). Using the REGENCY Week 76 CRR definition and the TULIP IFN-I gene signature yielded similar results. A multivariable logistic regression analysis using treatment and baseline IFN-I status as covariates did not reveal a statistically significant association between IFN-I status and response (P=0.6221; OR [80% CI], 1.4 [0.5 to 3.64]. Across subgroups defined by baseline complement, anti-dsDNA and other autoantibodies, more CRRs were observed with obinutuzumab vs placebo, including in pts with high serological activity (Figure 1). Results were generally consistent using the Week 76 REGENCY CRR definition.
Conclusion: Analyses suggest that obinutuzumab may be an effective therapy in pts with LN regardless of baseline serological biomarker status. A significant CRR benefit was observed in the IFNhi subgroup and a similar trend was seen in the IFNlo subgroup. Obinutuzumab generally demonstrated greater efficacy vs placebo across baseline serological biomarker subgroups. Whilst limited sample size restricted significance, similar ORs across subgroups suggest a consistent trend favoring obinutuzumab regardless of serological status.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vital E, Vargas B, Rae J, Wang T, Hackney J, Looney C, Pendergraft W, Lightstone L, Rovin B, Furie R, Raghu H. Obinutuzumab Shows Promise in Lupus Nephritis Regardless of Baseline Serological Markers: An Exploratory Post Hoc Analysis of a Phase II Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obinutuzumab-shows-promise-in-lupus-nephritis-regardless-of-baseline-serological-markers-an-exploratory-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-ii-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obinutuzumab-shows-promise-in-lupus-nephritis-regardless-of-baseline-serological-markers-an-exploratory-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-ii-trial/

.jpg)