Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: T Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Nearly all patients with mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) have IgG autoantibodies (autoAb) specific for U170k, a component of the U1-snNRP spliceosomal complex. A genetic link to the MHC II molecule HLA-DRB1*0401 (DR4) and formation of IgG autoAb strongly suggest the importance of CD4+ T cells in MCTD pathogenesis. Defining specific, self-reactive CD4+ T cell populations in MCTD could help drive progress towards specific therapies.
Methods: We used a peptide:MHCII binding prediction algorithm (NetMHCIIpan3.2) to identify U170k peptides likely to bind DR4. We generated fluorophore-labeled HLA-DR4 tetramers loaded with these peptides and subsequently used them to stain and magnetically enrich U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells from naïve and immunized DR4 transgenic (DR4-Tg) mice and from DR4+ healthy human donors.
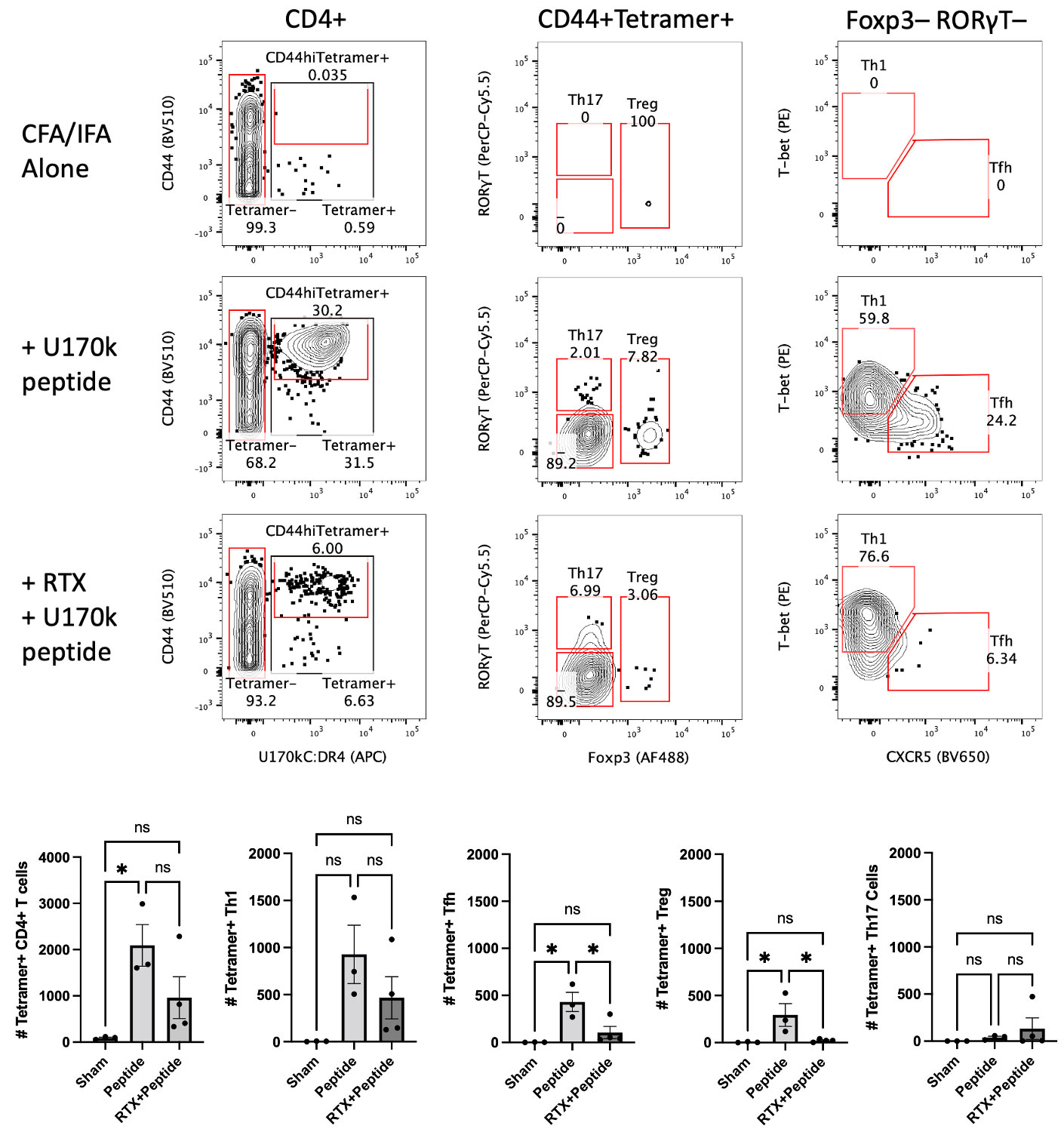
Results: Three peptides from the RNA binding domain of U170k were predicted to bind DR4: QGDAFKTLFVARVNY, FKTLFVARVNYDTTE, PIKRIHMVYSKRSGK (nonamer cores underlined). Magnetic tetramer enrichment with tetramers loaded with these peptides allowed detection of rare, naïve U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells in HLA-DR4 transgenic mice (DR4-Tg) mice. These cells expanded 5-10 fold and upregulated CD44 after immunization with U170k peptides in Complete Freund’s Adjuvant followed by a boost in Incomplete Freund’s Adjuvant 30-40 days later (Fig. 1). A single peptide-CFA immunization was insufficient to induce activation of U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells (i.e., a secondary boost with IFA is required; data not shown). Most U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells became T follicular helper (Tfh) cells or T helper type 1 (Th1) cells. Notably, pretreatment of mice with anti-CD20 IgG2c prior to boosting with peptides abrogated the ability to form U170k:DR4-specific Tfh and Tregs (Fig. 2). In healthy human HLA-DR4+ donors, these novel reagents also detected rare, naïve (i.e., not activated) U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that novel DR4 tetramers can detect rare, naïve CD4+ T cells specific for U170k:DR4 in DR4-Tg mice and in healthy human DR4+ subjects. U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells expand 5-10-fold and become activated in mice after immunization, chiefly differentiating into Tfh and Th1 cells. Anti-CD20 IgG2c treatment blocked the ability to form U170k:DR4-specific Tfh and Treg cells, suggesting B cells play a role in the activation and differentiation of these antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. We are now using these tetramers in an established DR4-Tg MCTD mouse model that recapitulates some features of human MCTD, specifically development of anti-U170k autoAb and interstitial lung disease (ILD). We aim to determine how the balance of U170k:DR4-specific effector and regulatory CD4+ T cell populations influences autoantibody development and ILD pathogenesis. Moreover, we are preparing to study pediatric and adult patients with anti-U170k antibodies to determine if there are increased numbers of activated U170k:DR4-specific CD4+ T cells in active disease, whether they have altered effector and regulatory phenotypes, and whether this correlates specific disease features such as arthritis, ILD, and/or response to therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mahmud S, Dileepan T, Binstadt B, Jenkins M. Novel Human Class II MHC Tetramers Detect Rare, Self-Reactive CD4+ T Cells Relevant to Mixed Connective Tissue Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-human-class-ii-mhc-tetramers-detect-rare-self-reactive-cd4-t-cells-relevant-to-mixed-connective-tissue-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-human-class-ii-mhc-tetramers-detect-rare-self-reactive-cd4-t-cells-relevant-to-mixed-connective-tissue-disease/