Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Neutrophil activation and formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Calprotectin, a neutrophil activation marker, correlates with RA disease activity and is a novel biomarker that can be used to distinguish RA patients in remission and active disease and to predict disease progression. Abatacept is a CTLA-4-Ig fusion protein, which is widely used as a treatment for RA. However, the response rates to abatacept are variable in heterogeneous RA patients. We conducted this study to determine the effect of abatacept on neutrophil-related markers and to explore whether these markers could predict the therapeutic efficacy of abatacept in RA patients.
Methods: A total of 23 RA patients, who had an inadequate response to methotrexate and other conventional DMARDs, were enrolled in this study. All participants fulfilled the 1987 ACR criteria or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria, with clinical disease activity index (CDAI) ≥16. Plasma samples were collected at baseline, week 6, week 14, and week 24. Levels of calprotectin, myeloperoxidase (MPO)-DNA, and neutrophil elastase (NE)-DNA complexes were determined by ELISA. Responders (n=10) were defined as subjects who achieved ACR50 Response at week 24. Changes in these markers were compared before and after treatment using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. Baseline levels of these markers were compared between the responder and non-responder groups by the Mann-Whitney test.
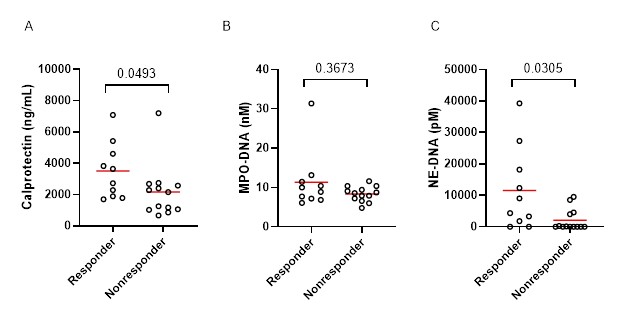
Results: Plasma levels of calprotectin and MPO-DNA complexes were significantly decreased at week 6 (p=0.0011 and p=0.0025, respectively), week 14 (p=0.0003 and p=0.0002, respectively), and week 24 (p=0.0121 and p=0.0037, respectively) with the treatment of abatacept when compared to baseline. Abatacept reduced the levels of NE-DNA only at week 14 (p=0.0085). Compared to the non-responders, the responders had a numerically higher percentage of anti-CCP antibodies (90% vs 62%, p=0.1790) and RF (90% vs 54%, p=0.0886). Baseline levels of calprotectin (3190 ng/mL vs 2167 ng/mL, p=0.0493) and NE-DNA complexes (6708 pM vs 0 pM, p=0.0305) were significantly higher in responders when compared to non-responders (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Abatacept significantly decreased neutrophil activation in RA patients. Calprotectin and NE-DNA complexes may serve as useful markers in predicting the therapeutic efficacy of abatacept in moderate to severe RA patients.
Comparison of plasma levels of calprotectin (A), MPO-DNA (B), and NE-DNA in circulation at baseline in patients treated with abatacept. Differences between groups were determined by the Mann-Whitney test.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang T, Giltiay N, Lood C, Han B. Neutrophil Activation and Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Associated with Response to Abatacept in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neutrophil-activation-and-formation-of-neutrophil-extracellular-traps-are-associated-with-response-to-abatacept-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neutrophil-activation-and-formation-of-neutrophil-extracellular-traps-are-associated-with-response-to-abatacept-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/