Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Numerous cross-sectional and animal studies have linked an altered gut microbiome to osteoarthritis (OA). Human studies are needed to explore the association between the gut microbiome and incident OA. Assessing microbiomes can be challenging; however, blood measures (e.g., metabolites) have offered insights into the gut microbiome and its relationship with prevalent OA. Hence, we explored whether blood-based metabolites, reflective of the gut microbiome, relate to incident knee OA during the subsequent 7 years.
Methods: We performed a secondary analysis of a case-cohort study that included 603 participants from the Osteoarthritis Initiative, comprising 237 incident knee OA cases and 366 non-cases from a randomly selected sub-cohort over an 8-year follow-up. Plasma metabolomes were analyzed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Among the measured metabolites, 47 were previously identified in the literature as microbial metabolites (Rushing BR et al., 2021). We averaged metabolite levels at baseline and year 1 as the exposure and identified incident OA cases as knees with a Kellgren and Lawrence grade ≥2 in subsequent follow-ups. Weighted logistic regression, which accounted for the study design and adjusted for age and gender with and without body mass index (BMI), was used to examine associations between these metabolite concentrations and knee OA incidence. As an exploratory analysis, multiple comparison correction was not applied.
Results: Among the 603 participants, 70% of OA cases (mean [SD] age = 60 [9] years, BMI = 28.6 [4.7] kg/m2), and 55% of non-cases were female (age = 58 [9], BMI = 26.9 [8.0] kg/m2). When adjusting only for age and gender, the upper quartile of 4 metabolites had a statistically significant association with greater odds of incident knee OA (2 had a significant p for trend; Table 1): 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid (OR = 1.90, p trend = 0.048), N,N-Dimethylglycine (OR = 1.65, p trend = 0.016), Kynurenic acid (OR = 1.51), N-Acetyl-L-phenylalanine (OR = 1.62). Only 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid remained statistically significant after adjusting for BMI (OR = 1.90, Table 2). Three metabolites had evidence suggestive that higher levels related to lower odds of incident OA: Benzoic acid (ORs range = 0.54-0.74), Butyric acid (OR range = 0.63-0.84), and Phenylacetic acid (OR range = 0.66-0.87). Benzoic acid (OR range = 0.62-0.74) and Butyric acid (OR range = 0.66-0.88) remained statistically significant after adjusting for BMI (Table 2). Furthermore, after adjusting for BMI, 10 other metabolites had evidence that higher levels related to lower odds of incident OA, including 3 with a p for trend < 0.05: 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid, Pyruvic acid, and Glucose.
Conclusion: Our results complement a prior cross-sectional analysis using fecal metabolomes, which suggested OA was associated with perturbed pathways, including amino acid metabolism (e.g., glycine, serine, tryptophan, phenylalanine), fatty acid metabolism, dietary polyphenol metabolism, and pyruvate metabolism. Unlike the prior study, we offer longitudinal evidence that these metabolites are altered before the onset of knee OA and may be modifiable risk factors, which can be monitored in blood samples.
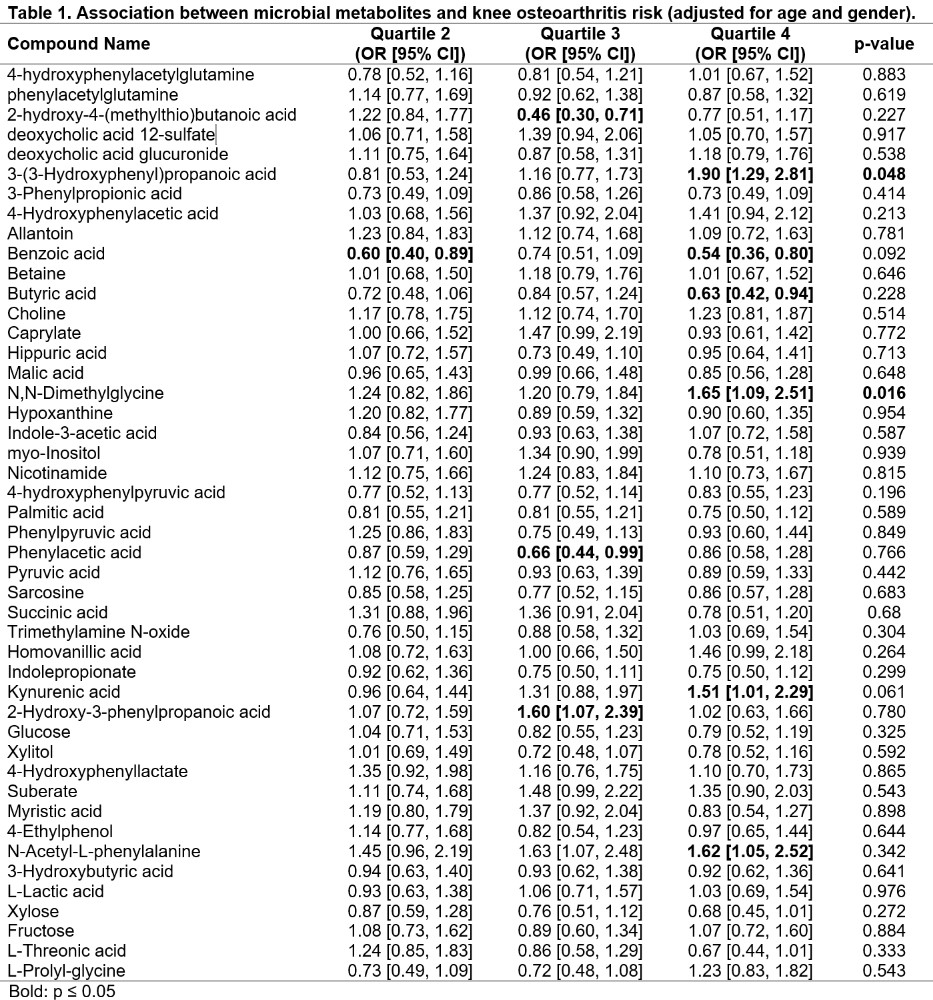 Table 1. Association between microbial metabolites and knee osteoarthritis risk (adjusted for age and gender)
Table 1. Association between microbial metabolites and knee osteoarthritis risk (adjusted for age and gender)
.jpg) Table 2. Association between microbial metabolites and knee osteoarthritis risk (adjusted for age, gender, and body mass index)
Table 2. Association between microbial metabolites and knee osteoarthritis risk (adjusted for age, gender, and body mass index)
Disclosures: J. Driban: None; S. Xu: None; T. McAlindon: Anika, 2, Grunenthal, 2, Kiniksk, 2, Kolon TissueGene, Inc., 2, Medipost, 2, Novan, 2, Organogenesis, 2, Regeneron, 2, Remedium-Bio, 2, Samumed, 2, Sanofi, 2, Scarcell, 2, Visor, 2; J. Haran: None; J. Patarini: None; B. Lu: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Driban J, Xu S, McAlindon T, Haran J, Patarini J, Lu B. Metabolites Reflective of the Gut Microbiome Relate to Future Incident Knee Osteoarthritis: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/metabolites-reflective-of-the-gut-microbiome-relate-to-future-incident-knee-osteoarthritis-data-from-the-osteoarthritis-initiative/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/metabolites-reflective-of-the-gut-microbiome-relate-to-future-incident-knee-osteoarthritis-data-from-the-osteoarthritis-initiative/
