Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the complement system is activated and commonly thought to occur through the classical pathway (CP) [1]. However, our previous research have demonstrated several of the lectin pathway (LP) proteins change with disease activity and specific SLE manifestations[2].
Traditionally, when diagnosing SLE or assessing disease activity, measurement of low C3 or C4 are used as proxies for complement activation [3]. However, measurement of C3 and C4 does not differentiate which complement pathway initiated the activation [1, 4].
C1-esterase inhibitor (C1inh) is one of the key regulators of the complement system. C1inh is the exclusive inhibitor of the active CP enzymes C1r and C1s [5], and the major inhibitor of active LP enzymes MASP-1 and MASP-2 [6]. A possible way of assessing complement activation through a specific pathway is by measuring activated enzymes complexed with C1inh in plasma, as these complexes only exist after complement enzyme activation.
Our aim was to investigate specific activation of the complement system through the LP or the CP in SLE by measuring the protein complexes MASP1/C1inh (LP specific activation) and C1s/C1inh (CP specific activation) in relation to disease activity and lupus nephritis (LN).
Methods: A cross sectional cohort of 150 patients with SLE fulfilling the 1997 ACR classification criteria for SLE were included. Disease manifestations and disease activity using SLEDAI-2K was assessed at inclusion. Fifty blood donors were used as controls. Both C1s/C1inh and MASP1/C1inh complexes were measured in all samples using two newly developed sandwich ELISAs (C1s/C1inh: cat# HK399; MASP1/C1inh: Cat#3001, Hycult Biotech, Uden, The Netherlands).
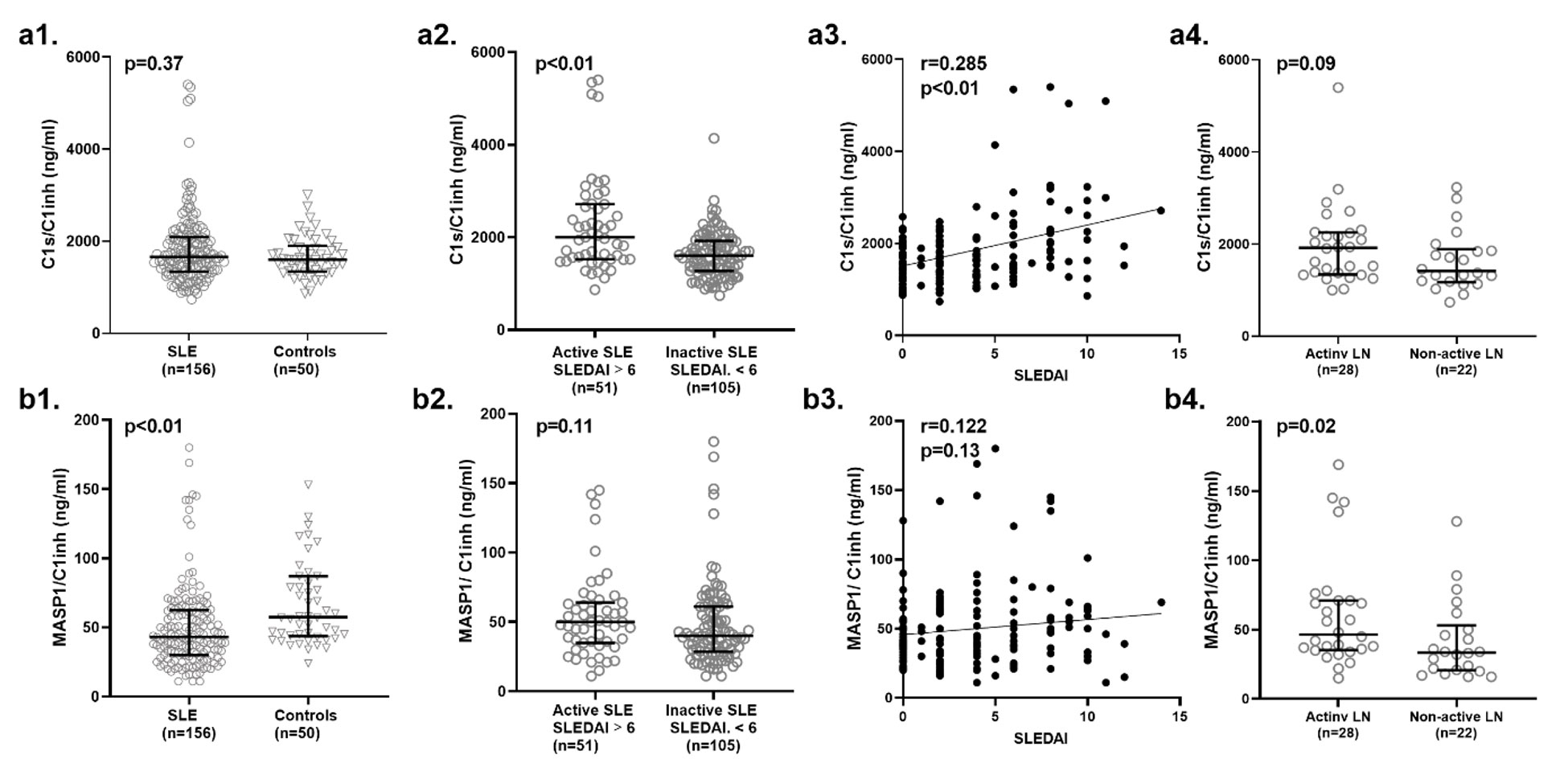
Results: When comparing SLE patients to controls, we observed a lower concentration in plasma of MASP1/C1inh (p< 0.01), whereas no difference was observed regarding C1s/C1inh (fig. a1 and b1).
C1s/C1inh concentrations were significantly increased in active SLE patients (SLEDAI >6) compared to SLE patients with low disease activity (SLEDAI < 6, p< 0.01) and C1s/C1inh concentrations correlated with SLEDAI score (r=0.285, p< 0.01) (fig. a2 and a3). C1s/C1inh concentrations were not significantly increased in SLE patients with active LN compared to non-active LN (p=0.09) (fig.a4).
MASP1/C1inh plasma concentrations were not associated with disease activity (p=0.11), and we did not observe a significant correlation with disease activity (r=0.12, p=0.13) (fig.b2 and b3). In active LN, plasma concentrations of MASP1/C1inh were significantly elevated compared to non-active LN (p=0.02) (fig. b4). No difference was observed between different classes of LN for neither MASP1/C1inh nor C1s/C1inh (p=0.143 and p=0.254, respectively) (fig. 2).
Conclusion: Our data support that the general complement activation seen in active SLE is associated with activation of the CP of complement activation. However, activation of the LP might be more specific to particular disease manifestations like LN.
Our findings warrant further research into activation of the specific complement pathways in relation to specific disease manifestations in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Troldborg A, Larsen M, Toonen E, Hurler L, Prohaszka Z, Cervenak L, Hansen A, Thiel S. Measurements of Specific Activation Through the Lectin -or Classical Pathway of Complement in Patients with SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measurements-of-specific-activation-through-the-lectin-or-classical-pathway-of-complement-in-patients-with-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measurements-of-specific-activation-through-the-lectin-or-classical-pathway-of-complement-in-patients-with-sle/