Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-5:50PM
Background/Purpose: In gout, long-term xanthine oxidase inhibitor treat to target urate lowering therapy (XOIT2T) markedly reduces flares and synovitis, despite delayed resolution of tissue crystal deposits. XOI drugs inhibit oxidative stress and the NLRP3 inflammasome in cultured leukocytes, but XOI effects on immune cells in vivo are poorly understood. To better define mechanisms and markers of long-term XOIT2T effects on gouty inflammation in vivo we curated PBMCs in a sub-cohort (n=32) of allopurinol vs. febuxostat comparative effectiveness trial CSP594 “STOP GOUT”.
Methods: All subjects reported recurrent acute flare activity and poorly controlled serum urate ( >6.8 mg/dL) at enrollment. Serum cytokine quantification used mesoscale discovery immunoassay. PBMCs were analyzed by multiplexed, quantitative proteomics. Significantly altered proteins (via p-value and fold-change; pi score > 0.6) were subject to K-means clustering, then pathway and network analyses.
Results: At study endpoint (EP: 48 weeks XOIT2T), serum urate dropped by >30% to reach normouricemia, and gout flares dropped by ~50% from baseline (BL)(P< 0.05 for both). Two subgroups of patients were clearly separable by BL serum IL-8, though indistinguishable by age, comorbidities, and gout flare rates. One subgroup had elevated IL8 at BL that fell until EP (“IL8+” group); the other subgroup had consistently low IL8 (“IL8-” group). To probe for differential responses to XOIT2T, we stratified samples into the 2 subgroups. At study EP, we saw broad PBMC proteome changes, with many prominent in the IL8+ subgroup. Specifically, we found increased mitochondrial and oxidative phosphorylation proteins, as well as nucleosome, ribonucleoprotein, and AP protein coat complexes (Fig 1). To assess how the proteome changes related to known gout pathways, we “pin-dropped” known central gout signaling molecules into a protein association network derived from the proteomic data (Fig 2). From this analysis, we defined a core XOIT2T response linked to known gout mediators (Fig 2 – black outline), that included increased M2 macrophage markers (TGFB1, PSMB5) and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition (SUMO3) (Fig 3). Differential keratin and 14-3-3 protein expression suggested that XOIT2T alters IL8+ subgroup gout monocytes to limit both a keratinocyte-like subset linked to MMP1 tissue remodeling, and hypermigratory, pro-atherogenic monocytes physiologically suppressed by 14-3-3zeta. However, XOIT2T, which promoted early gout flares, significantly reduced SETDB1, a xanthine oxidase expression regulating histone modifier that also blunts TLR4 inflammatory signaling.
Conclusion: Serum cytokine immunoassays merged with leukocyte quantitative proteomics identified novel markers and mechanisms for gouty arthritis altered by long term flare-reducing XOIT2T. Prior to XOIT2T, gout patients were stratifiable into high and low serum IL8 subgroups. XOIT2T reduced the anti-inflammatory histone H3 modifier SETDB1, a novel potential contributor to early gout flares. However, overall, and especially in IL8+ patients, XOIT2T re-wired the PBMC proteome, promoting mitochondrial function and manifold inflammation resolving mechanisms.
 Figure 1 – Overview of PBMC Proteomic Response to XOIT2T. (A) K-means clustered heatmap of significantly altered proteins (pi score > 0.6) in response to XOIT2T. Clusters are colored and matched with their respective average profiles and gene ontology analyses. Heatmaps of mitochondrion protein (B), nucleosome protein (C) and ribonucleoprotein (D) fold-changes from cluster 4. Heatmaps of oxidative phosphorylation (E) and AP complex protein (F) fold-changes from cluster 5.
Figure 1 – Overview of PBMC Proteomic Response to XOIT2T. (A) K-means clustered heatmap of significantly altered proteins (pi score > 0.6) in response to XOIT2T. Clusters are colored and matched with their respective average profiles and gene ontology analyses. Heatmaps of mitochondrion protein (B), nucleosome protein (C) and ribonucleoprotein (D) fold-changes from cluster 4. Heatmaps of oxidative phosphorylation (E) and AP complex protein (F) fold-changes from cluster 5.
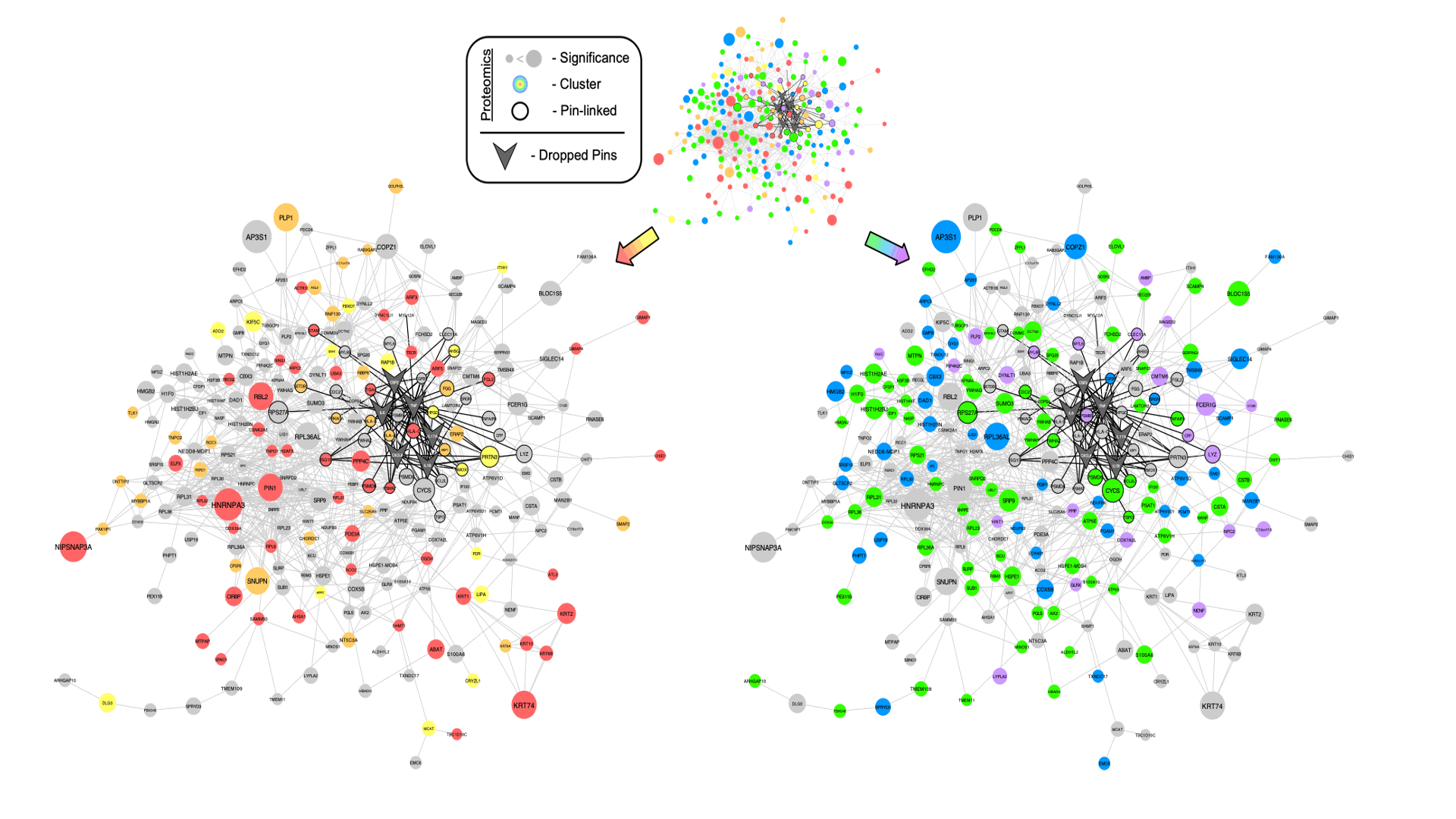 Figure 2 – Linkage of Known Gout Mediators to PBMC Proteome Changes Induced by XOIT2T. STRING-db protein association network of significantly altered proteins (pi score > 0.6) and known gout mediators (TNF, IL6, IL1B, IL17A, CXCL8 and CSF2). Proteomic nodes are sized by average significance (ie. pi score) across stratified groups, colored according to K-means clusters in Fig 1 and have black border if directly linked to pin-dropped gout mediators.
Figure 2 – Linkage of Known Gout Mediators to PBMC Proteome Changes Induced by XOIT2T. STRING-db protein association network of significantly altered proteins (pi score > 0.6) and known gout mediators (TNF, IL6, IL1B, IL17A, CXCL8 and CSF2). Proteomic nodes are sized by average significance (ie. pi score) across stratified groups, colored according to K-means clusters in Fig 1 and have black border if directly linked to pin-dropped gout mediators.
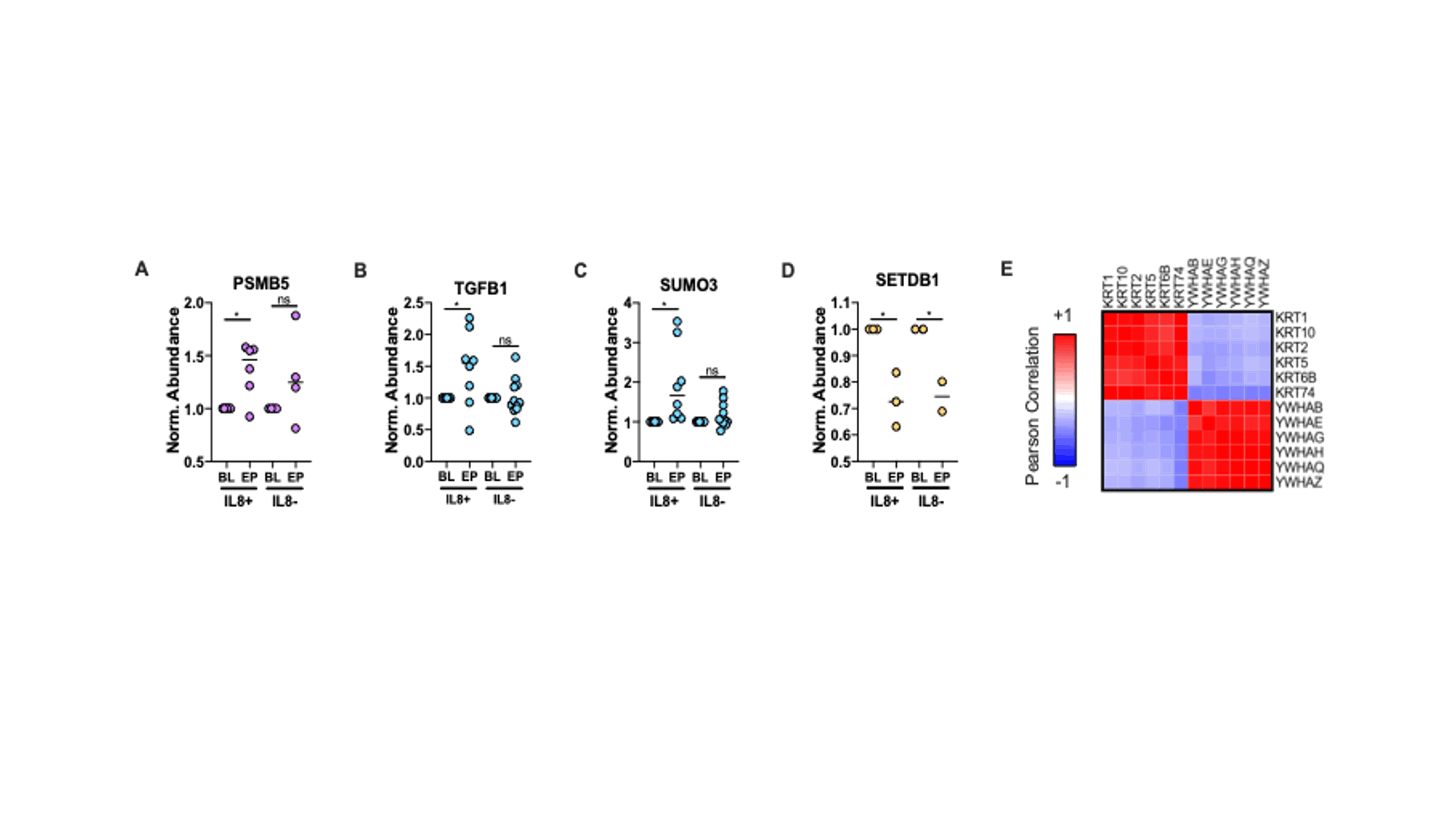 Figure 3 – Specific PBMC Proteins of Interest Altered by XOIT2T. Expression of PSMB5 (A), TGFB1 (B), SUMO3 (C) and SETDB1 (D) across all groups normalized to patient BL (*pi score > 0.6; points are colored according to their K-means clusters in Fig 1). (E) Correlation matrix of keratin and 14-3-3 proteins significantly altered by XOIT2T.
Figure 3 – Specific PBMC Proteins of Interest Altered by XOIT2T. Expression of PSMB5 (A), TGFB1 (B), SUMO3 (C) and SETDB1 (D) across all groups normalized to patient BL (*pi score > 0.6; points are colored according to their K-means clusters in Fig 1). (E) Correlation matrix of keratin and 14-3-3 proteins significantly altered by XOIT2T.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wozniak J, Bryan R, Gonzalez D, Terkeltaub R. Long-term Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Treat to Target Urate Lowering Therapy Coordinately Re-wires the Mononuclear Leukocyte Mitochondrial and Inflammatory Proteome in Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-xanthine-oxidase-inhibitor-treat-to-target-urate-lowering-therapy-coordinately-re-wires-the-mononuclear-leukocyte-mitochondrial-and-inflammatory-proteome-in-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-xanthine-oxidase-inhibitor-treat-to-target-urate-lowering-therapy-coordinately-re-wires-the-mononuclear-leukocyte-mitochondrial-and-inflammatory-proteome-in-gout/
