Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster II: SLE, JDM, & Juvenile Scleroderma (0764–0785)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a systemic autoimmune disease with a prominent interferon (IFN) signature. Treatment often requires prolonged high-dose steroids and other immunosuppressive medications. In a compassionate use program, we assessed baricitinib (JAK 1/2 inhibitor) in active, refractory JDM and recently demonstrated efficacy by clinically relevant improvements in validated disease activity assessments and decreased IFN markers by 24 weeks.(1) Here we report patient-reported outcomes (PRO) and dosing with extended follow-up.
Methods: Baricitinib was dosed based on weight and renal function, with options to adjust dose based on established dosing and pharmacokinetics in pediatric interferonopathies.(2) One of the primary outcomes was reduction in symptom daily diary score (DDS) of weakness, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, and rash. Each symptom was graded based on impact from 0 (no impact, not present) to 4 (maximal impact, highest grade), with symptom categories averaged for diary scores. DDS were collected for at least 2 weeks prior to starting investigational drug and then daily throughout the program. Other PROs included Patient/Parent Global Assessment (PtGA) by visual analog scale, (Childhood) Health Assessment Questionnaire (C/HAQ), and Childhood Health Questionnaire–Physical Summary Score (CHQ-PhS). Linear mixed models were used to compare measures to baseline. Safety and tolerability were assessed.
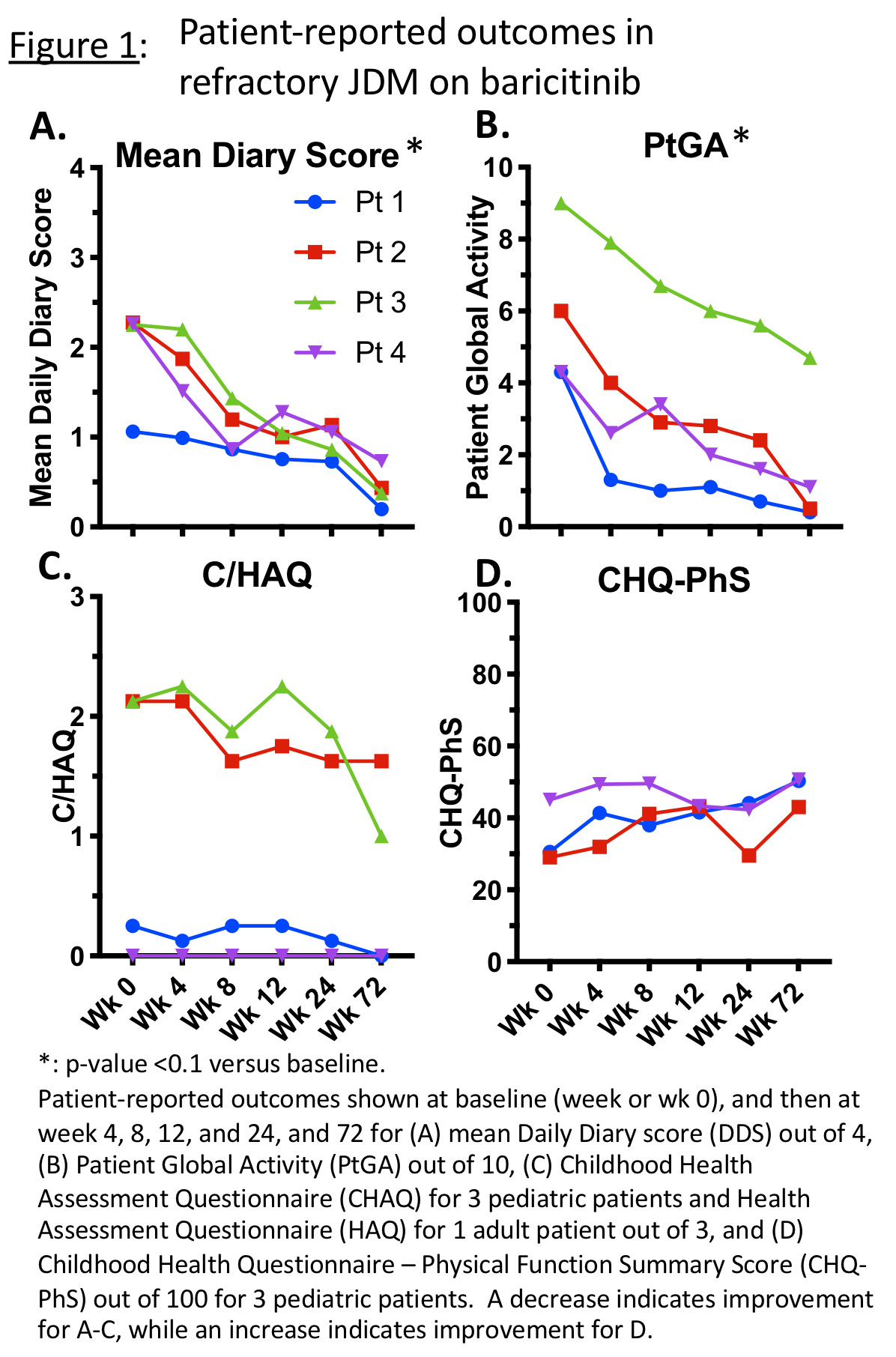
Results: Four patients with JDM (5.8-20.7 years old) were enrolled (NCT01724580), with at least 72 weeks of follow-up data collected. Patient diaries were collected for a total of 2167 days, with 2163 (99.8%) days of diary entries completed. At 72 weeks, DDS changed from a mean of 2.0/4.0 (range 1.1-2.3) to 0.4 (0.2-0.7; 68-83% decrease, p< 0.01) (Fig 1A). PtGA decreased from a mean of 5.9/10.0 (4.3-9.0) to 1.7 (0.4-4.7; 48-92% decrease, p< 0.01) (Fig 1B). C/HAQ decreased from mean 1.13/3.0 (range 0.0-2.13) to 0.66 (0.0-1.63, 0-100% decrease), indicating less disability (Fig 1C). CHQ-PhS (n=3) increased from mean 34.9/100 (29.1-45.0) to 48.0 (43.0-50.7; 13-65% increase), indicating improved physical function-related quality of life (Fig 1D). Patients were started on baricitinib 4-8mg PO per day divided BID or TID, and at last time point were on 5-12 mg/day divided BID. Dose adjustments were made based on renal function, safety laboratories, and/or efficacy in three patients. Baricitinib was generally well tolerated. There were no serious adverse events (AEs). Infections were the most common AE; Most common infection was upper respiratory infection. No AEs required holding/discontinuing baricitinib.
Conclusion: Patient-reported outcome data using baricitinib in four patients with refractory JDM supports shows continued improvement in symptoms with less disability and better physical function-related quality of life. Minor baricitinib dosing adjustments within the dosing range for pediatric interferonopathies were generally well tolerated.
Disclosures: Baricitinib provided by Eli Lilly & Company, expanded access program sponsor. Other support: IRP of NIH, NIAMS, NIEHS, CC.
References:
1. Kim H et al, Ann Rheum Dis, 2020
2. Kim H et al, Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2018
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim H, Bergeron L, Dill S, O'Brien M, Li X, George J, Brundidge A, Millwood M, Rider L, Colbert R. Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibition with Baricitinib: Dosing and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Refractory Juvenile Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/janus-kinase-jak-inhibition-with-baricitinib-dosing-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-refractory-juvenile-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/janus-kinase-jak-inhibition-with-baricitinib-dosing-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-refractory-juvenile-dermatomyositis/