Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc) is challenging, and in the last 2 decades there has been an increasing interest for immunoglobulin (Igs) treatment as it exhibits both immunomodulatory and antifibrotic properties. Currently, its efficacy on gastrointestinal (GI), skin and muscle involvement has been described only in case series with limited numbers of patients. With this study we wanted to evaluate the efficacy of Ig therapy on GI, cutaneous, and vascular involvement of SSc.
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted enrolling patients with diagnosis of SSc (ACR/EULAR 2013) and that were treated with Ig (intravenously or subcutaneously) at a 2 gr/kg/month dosage for at least 6 months. Demographical data, antibodies positivity, associated therapies (vasoactive and immunosuppressants) and disease duration were collected from clinical records. Moreover, the presence of diarrhea, gastroesophageal reflux (GER), digital edema, digital ulcers (DUs), as well as the modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and videocapillaroscopic pattern (VCP; normal, early, active, late) were assessed at baseline (BL) and after 6 (T6) and 12 (T12) months of Ig therapy. Variation of these items from BL to T6 and T12 was tested by Paired T Test, Mc Nemar test, Wilcoxon’s signed rank test as appropriate. Regression analysis were than performed to assess influence of possible confounders variables (vasoactive and immunosuppressants drugs) on outcome variables (VCP, digital edema, DUs)
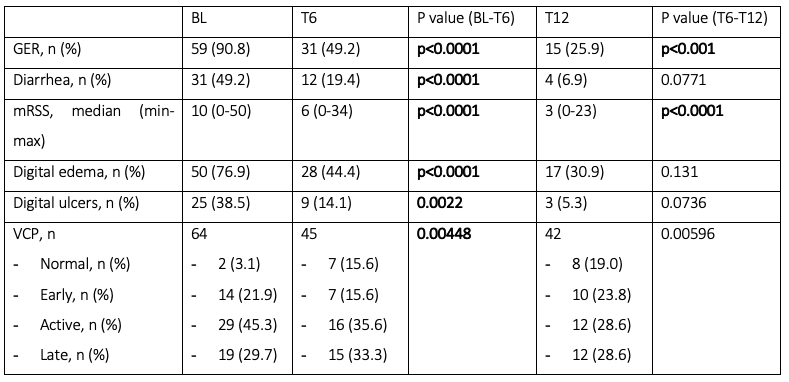
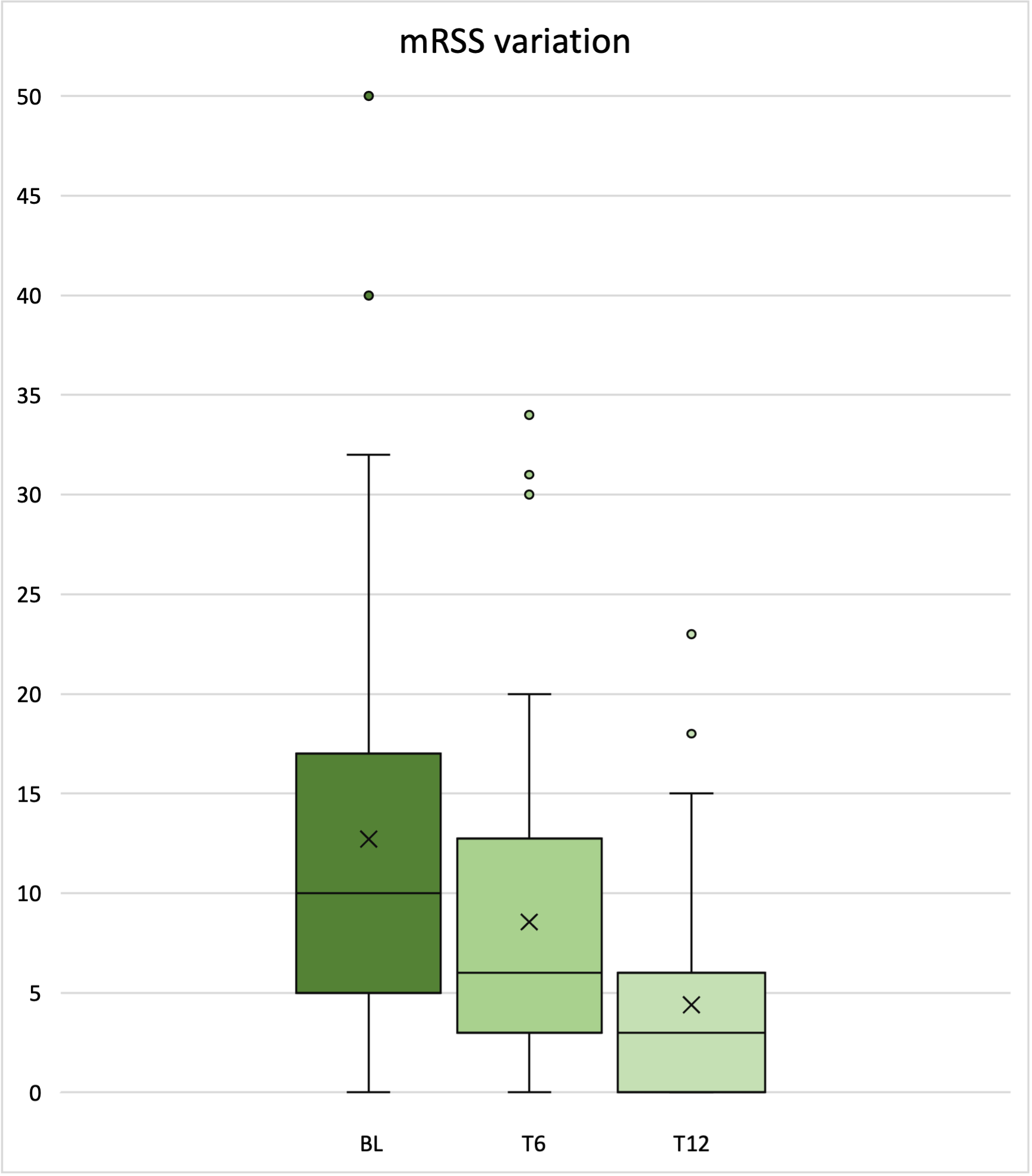
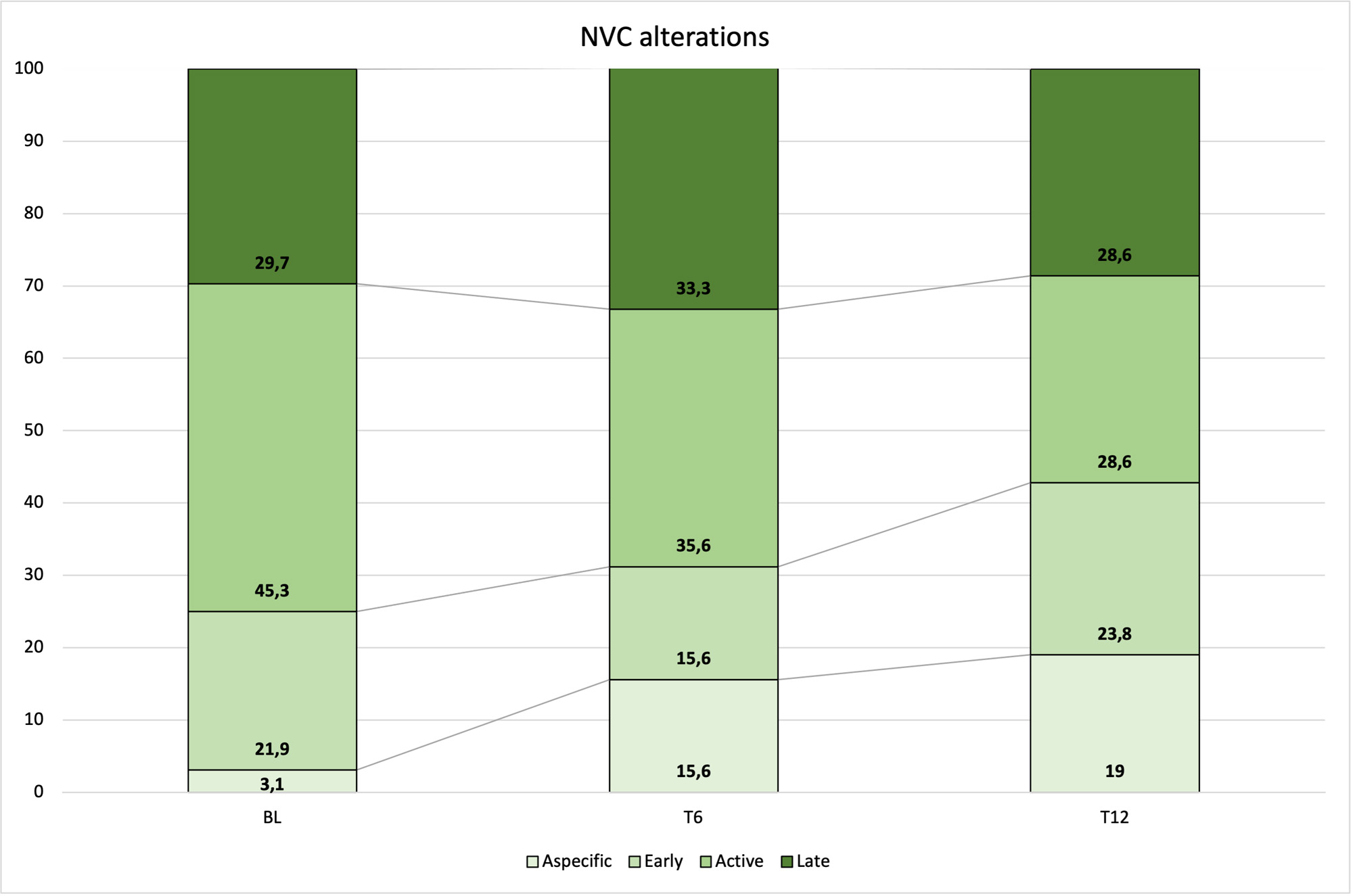
Results: Sixty-five patients were enrolled, and their clinical data were analyzed. Mean age was 56.18 (± 12.32) and median disease duration was 10.00 years (min-max 1.00-38.00). Sixty-three patients (96.9%) were ANA positive, with positivity for anti-centromeric antibodies in 23 (35.4%), Scl-70 in 27 (41.5%) and RNA polymerase III in 8 (12.3%) patients. Fifty-five patients received the treatment intravenously, the remaining subcutaneously. Table 1 summarizes the trend and significancy of clinical items from BL to T12. At BL, 49.2% of patients complained diarrhea, 90.8% GER, 76.9% digital edema; 38.5%DUs. VCP was normal in 3.1% of patients, early in 21.9%, active in 45.3%, and late in 29.7%. Also, median mRSS was 10 (min-max 0-50). At T6, median mRSS significantly improved [6 (min-max 0-34), p< 0.0001] together with VCP (normal in 15.6%, early in 15.6%, active in 35.6%, and late in 33.3%, p=0.00448). Moreover, a significant reduction of the prevalence of GER (49.2%, p< 0.0001), diarrhea (19.4%, p< 0.0001), digital edema (44.4%, p< 0.0001), DUs (14.1%, p=0.0022) was found. At T12, median mRSS improved even more [3 (min-max 0-23), p< 0.0001] along with VCP (normal in 19.0%, early in 23.8%, active in 28.6%, and late in 28.6%, p=0.00596). Also, the prevalence of GER was lower (25.9%, p< 0.001).Regression analysis did not evidence any influence of other treatments on the tested outcome variables.
Conclusion: Our data confirm the efficacy of Ig on GER and diarrhea and skin involvement and, for the first time, also a possible positive effect on VCP. Further studies on larger samples are required to confirm these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bonomi F, Damiani A, Coccia C, Levani J, Fiorentini e, peretti s, Lepri G, orlandi m, bartoli f, Matucci Cerinic m, bellando randone s, guiducci s. Intravenous or Subcutaneous Immunoglobulins as Potential Treatment for Gastrointestinal, Cutaneous and Vascular Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: Data from an Italian Cohort of 65 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intravenous-or-subcutaneous-immunoglobulins-as-potential-treatment-for-gastrointestinal-cutaneous-and-vascular-involvement-in-systemic-sclerosis-data-from-an-italian-cohort-of-65-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intravenous-or-subcutaneous-immunoglobulins-as-potential-treatment-for-gastrointestinal-cutaneous-and-vascular-involvement-in-systemic-sclerosis-data-from-an-italian-cohort-of-65-patients/