Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science (1734–1739)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:15AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is an age-related joint disease that cause chronic pain and reduced mobility. Current treatments mainly relieve pain and inflammation, often with corticosteroid injections. However, no therapy modifies disease progression, highlighting the need for new strategies. Our team is investigating intra-articular GLP-1 analogs for their anti-inflammatory and protective properties. This study evaluates liraglutide, a GLP-1 analogue, in a rat model of OA, focusing on its effects on synovial membrane and cartilage structure.
Methods: The effects of one, two, or eight intra-articular (IA) injections of liraglutide or vehicle were evaluated in a rat OA model induced by ACLT/pMMx surgery, compared to eight injections of dexamethasone. Sham-operated animals were used as controls. Body weight was monitored. Synovial membrane (Krenn [0–9] and Obeidat scores) and cartilage (OARSI [0–26]) were blindly assessed per joint quadrant (MTP, MFC, LTP, LFC) by two independent investigators. The Krenn score evaluates the inner synovial layer, cell density, and inflammation; the Obeidat score evaluates hyperplasia, cellularity, and fibrosis; the OARSI score quantifies the depth and extension of of cartilage lesions.
Results: The total synovitis score using Krenn methods showed a significant increase in synovial inflammation in ACLT/pMMx/vehicle groups vs. respective sham controls (p< 0.001), while treatment significantly reduced this score by ±48–63% for liraglutide and 38% for dexamethasone (p< 0.001 and p< 0.0001 for liraglutide groups, p< 0.0001 for dexamethasone). Liraglutide 60 µg significantly improved all synovitis parameters compared to vehicle, with superior effects to dexamethasone (p< 0.05 for density, p< 0.01 for layer, inflammatory, and total synovitis scores). These results suggest that liraglutide reduces the severity of synovitis, with 2 or 8 injections showing the greatest improvement. Obeidat scores showed increased hyperplasia, cellularity, and fibrosis across all quadrants (MTP, MFC, LTP, LFC) in the vehicle versus sham groups. Both treatments significantly reduced these scores compared to vehicle, with liraglutide showing broader effects. In particular, liraglutide 60 µg was more effective than dexamethasone in reducing medial cellularity and fibrosis. OARSI scores showed significantly increased cartilage degradation in the vehicle groups compared to sham (p< 0.01). Liraglutide reduced degradation by 34–55%, while dexamethasone had no significant effect (17%). The global severity index confirmed these findings: liraglutide improved cartilage integrity (p< 0.05, p< 0.001, p< 0.01 for 1, 2, 8 injections vs. vehicle), while dexamethasone showed no benefit (Figure 1, Table 1).
Conclusion: These results show that intra-articular liraglutide effectively reduces synovial inflammation and protects joint structure. It outperforms dexamethasone by preserving both synovial tissue and cartilage, highlighting its potential as a superior OA treatment offering symptomatic relief and structural preservation, unlike dexamethasone, which lacks cartilage protection and may be harmful in the long-term.
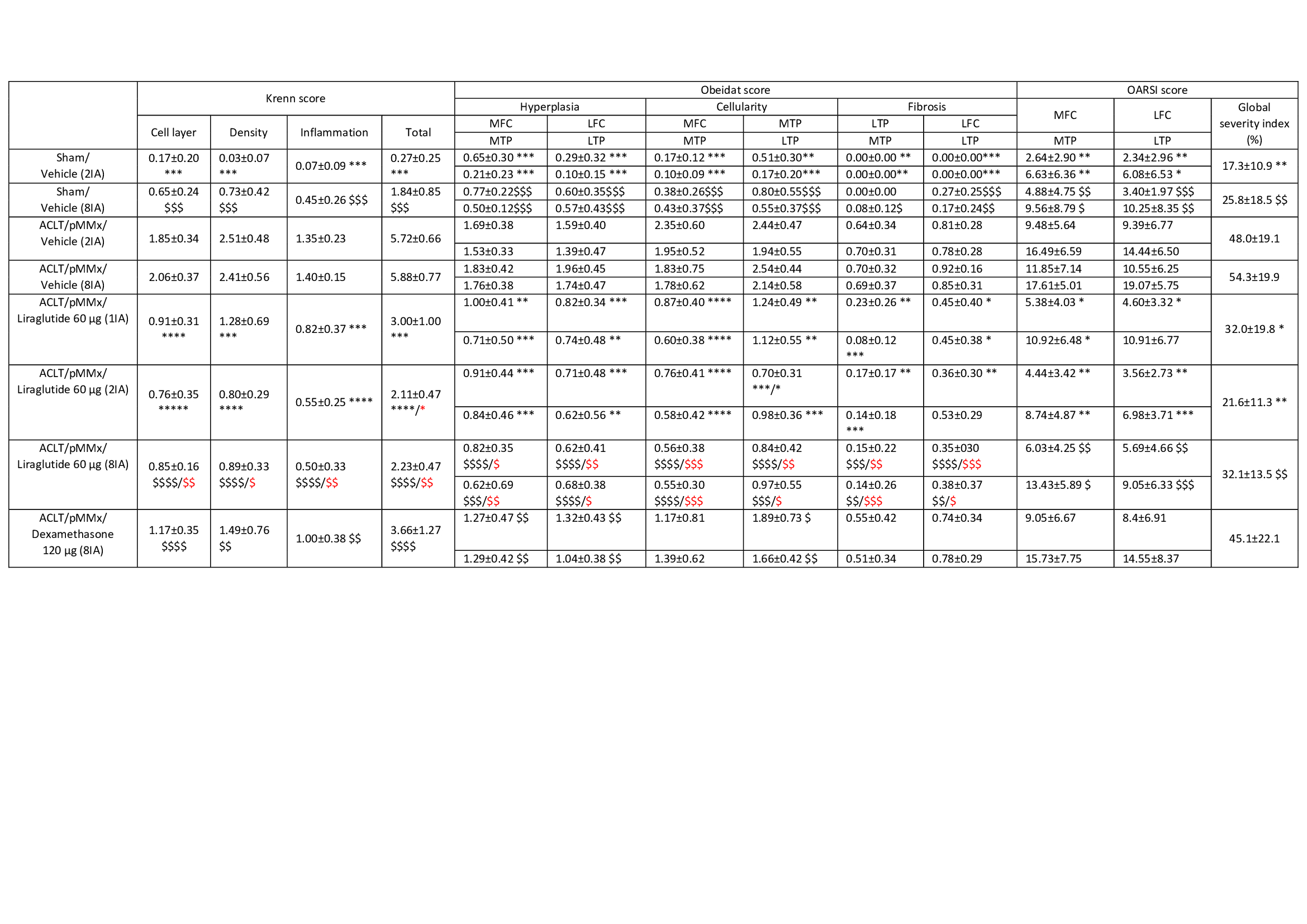 Table 1: Krenn, Obeidat and OARSI score in ACLT/pMMx rat model
Table 1: Krenn, Obeidat and OARSI score in ACLT/pMMx rat model
Mean ± SD, Statistical analyses: Mann-Whitney test: * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001 vs 3M - ACLT/pMMx/vehicle (2IA) group; *p < 0.05, vs 5M - ACLT/pMMx/ Liraglutide 60 µg (1IA) group; $ p < 0.05, $$p < 0.01, $$$ p < 0.001 and $$$$ p < 0.0001 vs 4M - ACLT/pMMx/vehicle (8IA) group. $ p < 0.05, $$p < 0.01, $$$ p < 0.001 vs 8M - ACLT/pMMx/ Dexamethasone 120 µg (8IA) group. Nf5-6 for Sham groups (1M-2M) and 11-12 for ACLT/pMMx groups (3M to 8M).
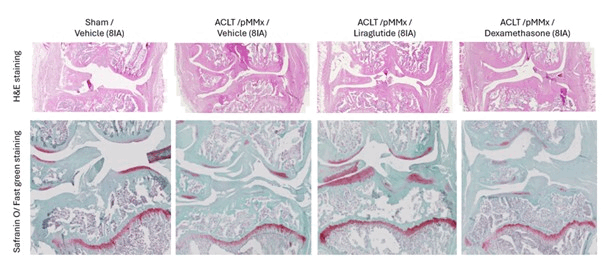 Figure 1: Representative picture of Hematoxylin eosin and Safranin O/Fast green staining to determine the Krenn, Obeidat and OARSI score
Figure 1: Representative picture of Hematoxylin eosin and Safranin O/Fast green staining to determine the Krenn, Obeidat and OARSI score
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Meurot C, Martin C, Vieubled M, Toillon I, Deldycke C, Cheron V, Trombetta S, Sibran W, Rattenbach R, BERENBAUM F. Intra‑articular Liraglutide Halts Osteoarthritis Progression, Surpassing Dexamethasone in Synovial and Cartilage Protection [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intra%e2%80%91articular-liraglutide-halts-osteoarthritis-progression-surpassing-dexamethasone-in-synovial-and-cartilage-protection/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intra%e2%80%91articular-liraglutide-halts-osteoarthritis-progression-surpassing-dexamethasone-in-synovial-and-cartilage-protection/
