Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite the emergence of new therapies, a considerable proportion of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) still endure symptoms, giving rise to the concept of “refractory RA”. This concept reflects the complex pathogenesis of this autoimmune disease, in which both inflammation and angiogenesis play a key role. This study aimed to pinpoint specific circulating angiogenic and inflammatory markers of refractory and active RA.
Methods: We used Luminex technology to measure the concentrations of 17 serum angiogenic (angiopoietin-1, neuropilin-1, Tie-2, endostatin, CXCL4, VCAM-1, VEGF, PlGF) and inflammatory (interferon-gamma, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-alpha, MMP-1, and BAFF) markers in 211 RA patients.
RA patients were categorized into three groups :
– Refractory (failure of 2 or more targeted therapies) active (persistence of objective signs of disease activity) RA
– Non-refractory (failure of ≥1 csDMARDs or a first line of targeted therapy) active RA
– Non-active RA (DAS28≤3.2).
The main objective was the identification of circulating markers that would differ specifically in the active and refractory RA population. Secondary outcomes were the detection of markers associated with disease activity and identification of correlations between the various markers and disease activity indicators.
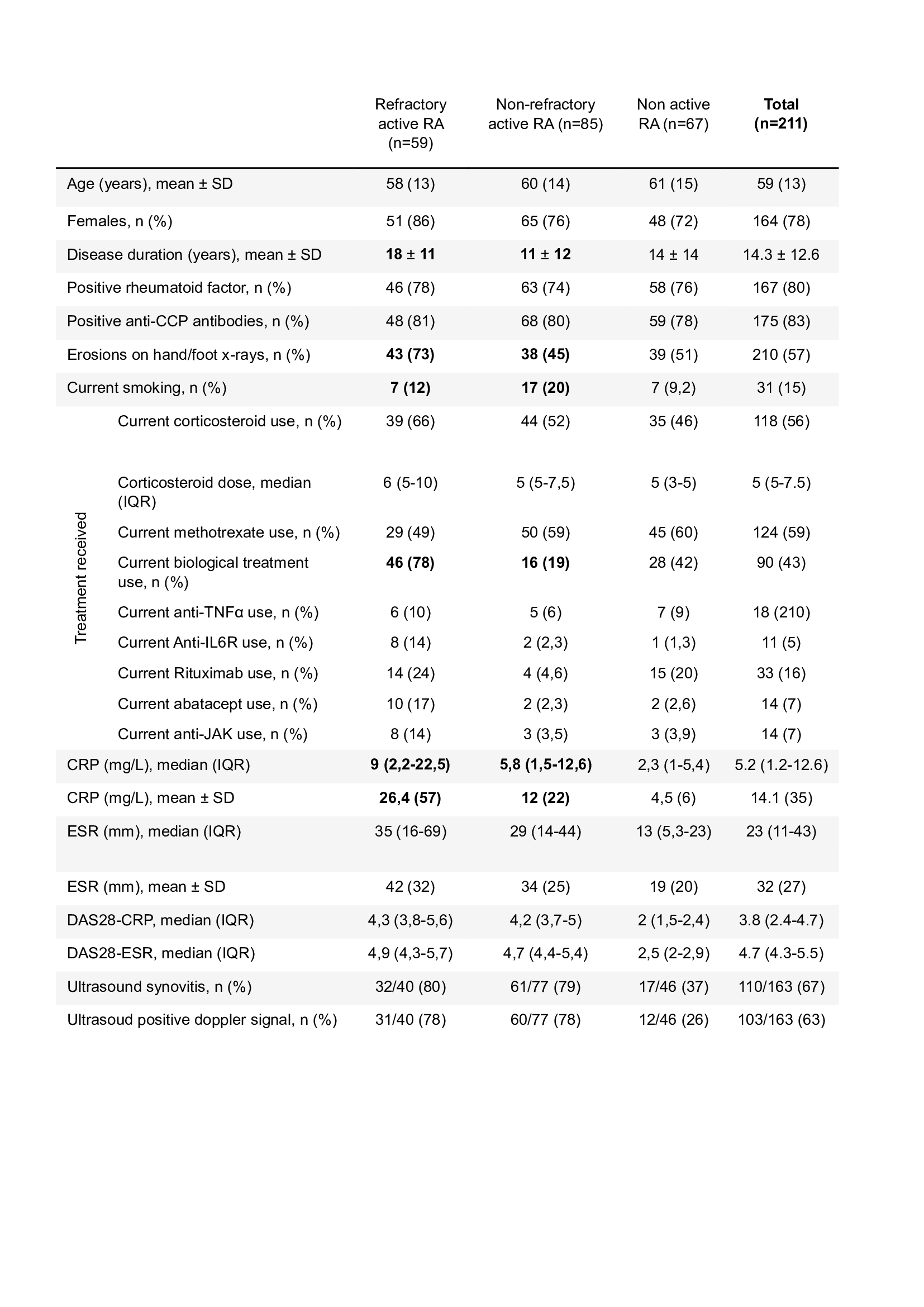
Results: Refractory and non-refractory active RA patients differed in disease duration (18 years in refractory active RA versus 11 years non-refractory active, p< 0.001), structural damages (73% in refractory and active versus 45% in non-refractory active, p< 0.001) and the utilization of biologic therapy (78% in refractory and active versus 19% in non-refractory active, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
The concentrations of the 17 markers failed to distinguish refractory from non-refractory RA patients. The comparison of active and non-active RA only revealed a strong increase of IL-6 concentration in active RA.
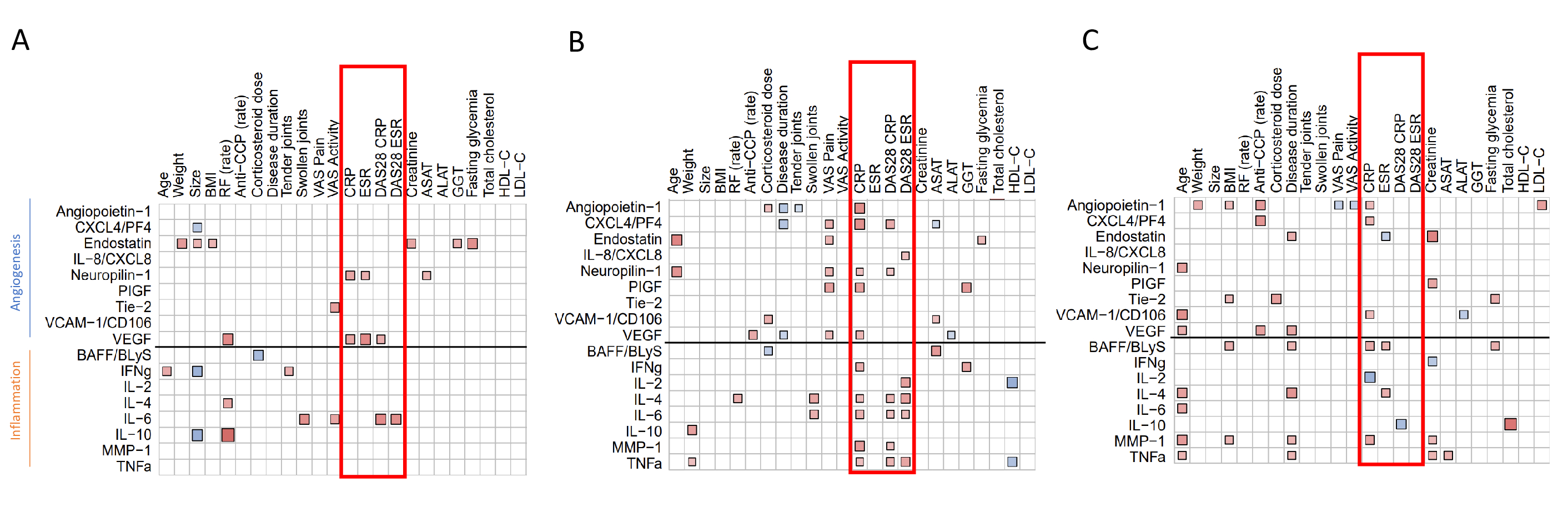
Then, correlograms were conducted to examine the relationships between angiogenic and inflammatory markers with RA disease characteristics. Refractory active RA exhibited a limited correlation profile showing only three correlations (VEGF, Neuropilin-1 and IL-6) with markers of disease activity (CRP or DAS28 CRP). By contrast, in non-refractory active RA patients, correlograms revealed an extensive proinflammatory and proangiogenic correlation profile with 12 markers correlating with inflammation markers or disease activity (Figure 1B). Refractory active RA showed a serum profile closer and even poorer than that of non-active in which 6 biomarkers correlated with CRP. (Figure 1C).
Conclusion: No classical marker of RA emerged as specific for refractory disease in this study. Moreover, refractory and active RA patients exhibited only few correlations with disease activity markers, despite the persistence of clinical and biological signs of disease activity. This may suggest that additional molecules may be implicated in refractory disease outside those herein selected. These findings also highlight the potential limitations of serum analysis in refractory active RA.
CRP: C-Reactive Protein ; DAS: Disease Activity Score ; ESR : Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate ; IQR : Interquartile Range ; JAK: Janus Kinase ; RA : Rheumatoid Arthritis ; TNF : Tumor Necrosis Factor ; SD : Standard Deviation.
ALAT: Alanine Aminotransferase ; ASAT: Aspartate Aminotransferase ; BAFF: B-cell activating factor ; BMI: Body Mass Index ; CRP: C-Reactive Protein ; CXCL4/PF4: Platelet Factor 4 ; DAS28 : Disease Activity Score 28 ; ESR : Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate ; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase ; HDL-C : High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ; IFN: Interferon ; LDL-C : Low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ; RF : Rheumatoid factor ; IL: Interleukine ; MMP_1: Matrix Metalloproteinase_1 ; PlGF : Placenta Growth Factor ; RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis ; TNF: Tumor Necrosis Factor ; VAS: Visual Analogue Scale ; VCAM_1 : Vascular Cell Adhesion Protein 1 ; VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lesturgie-Talarek M, Gonzalez V, COMBIER A, THOMAS M, Boisson M, Carves S, Wanono S, Poiroux L, Cauvet A, Hecquet S, Allanore Y, Avouac J. Inflammatory and Angiogenic Serum Profile of Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammatory-and-angiogenic-serum-profile-of-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammatory-and-angiogenic-serum-profile-of-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/