Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0934–0954) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Recently, traditional ex vivo-generated chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapies have shown success in the clinic for autoimmunity indications. However, manufacturing, safety, and accessibility remain potential challenges in the ex vivo CAR-T approach. The prospect of an in vivo CAR-T cell therapy, without the need for patient cell isolation, cell culturing, and the safety risks associated with preconditioning regimens, remains a therapeutic goal. Orna Therapeutics’ panCAR™ combines a synthetic, circular, coding RNA platform (oRNA®) and proprietary immunotropic lipid nanoparticle (LNP) to drive CAR expression on the surface of immune effector cells after in vivo administration, with a potential to provide a transient, re-dosable, and scalable immune cell therapy without the need for preconditioning lymphodepletion.
Methods: anti-CD19 panCAR™ is a non-viral platform combining anti-CD19 CAR expressing oRNA with a proprietary immunotropic LNP. Anti-CD19 panCAR was evaluated for expression in T cells and depletion of target B cells in vitro and in vivo in humanized CD34+ models upon intravenous injection. In a humanized model of lupus, anti-CD19 panCAR was dosed four times weekly, B cell levels and anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) titers were evaluated. In cynomolgus macaques, anti-CD19 panCAR was dosed intravenously twice three days apart (Q3Dx2) at three doses levels (0.1, 0.5, and 1mpk). B cell levels were then evaluated in periphery and in lymphoid tissues by flow cytometry.
Results: With anti-CD19 panCAR oRNA-LNP, high surface expression of anti-CD19 CAR was observed in a dose-dependent manner and was maintained over 96 hours on human and NHP immune cells in vitro. Furthermore, CAR-mediated cytotoxicity was observed for T cells from both species, killing CD19-expressing cell lines. In the humanized mouse model, anti-CD19 CAR oRNA-LNP when administered intravenously showed significant B cell reductions in peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow at 24 hours (55-95%) and sustained depletion 7 days after a single dose. The functional activity of anti-CD19 panCAR can be adjusted by the dose level and dose number administered, demonstrating the tunability of the platform. in vivo panCAR, injected in a humanized mouse model of lupus, showed complete reduction of B cells accompanied by anti-dsDNA titer reduction. While mice receiving rituximab exhibited reduced B cell numbers, the depletion did not correlate with reduced anti-dsDNA titers. Finally, in NHPs, our cross-reactive anti-CD19 compound showed complete ( >98%) and sustained depletion of B cells in peripheral blood two weeks after the last dose and showed robust depletion in the spleen ( >99%), lymph nodes ( >97%), and bone marrow ( >96%) three days after the last dose.
Conclusion: Our platform provides a non-viral, transient, tunable, and scalable approach without the need for preconditioning lymphodepletion that shows robust activity in vitro and in vivo. In NHPs intravenous dosing resulted in deep B cell depletion in peripheral blood and lymphoid tissues. Collectively, our pre-clinical data demonstrates the potential of Orna’s in vivo panCAR therapy to treat B cell mediated autoimmunity.
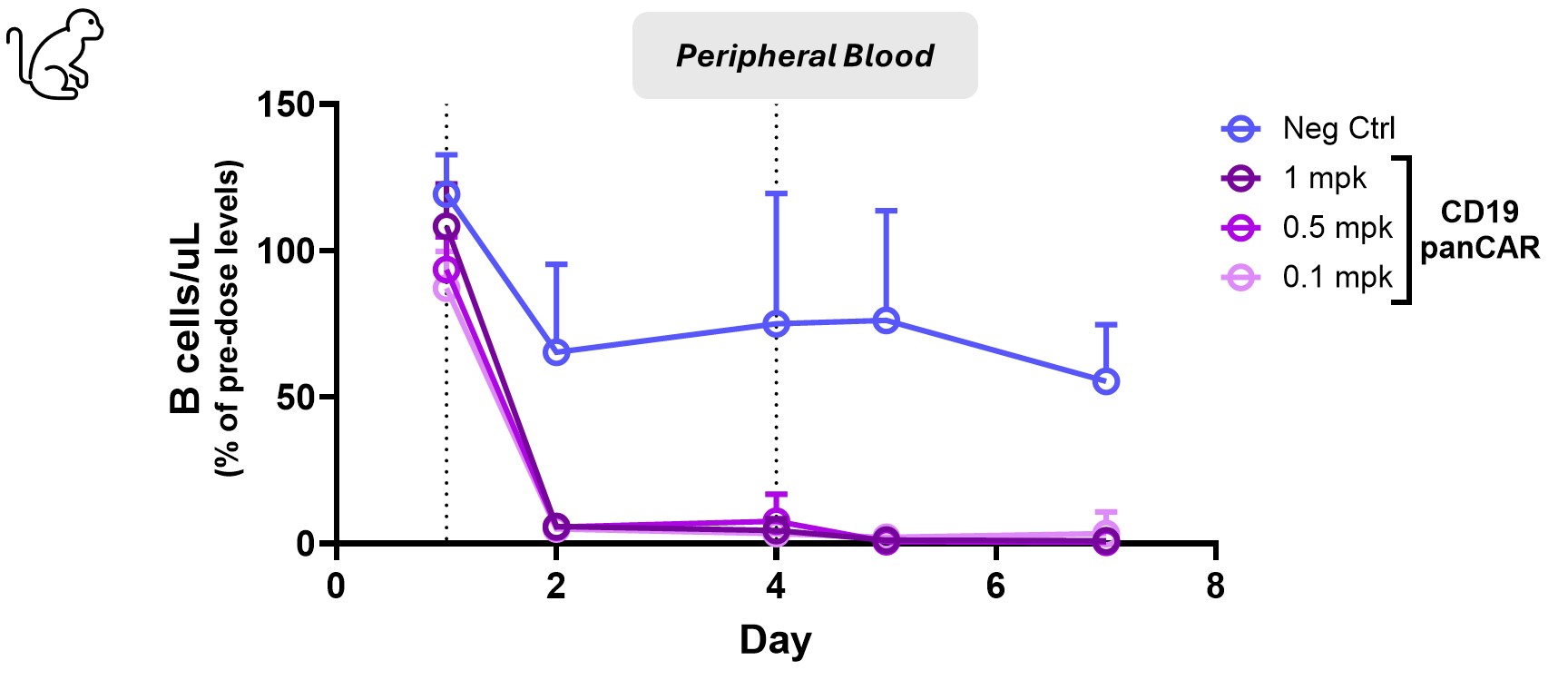 CD19 panCAR completely depletes B cells in peripheral blood in NHPs: Cynomolgus macaques were dosed day 1 and day 4. CD20+ B cell levels were measured in peripheral blood by flow cytometry. Levels are normalized to average B cell levels from two pre-dose timepoints for each animal. mean+/- st dev
CD19 panCAR completely depletes B cells in peripheral blood in NHPs: Cynomolgus macaques were dosed day 1 and day 4. CD20+ B cell levels were measured in peripheral blood by flow cytometry. Levels are normalized to average B cell levels from two pre-dose timepoints for each animal. mean+/- st dev
.jpg) CD19 panCAR robustly depletes B Cells in lymphoid tissues in NHPs. Animals were taken down 3 days post last dose and CD20+ B cell levels were measured in lymphoid tissues by flow cytometry.
CD19 panCAR robustly depletes B Cells in lymphoid tissues in NHPs. Animals were taken down 3 days post last dose and CD20+ B cell levels were measured in lymphoid tissues by flow cytometry.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Crabtree J, Lee T, Soto D, Vyas P, Emmanuel A, Theisen M, Kosakowska K, Sedic M, Das R, Jayaraman M, Hoban M, Bolen J, Dalkilic-Liddle I. In Vivo PanCAR Therapy Utilizing Circular RNA for Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vivo-pancar-therapy-utilizing-circular-rna-for-treatment-of-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vivo-pancar-therapy-utilizing-circular-rna-for-treatment-of-autoimmune-diseases/
