Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0210–0232) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Annual screening for pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) reduces mortality. The American College of Radiology, European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society, and the 6th World Symposium of PH all recommend yearly screening with 1) Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT) with diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), 2) Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE), and 3) B-natriuretic peptide (BNP). However, clinician adherence is variable, with one study reporting rates as low as 34% (Pauling JD et al.). We previously conducted a retrospective study assessing PH screening in our quaternary medical center, presented at ACR 2024. Based on these findings, we implemented a quality improvement (QI) intervention consisting of a departmental presentation outlining our adherence rates and a streamlined electronic order set for all three tests.
Methods: To evaluate the impact of this intervention, we analyzed screening compliance over a six-month period (September 17, 2024 to March 17, 2025). Inclusion criteria matched our prior study: 1) rheumatologist-diagnosed SSc, 2) age over 18 years at diagnosis, 3) seen in our rheumatology clinics, and 4) no prior PH diagnosis. We reviewed charts for completed PFTs, TTEs, and BNPs. “Full compliance” was defined as completion of all three tests within 12 months prior or 6 months after an outpatient visit. “Ever compliant” was defined as completion of at least one of these tests, maintaining consistency with our prior methodology.
Results: A total of 48 patients met these criteria, accounting for 70 outpatient visits. Demographically, 91% (44) of patients were female, 68.8% (33) White, 10.4% (5) Black, and 20.8% (10) Latino (Table 1). At the visit level, 74% (52) had at least one screening test completed, and 20% (14) had all three tests completed. Individually, 48.6% (34) of visits had a PFT, 67.1% (47) a TTE, and 30% (21) a BNP (Figure 1). Comparing pre- and post-intervention periods using a two-proportion Z test (Table 2), full compliance increased significantly from 10.7% to 20% (z=-2.234, p=0.0255), and BNP testing improved from 15.7% to 30% (z=-2.619, p=0.009). Changes in PFT, TTE, and ever-compliant rates were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Our QI intervention significantly improved adherence to full, guideline-based PH screening and BNP testing in SSc patients. Barriers remain for PFT and TTE completion, which require additional efforts in patient scheduling and follow-through. Future interventions will target these challenges through patient education materials and streamlined coordination support.
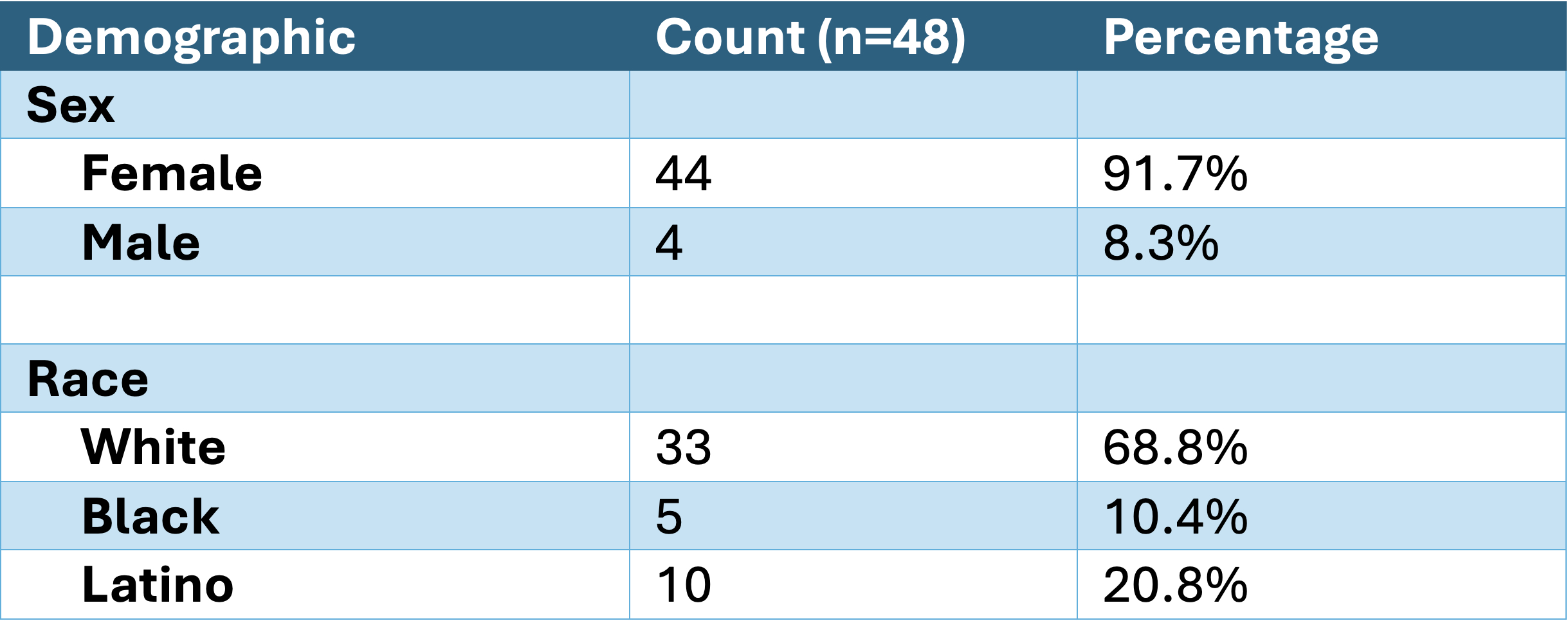 Table 1: Demographic data of patients in post-intervention analysis.
Table 1: Demographic data of patients in post-intervention analysis.
.jpg) Figure 1: Percentage compliance with recommended testing per appointment. “Ever” indicates completion of at least one of the three tests (PFT, TTE, BNP), while “Fully” indicates completion of all three within 12 months prior to or 6 months after the visit. Compliance is also shown for each individual test. Bars represent pre-intervention (red) and post-intervention (teal) proportions. p-values reflect two-proportion Z-tests comparing pre- and post-intervention groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
Figure 1: Percentage compliance with recommended testing per appointment. “Ever” indicates completion of at least one of the three tests (PFT, TTE, BNP), while “Fully” indicates completion of all three within 12 months prior to or 6 months after the visit. Compliance is also shown for each individual test. Bars represent pre-intervention (red) and post-intervention (teal) proportions. p-values reflect two-proportion Z-tests comparing pre- and post-intervention groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
.jpg) Table 2: Pre- & post-intervention analysis using two-proportion Z test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
Table 2: Pre- & post-intervention analysis using two-proportion Z test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hickernell J, Aouhab Z. Improving Adherence to Pulmonary Hypertension Screening in Systemic Sclerosis Patients: Post-Intervention Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-adherence-to-pulmonary-hypertension-screening-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-post-intervention-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-adherence-to-pulmonary-hypertension-screening-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-post-intervention-analysis/
