Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Autoantibodies (Aab) are frequent in systemic sclerosis (SSc).Recently, it has been shown that immunoglobulins G (IgG) from SSc promoted a proinflammatory and profibrotic phenotype in monocytes secretome. Fibroblasts (FB) are key effectors cells in SSc and data on FB proteins secretion in the presence of IgG from SSc patients are lacking. Our objective was to explore the FB secretome in the presence of purified IgG from SSc patients.
Methods: Normal dermal FB were cultured in the presence of purified IgG from patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) (n=20 [of whom 10 were anti-topoisomerase-I (ATA) positive and 10 were ATA negative]), limited cutaneous SSc anti-centromere positive (lcSSc ACA+) (n=10) or healthy controls (HC (n=10). After 72h of culture, the cell supernatants were collected, centrifuged and passed through a filter to remove the cells. After proteins digestion, secretome was explored using mass spectrometry coupled with liquid chromatography (LC-MS/MS). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and hierarchical clustering were used to identify proteins responses patterns.
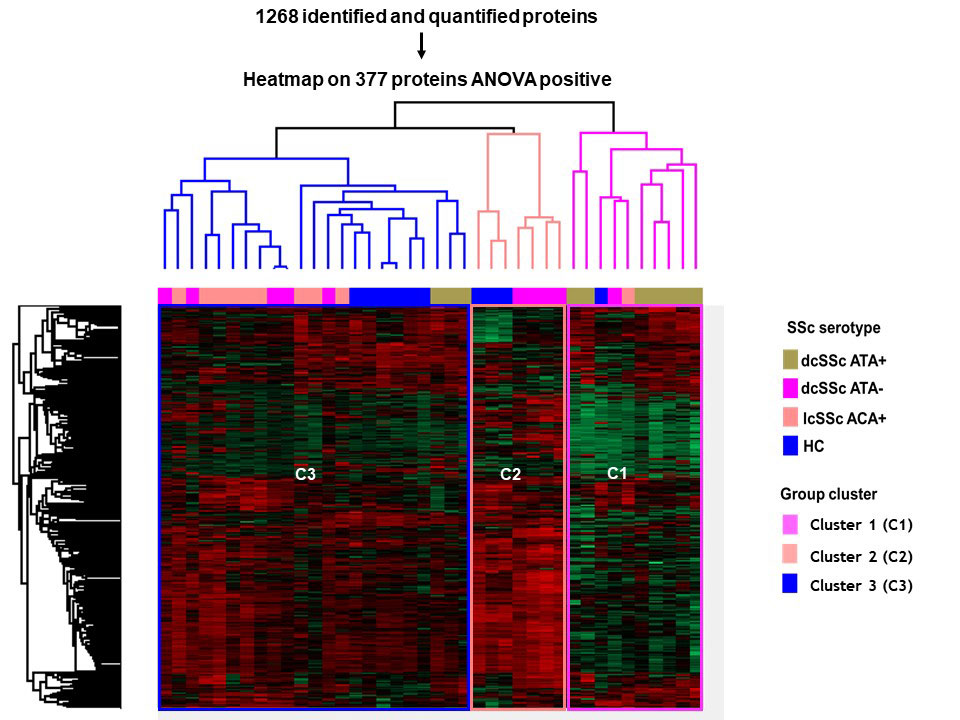
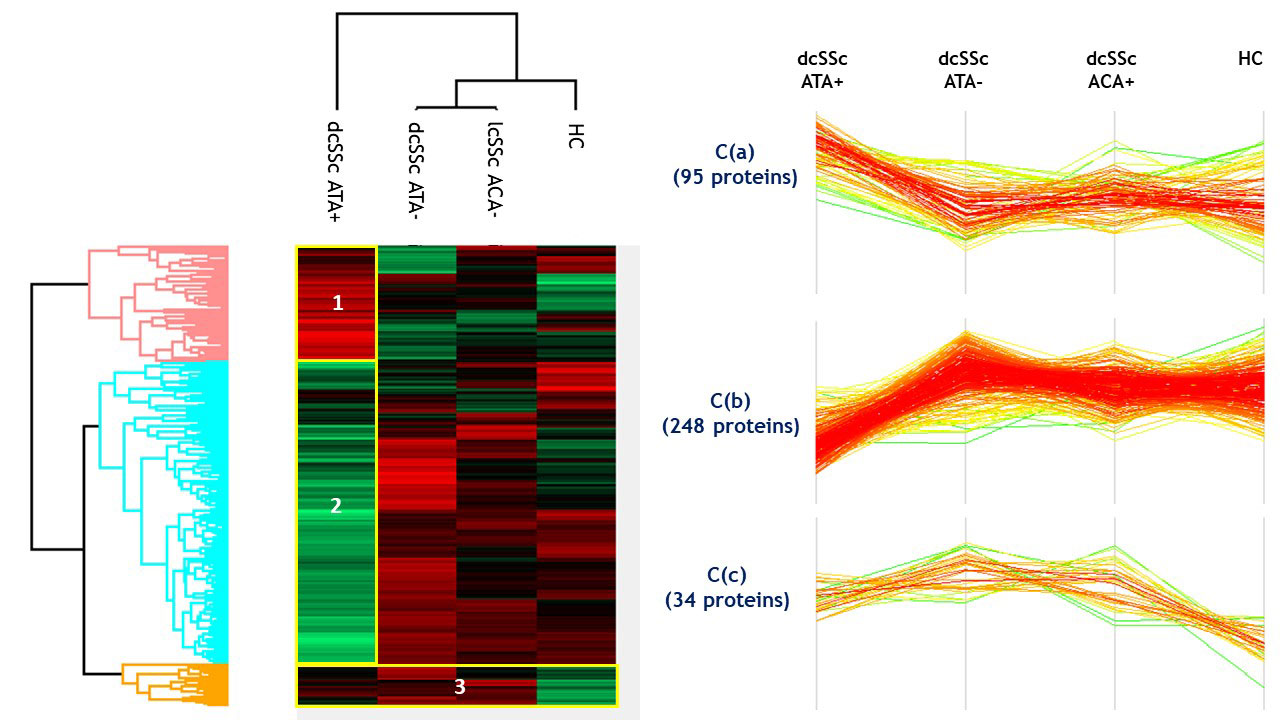
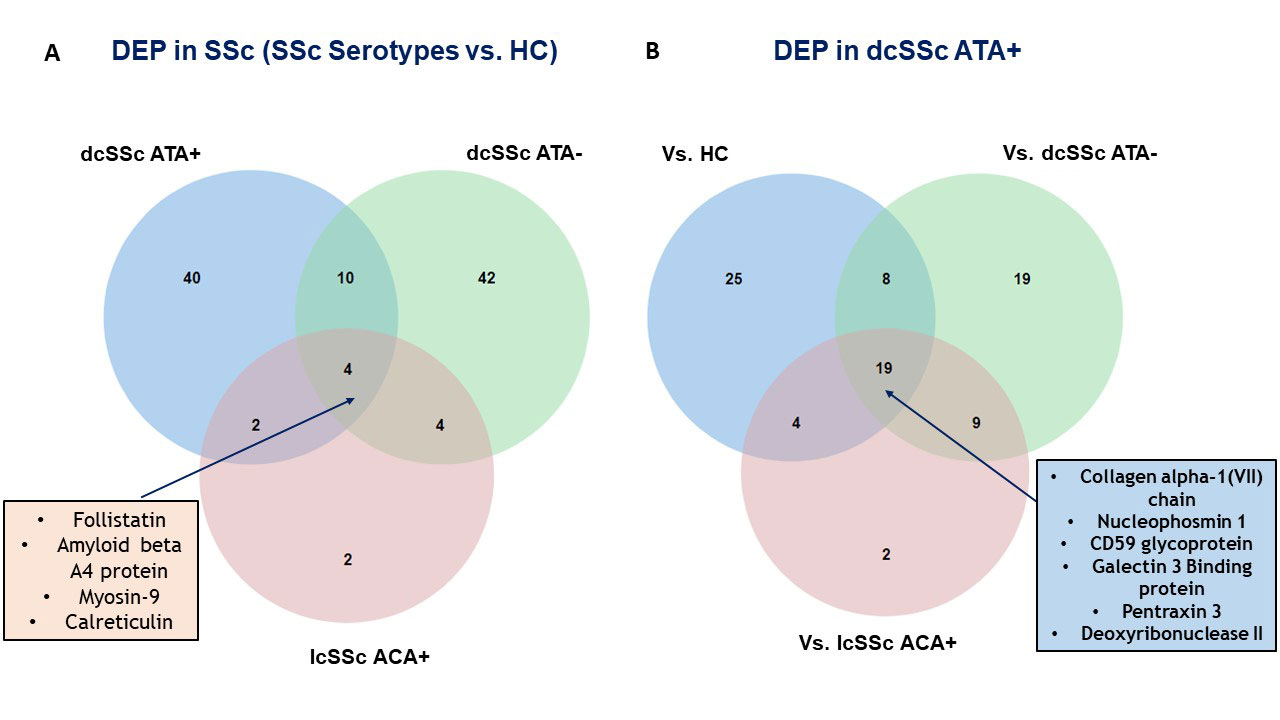
Results: Proteomics identified and quantified 1,268 proteins, among them 377 were significant after ANOVA. SSc and HC secretomes appeared distinct. Hierarchical clustering on significant proteins after ANOVA identified 3 clusters: C1 including mostly dcSSc ATA+ patients, C2 including mostly dcSSc ATA- patients, C3 was more heterogeneous including the majority of HC, lcSSc ACA+ patients and some dcSSc ATA- patients (figure 1). We then studied proteins patterns in the initial groups of subjects. Three main clusters were highlighted. C(a) regrouped 95 proteins which were overexpressed in the presence of purified IgG from dcSSc ATA+ patients (involved in calcium-dependent binding and extracellular matrix constituents). C(b) included 248 proteins mostly underexpressed in the presence of purified IgG from dcSSc ATA+ patients (involved in protein folding and actin filament depolymerization). C(c) gathered 34 proteins overexpressed in presence of purified IgG from all SSc groups (involved in amyloid-beta binding and ECM structural constituents) (figure 2). Finally, we performed differential analyses. Follistatin, amyloid beta A4 protein, myosin-9 and calreticulin were commonly overexpressed in all SSc subtypes. We identified 19 proteins exclusively overexpressed in dcSSc ATA positive patients such as collagen alpha-I type 7 and galectin 3 binding proteins (figure 3).
Conclusion: Using sensitive proteomic approach, we highligthed that purified IgG from SSc patients can modify the FB secretome. Along with similar results on monocyte secretome, these data suggest that SSc-IgG may influence the inflammatory and fibrotic phenotype of different cells.
IgG HC: purified IgG from healthy controls; IgG dcSSc ATA+: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I positive patients; IgG dcSSc ATA-: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I negative patients; IgG lcSSc ACA+: purified IgG from limited systemic sclerosis anti-centromere positive patients. ANOVA: analysis of variance.
IgG HC: purified IgG from healthy controls; IgG dcSSc ATA+: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I positive patients; IgG dcSSc ATA-: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I negative patients; IgG lcSSc ACA+: purified IgG from limited systemic sclerosis anti-centromere positive patients.
DEP: differentially expressed proteins; SSc: systemic sclerosis; IgG HC: purified IgG from healthy controls; IgG dcSSc ATA+: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I positive patients; IgG dcSSc ATA-: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I negative patients; IgG lcSSc ACA+: purified IgG from limited systemic sclerosis anti-centromere positive patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chepy A, Duhamel M, Vivier S, Guilbert l, Hachulla E, Dubucquoi S, Launay D, Salzet M, Sobanski V. Immunoglobulins G from Systemic Sclerosis Patients May Alter the Secretome of Dermal Fibroblasts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunoglobulins-g-from-systemic-sclerosis-patients-may-alter-the-secretome-of-dermal-fibroblasts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunoglobulins-g-from-systemic-sclerosis-patients-may-alter-the-secretome-of-dermal-fibroblasts/