Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Loss of galactose and sialic acid structures attached to the IgG-Fc-fragment switches the antibody effector function from anti-inflammatory to pro-inflammatory1. This study investigated the IgG- Fc-N-glycosylation profiles in patients from the Belgian Sjögren’s Syndrome Transition Trial (BeSSTT) in relation to disease state, salivary gland ultrasonography SGUS) and histopathology, and autoantibodies against SSA (Ro52/Ro60) and SSB.
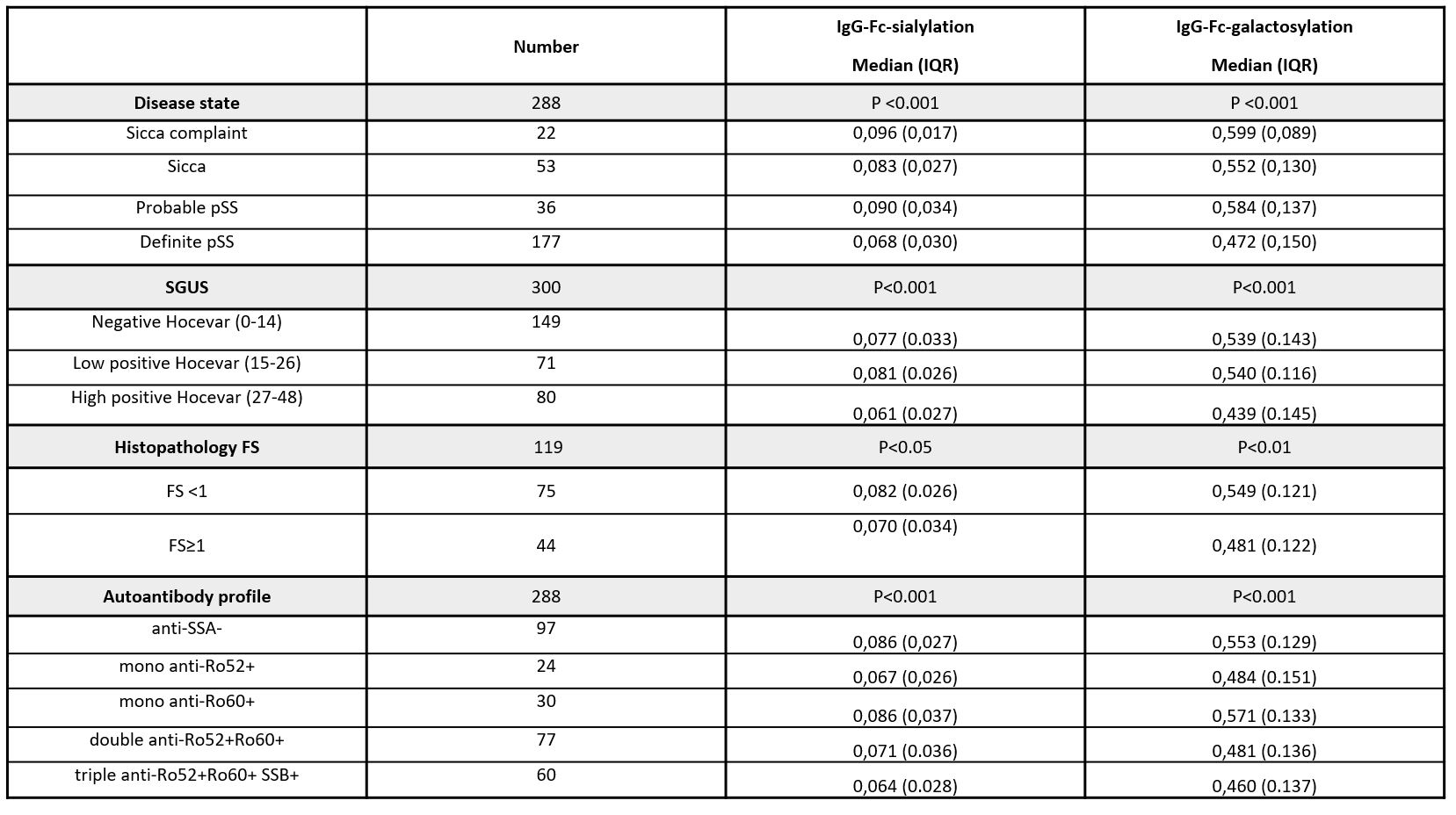
Methods: The relative amount of N-sialylated and N-galactosylated IgG was determined by capillary electrophoresis after using the endo-S glycosidase based assay. 300 serum samples of patients of the BeSSTT, an observational cohort of patients with definite pSS (n=177), fulfilling the 2016 ACR/EULAR classification criteria, and of patients with suspected pSS (n=111) due to presence of either objective sicca or one immunological criterion, were investigated. Groups were made based on the presence or absence of sicca complaints, objective sicca, anti-SSA reactivity and histopathology focus score. SGUS was assessed by Hocevar Score, categorized in negative (0-14), low positive (15-26) and high positive (27-48)2. Differences in levels of IgG-Fc-N-sialylation and -galactosylation were determined using Kruskal-Wallis testing. P-values ≤0.05 were considered statistically significant. Bonferroni correction was applied for post-hoc analyses.
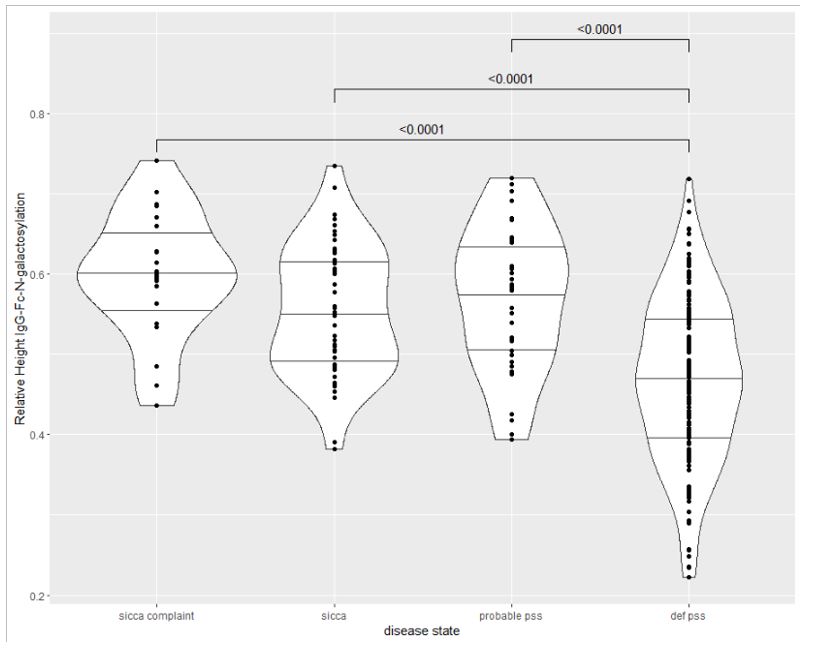
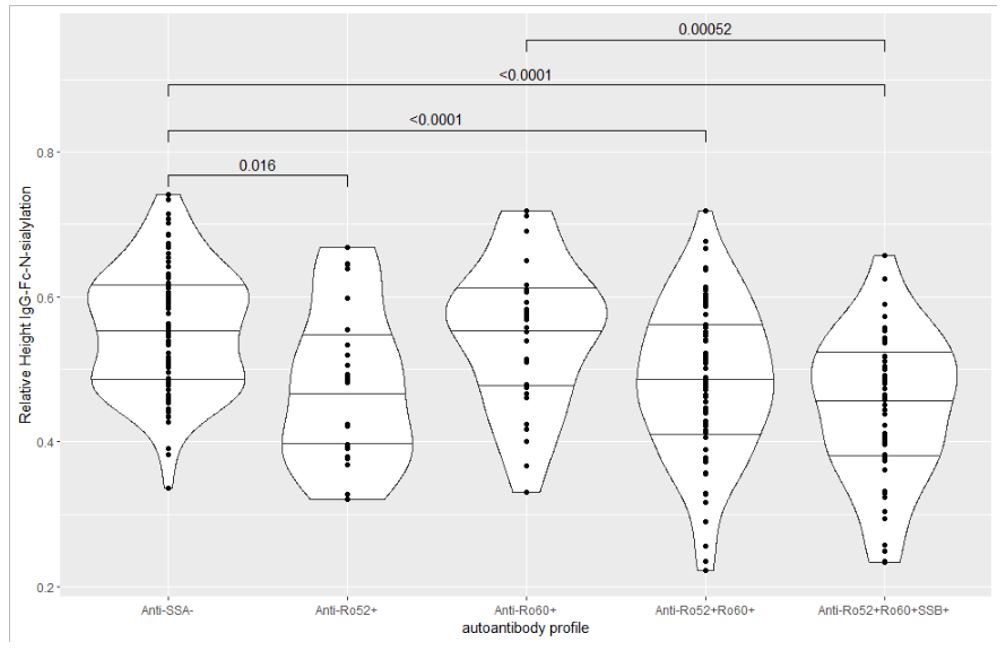
Results: IgG-Fc-N-sialylation and -galactosylation were significantly lower in definite pSS than in patients with sicca complaints, objective sicca or anti-SSA/SSB reactivity only (probable pSS) (Fig 1). Besides, IgG-Fc-N-sialylation and IgG-Fc-N-galactosylation were significantly lower in high positive SGUS- versus low positive and negative SGUS-scores and in positive versus negative focus scores. IgG-Fc-N-sialylation and -galactosylation were significantly lower in anti-Ro52+Ro60+SSB+, anti-Ro52+Ro60+ and anti-Ro52+ patients than in anti-SSA-/SSB- patients. Strikingly, IgG-Fc-N-sialylation and -galactosylation were also significantly higher in anti-Ro52+60+ and anti-Ro52+Ro60+SSB+patients than in anti-Ro60+ patients (Fig 2). Results are shown in Table 1.
Conclusion: There was a gradual loss of IgG-Fc-N-sialic acid and IgG-Fc-N-galactose as the disease became more prominent, as observed from sicca and probable pSS to definite pSS. The IgG-Fc-N-glycosylation profile was associated with the degree of salivary gland damage in pSS. Anti-Ro52+Ro60+SSB+, Anti-Ro52+Ro60+ and Anti-Ro52+ patients had a more pro-inflammatory IgG-Fc-N-glycosylation profile than anti-SSA- and strikingly also than anti-Ro60+ patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Achten H, Deroo L, De Boeck K, Jarlborg M, Decruy T, Deprez J, Dumas E, Elewaut D, peene i. IgG-Fc-N-Sialylation and -Galactosylation in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome (Pss) in Its Potential as Marker of Disease State and Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg-fc-n-sialylation-and-galactosylation-in-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-pss-in-its-potential-as-marker-of-disease-state-and-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg-fc-n-sialylation-and-galactosylation-in-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-pss-in-its-potential-as-marker-of-disease-state-and-disease-activity/