Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
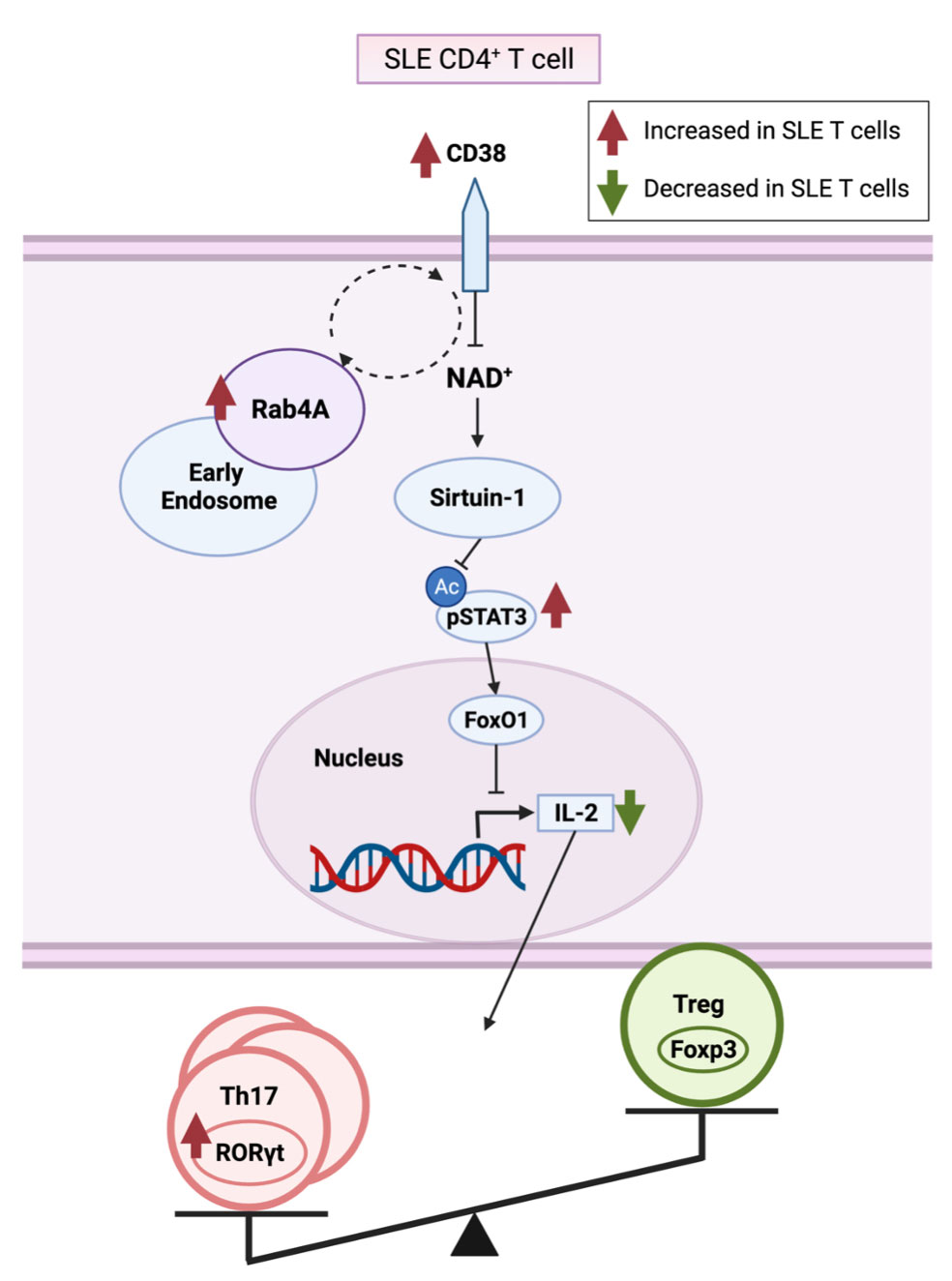
Background/Purpose: HRES-1/Rab4 (Rab4A) is a small GTPase that is overexpressed in SLE patient T cells1,2, mediates the enhanced recycling of CD3 and CD4 cell surface receptors1,2, and the activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR)3. Recently, increased expression of CD384, mTOR activation5, and loss of IL-2 production6,7 have been implicated in pro-inflammatory T cell development in SLE. In this study, we investigated the impact of Rab4A on the expression of CD38 and the secretion of IL-2.
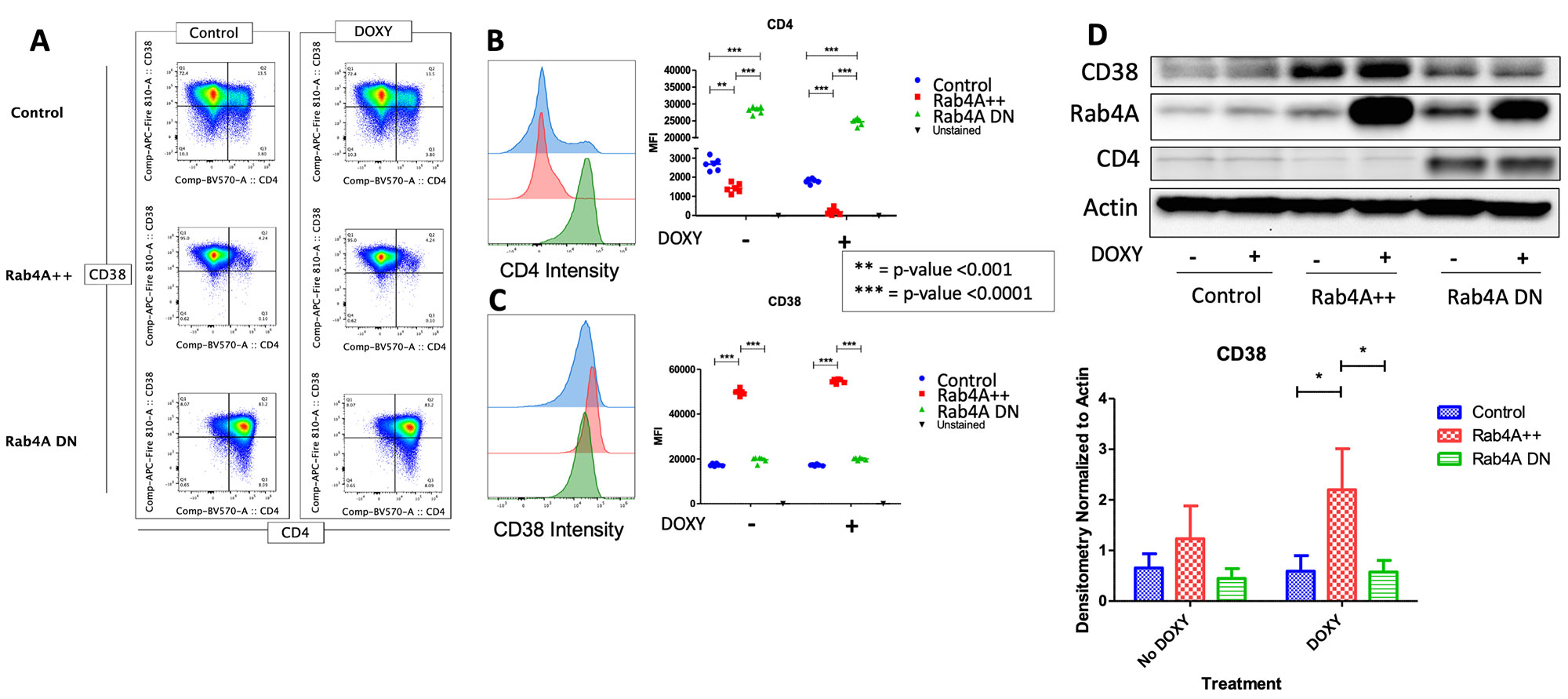
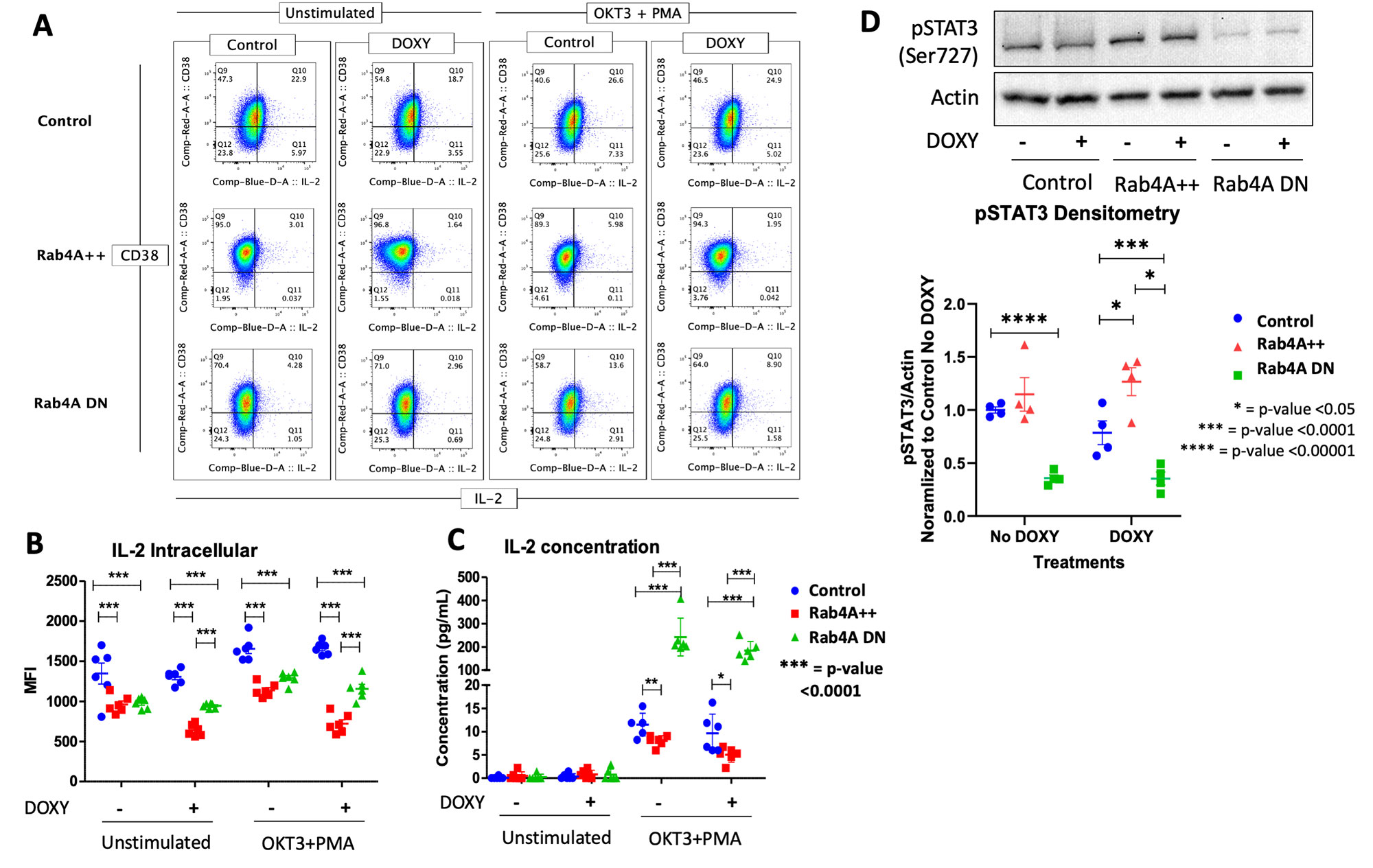
Methods: To understand the cellular consequences of Rab4A overexpression, our lab has created unique Rab4A-mutant Jurkat cell lines, which contain GFP-expressing vector alone (control), doxycycline-inducible vectors that overexpress Rab4A (Rab4A++) or the dominant-negative mutant Rab4AS27N (Rab4ADN)8. The three Rab4A-modified Jurkat lines were cultured in the presence and absence of 1 µg/mL of doxycycline. They were also separately stimulated with a combination of 1 µg/mL of anti-CD3 mAb (OKT3) and 50 ng/mL of phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) to induce cytokine production9. Cells were harvested after 24 hours and analyzed by flow cytometry using fluorochrome-tagged primary antibodies against CD4 and CD38 for surface staining and antibodies against IL-2 for intracellular staining. Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) was used for quantification. Cell lysates were run for Western Blot analysis, and Rab4A, CD4, CD38, and phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) (Ser727) were normalized to β-actin. Cell culture supernatant was used to measure cytokine secretion using the cytometric bead array (CBA) kit (BD Biosciences). For statistical significance, t-test was used; p-values < 0.05 were considered significant for hypothesis testing.
Results: CD38 was significantly upregulated in the Rab4A++ cells, compared to the control and Rab4ADN cells (fold change=2.014, p=2.49×10-13). Intracellular production and secretion of IL-2 were significantly decreased in the Rab4A++ cells (fold change=-0.566, p=1.16×10-7 and fold change=-0.481, p=0.0401, respectively) compared to the control. In the Rab4ADN cells, IL-2 secretion was significantly increased (fold change=18.091, p=7.513×10-7, respectively). In Rab4A++ cells, pSTAT3 is increased compared to the control (fold change=2.052, p=0.0318).
Conclusion: CD38 is an NAD+ hydrolase12, which has shown to regulate Sirtuin-1 activity13, a NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase that deacetylates and suppresses STAT3 activity14. We showed that CD38 is increased in the Rab4A++ cells, which may explain the increase in pSTAT3 seen in the Rab4A++ cells. Phosphorylation of STAT3 is required for STAT3 activity15. STAT3 binds to Forkhead box, class-O (FoxO)1 promoter, and FoxO1 protein inhibits IL-2 production16. We showed that IL-2, which inhibits TH17 differentiation while inducing Treg differentiation, is decreased in the Rab4A++ cells. The overexpression of Rab4A1,2 and CD3810,17,18, increased pSTAT319, and diminished IL-2 production6 reflect changes observed in SLE patients. Our results suggest that increased expression of Rab4A may in fact underlie the overexpression of CD38 and diminished secretion of IL-2 in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park S, Patel A, Perl A. HRES-1/Rab4 Controls the Overexpression of CD38 and Depletion of IL-2 in CD4+ T Cells; Potential Involvement in Proinflammatory Lineage Development in SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hres-1-rab4-controls-the-overexpression-of-cd38-and-depletion-of-il-2-in-cd4-t-cells-potential-involvement-in-proinflammatory-lineage-development-in-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hres-1-rab4-controls-the-overexpression-of-cd38-and-depletion-of-il-2-in-cd4-t-cells-potential-involvement-in-proinflammatory-lineage-development-in-sle/