Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an elevated risk for developing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD). Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is a key regulator of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) metabolism as it gives an increased breakdown of LDL-receptors on the liver resulting in enhanced LDL-cholesterol levels. We aimed to investigate i) the influence of glucocorticoids and biologic treatments on PCSK9 levels and ii) whether the presence of autoantibodies associates with the changes in the PCSK9 levels in DMARD-naïve early RA patients after treatment.
Methods: In this post-hoc analysis of the phase 4 NORD-STAR randomized controlled trial, PCSK9 levels were assessed in 330 Swedish patients who were randomised (1:1:1:1) to receive methotrexate (MTX) in combination with glucocorticoids (GC), certolizumab-pegol (CZP), abatacept (ABA), or tocilizumab (TCZ). PCSK9 levels were determined by commercial ELISA kit (R&D Systems, UK) at baseline and 24 weeks after the initiation of randomised RA treatment. The assay range of ELISA was 125.0–8000 pg/mL. Linear regression models were used to analyse the difference between the treatment groups on PCSK9 levels at 24 weeks. Analyses were adjusted for the baseline level of PCSK9, sex, age, BMI, DAS28-CRP, anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) status, rheumatoid factor (RF) status, and statin use at 24 weeks. In a second analysis, the interaction between the treatment groups and RF, ACPA and antinuclear antibody (ANA) were added to the model.
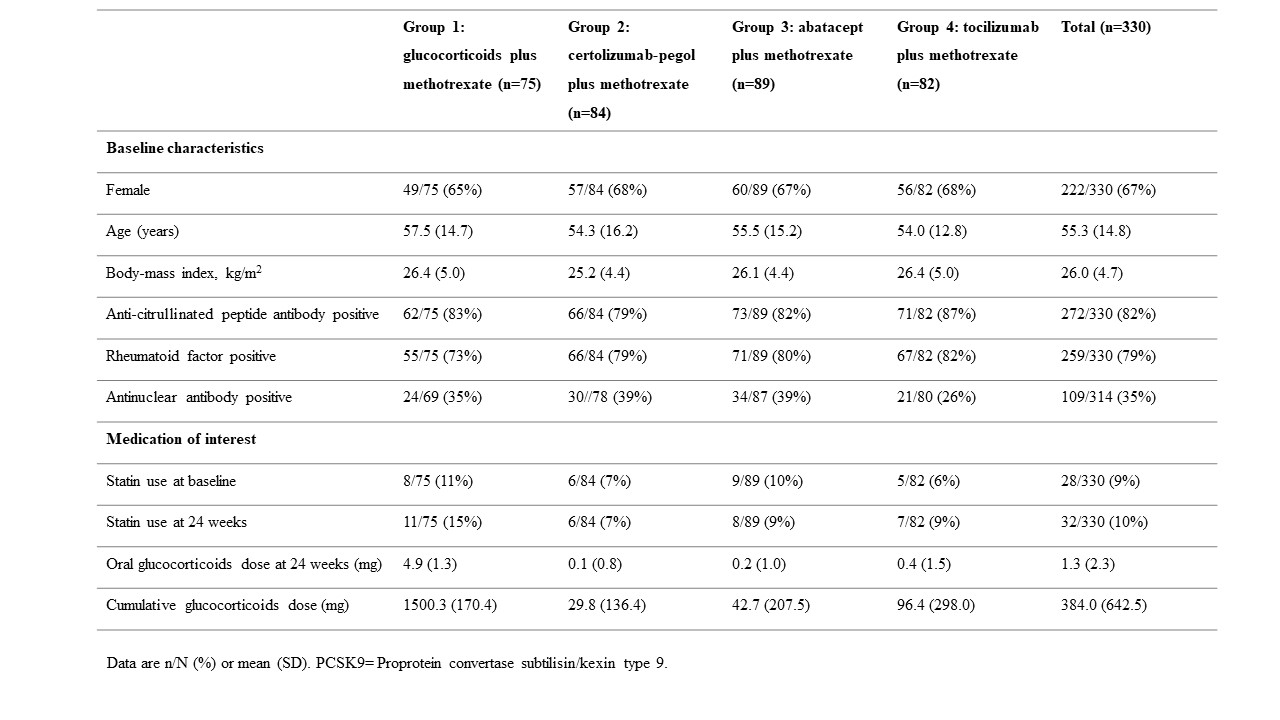
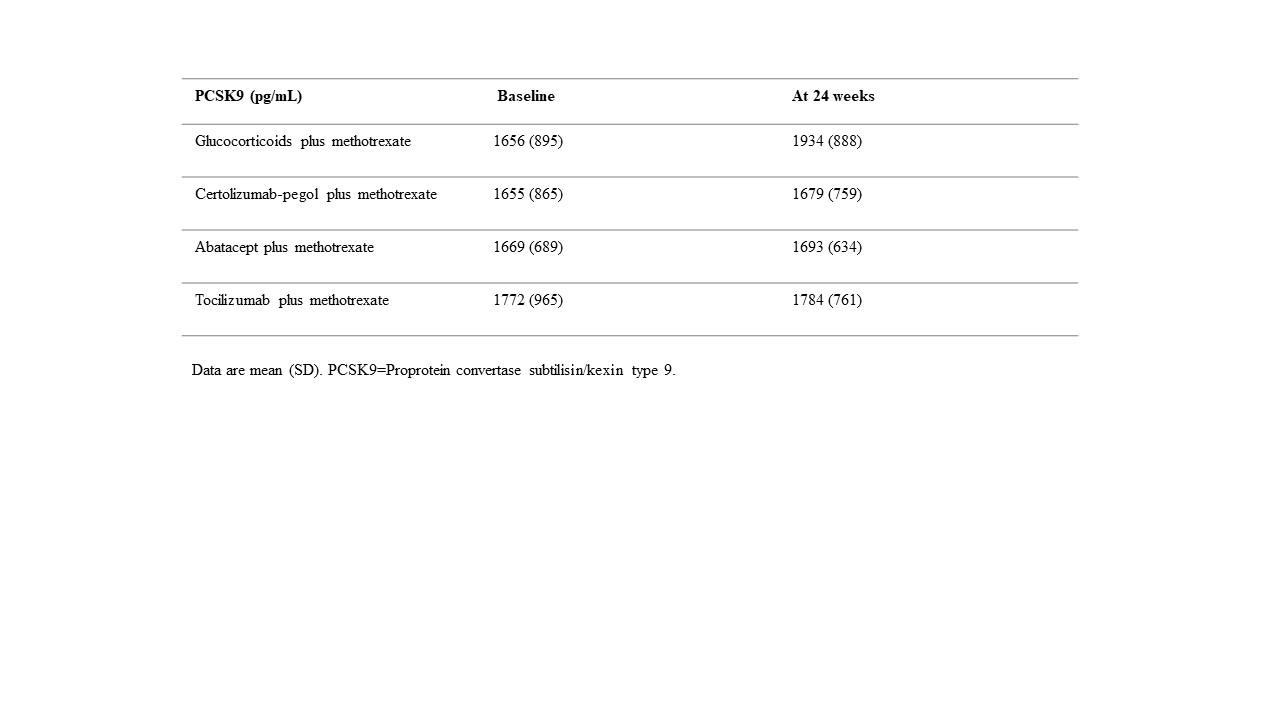
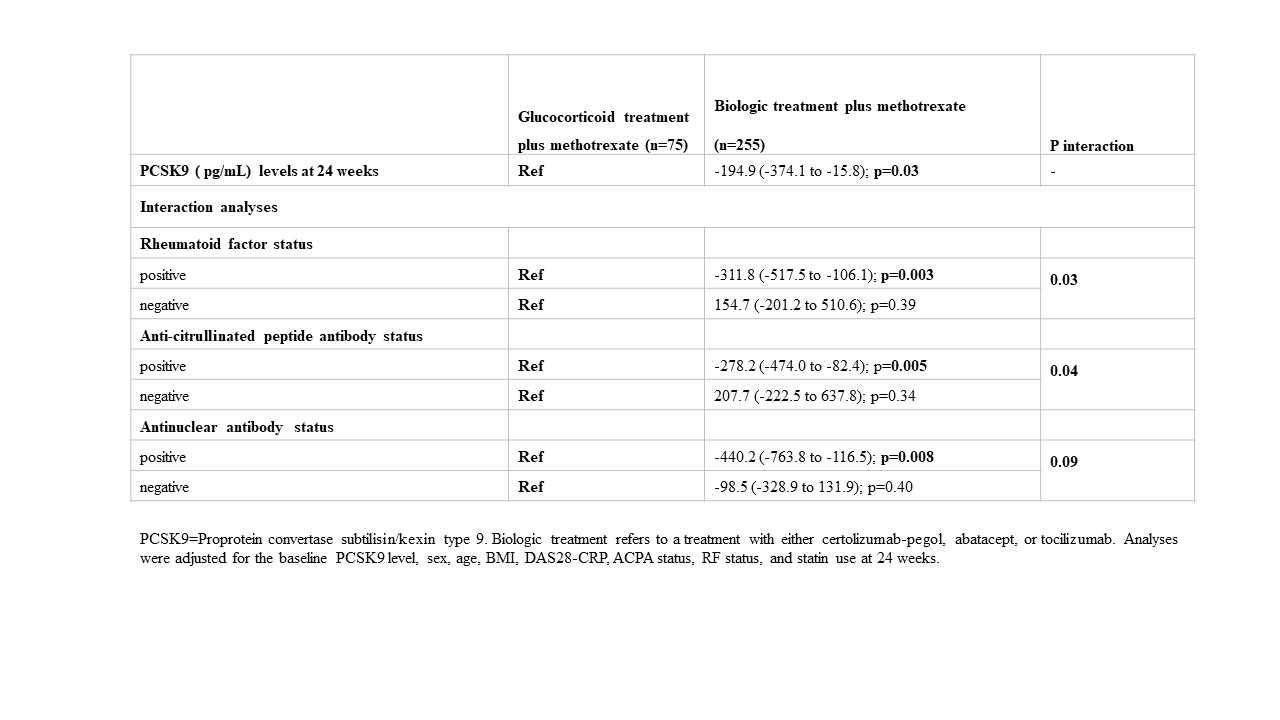
Results: Baseline characteristics and the medications of interest are shown in Table 1. The mean PCSK9 levels at baseline were similar across treatment groups. At 24 weeks, highest PCSK9 levels were observed in the MTX+GC treatment group (see table 2). The mean PCSK9 levels at 24 weeks were as follows: MTX+GC (1934 pg/mL [SD 888]); CZP+MTX (1679 [759]); ABA+MTX (1693 [634]); and TCZ+MTX (1784 [761]). Because the effect of the three biological treatment groups on PCSK9 levels at week 24 were more or less the same, for the analyses with the interactions with RF, ACPA and ANA, we combined the three biological treatment groups into one group in order to increase power. At 24 weeks, PCSK9 levels were significantly lower in the pooled biologic treatment group compared with the GC+MTX treatment group(β coefficient -194.9; 95% CI -374.1 to -15.8). Interaction analyses demonstrated that the differences between MTX+GC and biological treatments was most pronounced for RF, ACPA and ANA positive patients (See table 3).
Conclusion: Glucocorticoid treatment was associated with increased PCSK9 levels at 24 weeks. These increases were observed primarily in RF, ACPA, ANA positive patients. Our data provide a potential mechanistic link between glucocorticoid treatment and cardiovascular disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lend K, Twisk J, Kumar N, Lampa J, Rudin A, Hetland M, Uhlig T, Nordstrom D, Østergaard M, Schrumpf Heiberg M, Haavardsholm E, Gudbjornsson B, Sokka-Isler T, Grondal G, Hørslev-Petersen K, Nurmohamed M, van Vollenhoven R, Frostegård J. Glucocorticoid Treatment in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Associated with Increased Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Levels: A Post-hoc Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial (NORD-STAR) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucocorticoid-treatment-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-associated-with-increased-proprotein-convertase-subtilisin-kexin-type-9-pcsk9-levels-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucocorticoid-treatment-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-associated-with-increased-proprotein-convertase-subtilisin-kexin-type-9-pcsk9-levels-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-randomized-controlled-trial/