Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster I: Inflammatory Arthritis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) is widely regarded as a valuable tool for assessing the full extent of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In recent decades, numerous global ultrasound scores have been developed, however the number of joints, and choice of MSUS modality or elementary lesion (e.g. grey-scale [GS] and/or Doppler [D], synovial effusion [SE] and/or synovial hypertrophy [SH], etc.) to be included remained questionable. Following a systematic literature review (SLR) published in 2010 (1) which highlighted the heterogeneity of MSUS definitions, joint patterns and scoring systems to evaluate synovitis burden in RA, the OMERACT US Working Group developed a global synovitis scoring system (GLOESS) at joint and patient level (joint set), with standardised and validated definitions and grading of synovitis which advocates the use of a combined GS and D score, and synovial hypertrophy, but not synovial effusion as the elementary lesions denoting synovitis (2). Our goal was to analyse the implementation and metric properties of the proposed GLOESS as scoring system to evaluate synovitis burden in RA.
Methods: A SLR of Central, Embase and Medline databases was performed (31.3.2010 to 15.9.2023) by two independent reviewers updating our previous SLR (1). Original research reports written in English which assessed the reliability, validity and sensitivity of global MSUS scoring systems in RA were included and data extracted using a predefined extraction sheet.
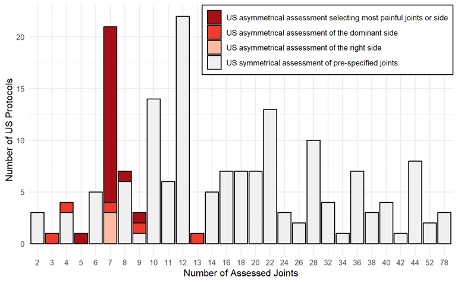
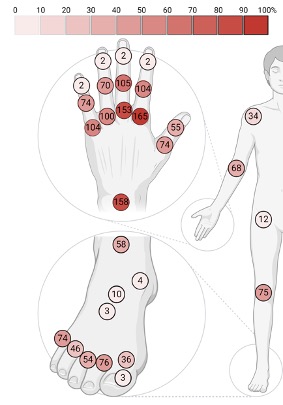
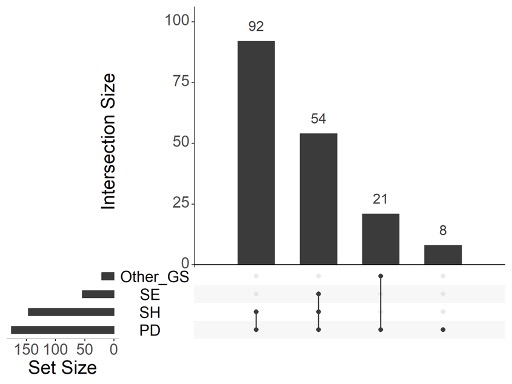
Results: 99/1564 identified reports were included in the final review. The majority of global scoring systems composed of individual joints were semiquantitative: 98% (97/99), while binary: 28% (28/99) or quantitative: 6% (6/99) scores were utilised less often. The joint set most commonly used was the 7-joint (wrist, metacarpophalangeal [MCP]2, MCP3, proximal interphalangeal [PIP]2, PIP3, metatarsophalangeal [MTP]2, MTP5 of the clinically more affected side) (15/99, 15%), 12-joint (bilateral elbow, wrist, MCP2, MCP3, knee, ankle) (15/99, 15%), 22-joint (bilateral wrist, MCP1-5, PIP 1-5) (12/99, 12%) and 28-joint (bilateral shoulder, elbow, wrist, MCP 1-5, IP1, PIP 2-5, knee) sets (9/99, 9%), while more extensive sets were investigated more rarely (Figures 1 and 2). 40% (40/99) considered only SH (i.e. GLOESS); 38% (38/99) articles considered both SH+SE – studies in this group were generally older. Composite score (GS+D) was evaluated in 22% (22/99), with most studies evaluating the domains separately (Figure 3). All included studies assessed face and content validity, while 73% (73/99) also assessed construct validity by comparison to clinical examination, laboratory findings or other imaging modalities. 34% (34/99) evaluated responsiveness and 42% (42/99) evaluated reliability. Time of evaluation varied from 15-60 min, increasing with the number of joints.
Conclusion: MSUS is a valuable tool for examining the global extent of synovitis in RA. GLOESS as a validated scoring system and use of SH as
the sole GS determinant of synovitis was clearly indicated in the more recently published articles. Reduced joint counts are used more frequently, particularly for evaluating responsiveness.
Created with Biorender.com.
Abbreviations: GS (Grey Scale), SE (Synovial Effusion), SH (Synovial Hypertrophy), PD (Power Doppler).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mandl P, Watschinger C, De Lorenzis E, Wildner B, Terslev L, Gessl I, Keen H, Pineda C, D'Agostino M. Global Ultrasound Scoring Systems for Assessing Synovitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/global-ultrasound-scoring-systems-for-assessing-synovitis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/global-ultrasound-scoring-systems-for-assessing-synovitis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/