Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality (1893–1896)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: The RA-FQ is a patient-reported measure of current disease activity in RA that can be used to identify disease flares. The RA-FQ queries pain, physical function, fatigue, stiffness, and participation and yields a score from 0-50. We previously reported on reliability, validity, and responsiveness. Our goal was to compare changes in the RA-FQ that represent minimal and meaningful improvement or worsening from the perspective of people living with RA, treating rheumatologists, and in relation to disease activity indices.
Methods: We used data from adults with early RA (symptoms < 1 year) enrolled in the CATCH (Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort), a prospective study of real-world patients treated across Canada. Participants completed the RA-FQ, Patient Global, and RA Global Change Impression item (a little vs. a lot better or worse or same) at 3- and 6-month visits. Rheumatologists recorded joint counts and MD Global. We compared mean change across categories of improvement and worsening disease activity using patient, physician and CDAI anchors and created cumulative distribution function curves to visually examine separation among categories.
Results: The 808 adults were mostly white (84%) women (71%) with a mean (SD) age of 55 (15) and moderate-high disease activity (85%) at enrollment. At the second visit, 79% of patients reported that their RA had changed; 59% were better and 20% worse. Patients who were a lot worse had a mean increase of 8.9 points whereas those who rated themselves as a lot better had a -6.0 decrease on the RA-FQ (Figure). Minimal worsening and improvement were associated with 4.7 and -1.8 change on the RA-FQ, respectively, while patients who rated their RA unchanged had stable RA-FQ scores (Table). Physicians and CDAI classified more patients as worse than patients, and minimal and meaningful RA-FQ thresholds differed by group. Similar changes were evident in CDAI, SDAI, and DAS indices (Table). Larger differences were observed with patient vs. physician global scores and tender vs. swollen joints. Across measures, the change associated with worsening was greater than for improvement. Results supported all prespecified hypotheses.
Conclusion: In this large cohort of adults with ERA, the RA-FQ was responsive to change and generally distinguished between minimal and meaningful improvement and worsening. These data add to growing evidence demonstrating robust psychometric properties of the RA-FQ and offer initial guidance about the amount of change associated with improvement or worsening, supporting its use in RA care, research and decision-making.
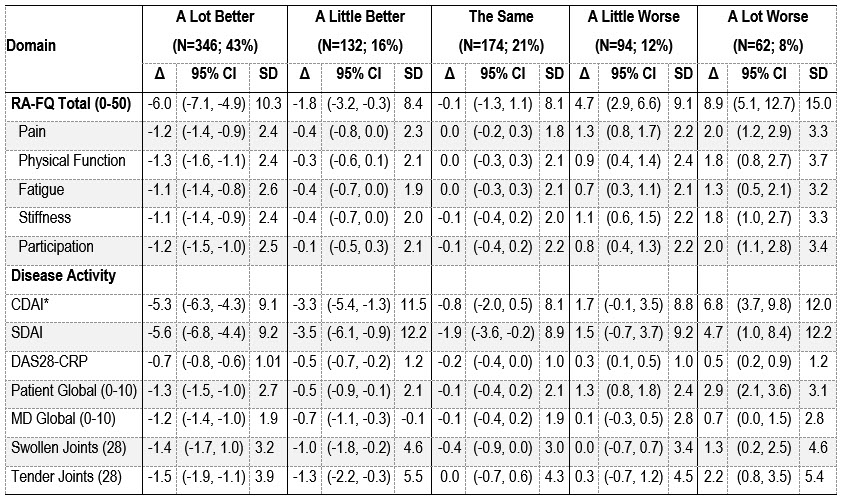 Change in RA-FQ scores between visits by patient ratings of RA status.
Change in RA-FQ scores between visits by patient ratings of RA status.
 Cumulative distribution function curves for patient, physician and CDAI anchors.
Cumulative distribution function curves for patient, physician and CDAI anchors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bartlett S, Bykerk V, Schieir O, Valois M, Bessette L, Boire G, Hazlewood G, Hitchon C, Keystone E, Pope J, Tin D, Thorne C, Bingham C, Investigators C. “From Where I Stand”: Using Multiple Anchors Yields Different Benchmarks for Meaningful Improvement and Worsening in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Flare Questionnaire (RA-FQ) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/from-where-i-stand-using-multiple-anchors-yields-different-benchmarks-for-meaningful-improvement-and-worsening-in-the-rheumatoid-arthritis-flare-questionnaire-ra-fq/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/from-where-i-stand-using-multiple-anchors-yields-different-benchmarks-for-meaningful-improvement-and-worsening-in-the-rheumatoid-arthritis-flare-questionnaire-ra-fq/

