Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0859–0885) Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Forkhead box O (FOXO) proteins are a family of transcription factors involved in lifespan, aging, and autophagy. FOXO are essential for maintaining cartilage homeostasis as reduced expression of FOXO1 and FOXO3 with aging, results in osteoarthritis (OA) due to reduction in the expression of autophagy-related genes. FOXO activity is strictly regulated by nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling. Drugs that promote nuclear FOXO and activity could be promising therapeutics for OA. Here, we discovered candidates of FOXO activators and evaluated their effects on chondrocytes.
Methods: We performed in silico drug prioritization of small molecules that enhance nuclear accumulation of FOXO1 or FOXO3 and selected 5 drug candidates, selinexor, dactolisib, cyproheptadine, LOM612, and psammaplysene-A from previously identified FOXO activators and confirmed their effects on FOXO nuclear translocation in human chondrocytes. Next, chondrocytes were treated with FOXO activators to evaluate their effects on the expression of autophagy-related genes, and the induction of catabolic factors after IL1β stimulation by qRT-PCR. RNA-sequencing of chondrocytes treated with cyproheptadine with or without IL1β stimulation was performed to clarify the target genes and mechanisms.
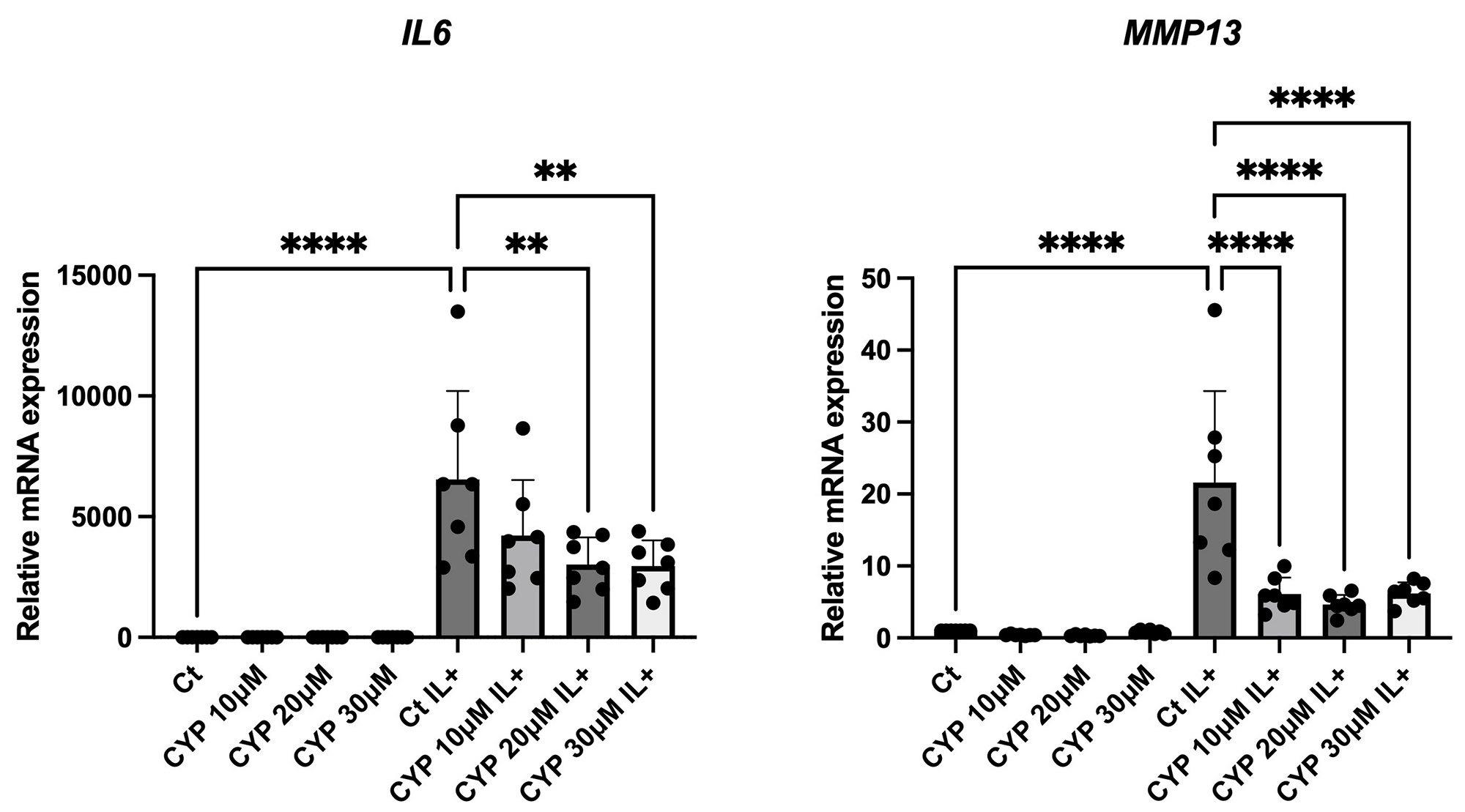
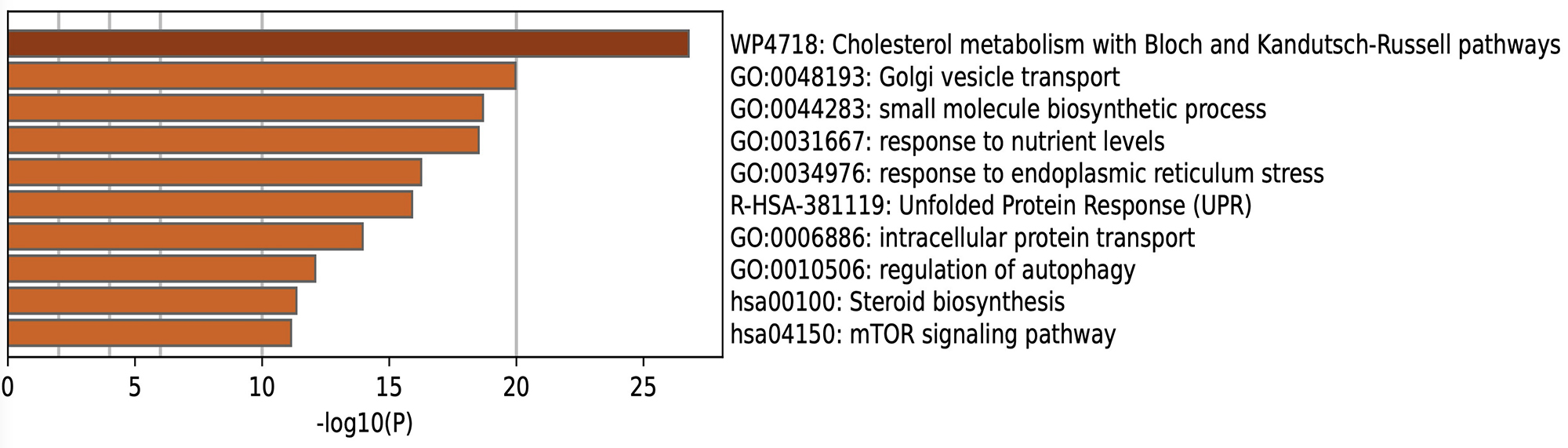
Results: Selinexor induced the nuclear accumulation both of FOXO1 and FOXO3, dactolisib and cyproheptadine induced FOXO3 nuclear accumulation, whereas LOM612 and psammaplysene A did not change FOXO translocation in chondrocytes. Among the 3 drugs which induced FOXO nuclear accumulation, cyproheptadine most effectively upregulated the expressions of autophagy-related genes (MAP1LC3B, GABALAPL1, ATG14) and inhibited the induction of catabolic factors (IL6 and MMP13) under IL1β stimulation (Figure 1). Enrichment analysis with the upregulated genes in RNA-seq showed that ‘Cholesterol metabolism’ was the most highly enriched pathway, suggesting that cyproheptadine modulates cholesterol levels in chondrocytes (Figure 2). Cyproheptadine also regulated ‘Autophagy’. In the presence of IL1β, the enrichment analysis with the downregulated genes showed cyproheptadine inhibited ‘Cytokine signaling’ via NFκB pathway.
Conclusion: Cyproheptadine induced FOXO3 nuclear accumulation and autophagy-related genes expression and inhibited catabolic factors. In addition, cyproheptadine showed a potential as a modulator of cellular cholesterol biosynthesis, which is associated with age-related diseases including OA. Further experiments in vitro and in vivo are ongoing to clarify the detailed effects of cyproheptadine as a candidate for drug-repurposing in OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kurakazu I, Olmer M, Myers K, Lotz M. FOXO Activators as Drugs for Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/foxo-activators-as-drugs-for-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/foxo-activators-as-drugs-for-osteoarthritis/