Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Peripheral neuroimmune crosstalk plays a crucial role in the inflammatory process and bone metabolism in joint. Serotonin receptor HTR2A was reported to be expressed on immune cells, of which gene polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of developing RA and other autoimmune disease. However, the expression and regulation of HTR2A in arthritis synovium remain poorly understood.
Methods: Differential expression of neurotransmitter receptors (NTRs) and their correlated inflammatory molecules was identified in RA and OA synovium from public scRNA-seq dataset[1]. IHC staining of synovial tissue from RA and OA patients was performed for validation. Expression of miRNAs potentially targeting HTR2A carried by synovial fluid extracellular vesicles (EVs) was screened in low- and high-grade inflammation RA from public dataset[2] and validated by qPCR.
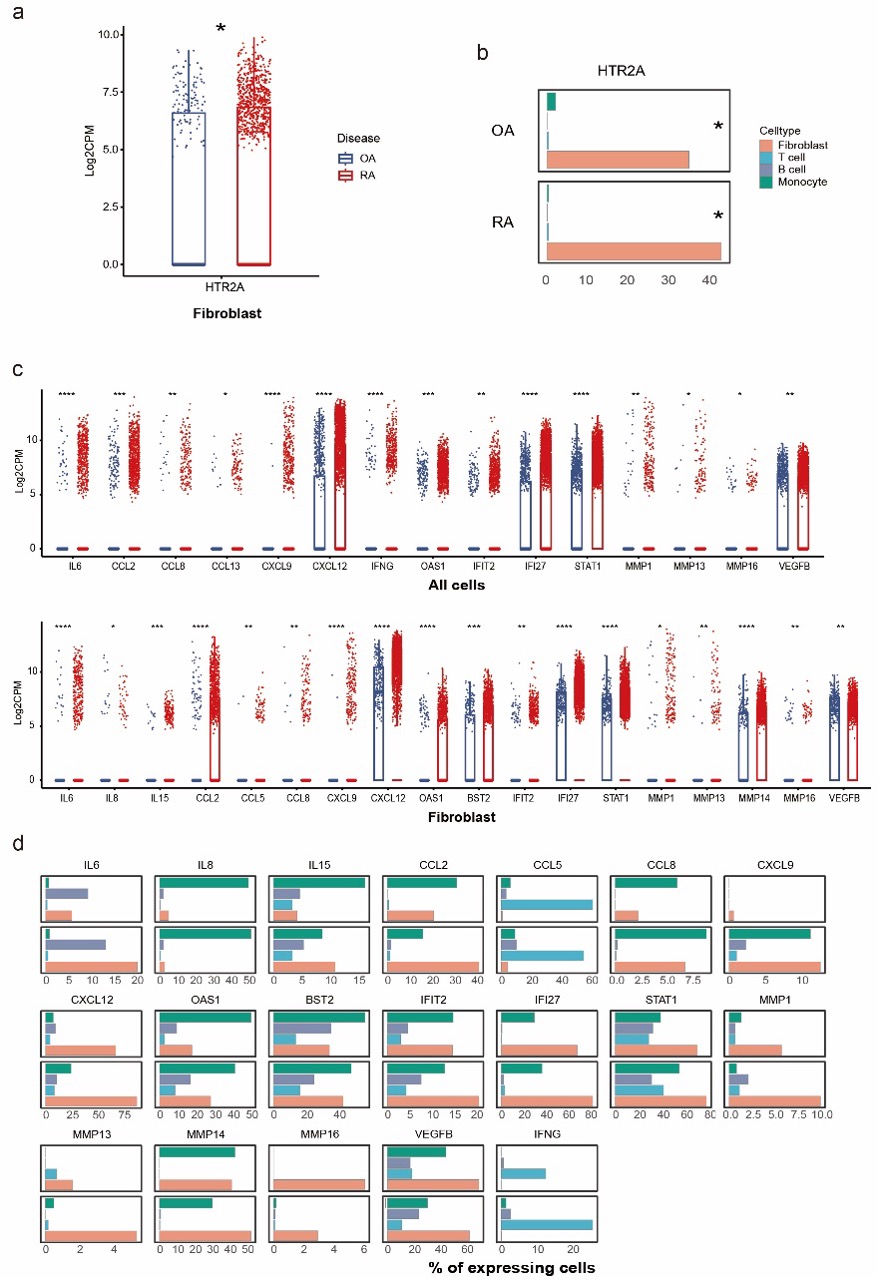
Results: HTR2A was expressed by 34.3% and 42.1% of fibroblasts in OA and RA synovium, while barely expressed by synovial leukocytes. Higher level of IL-6, IFN-????, IFN stimulated genes, chemokines including CCL2, CCL8, CCL13, CXCL9, and CXCL12, and MMPs and VEGFB were observed on all cell types in RA joint, indicating a highly inflammatory microenvironment in RA. (Fig.1).
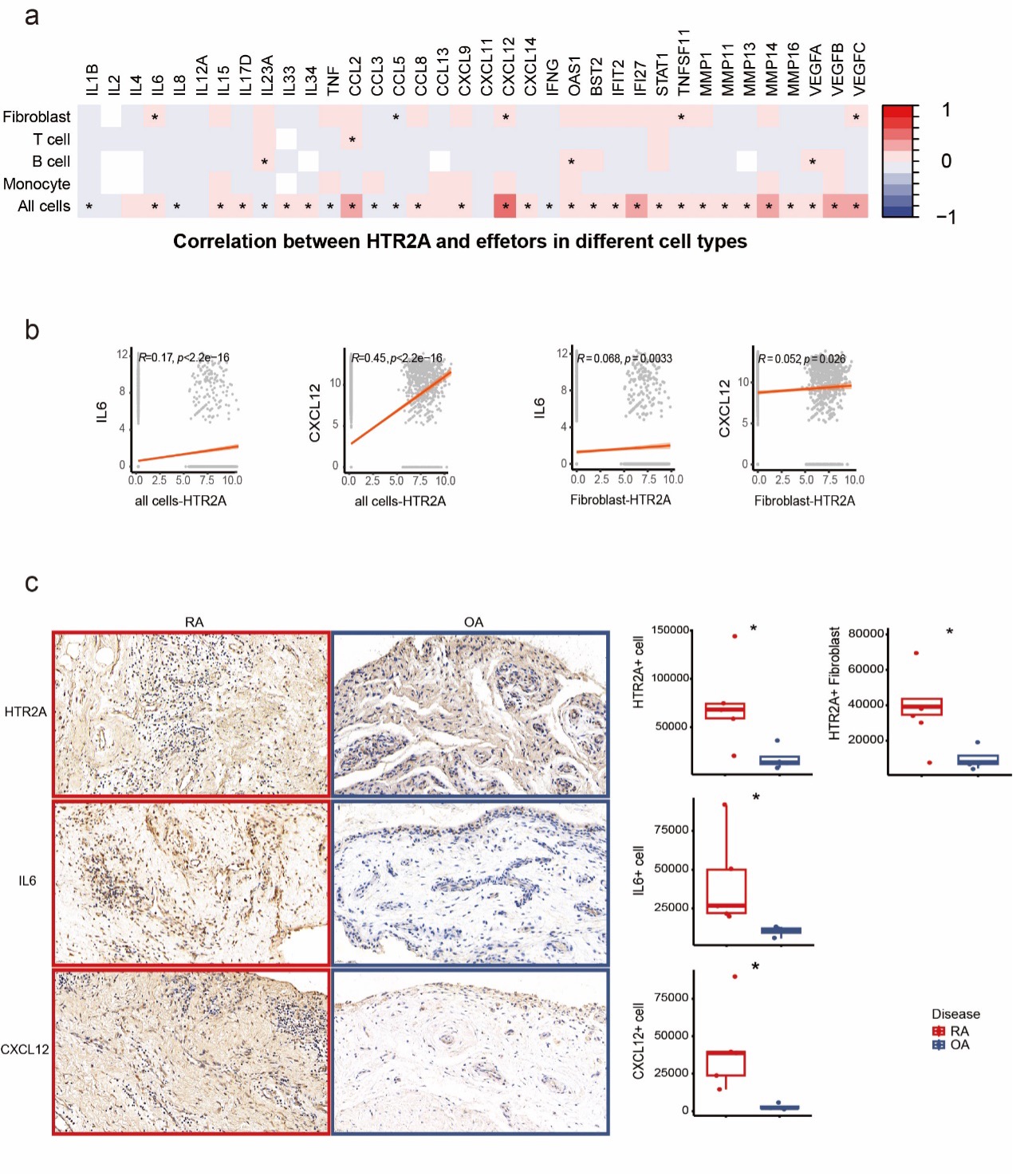
Correlation analysis showed positive correlation of HTR2A with IL6, CCL5, CXCL12, TNFSF11 and VEGFC expression in fibroblast specifically as well as in all synovial cells. The strongest correlation was found between HTR2A and CXCL12 (R=0.45). Transcriptomic findings above were confirmed on the protein level with IHC staining of RA and OA synovial tissue from patients. There was significantly upregulated expression of HTR2A on RA whole synovial tissue level and fibroblast level. Increased expression of IL-6 and CXCL12 was also found in RA synovial tissue (Fig.2).
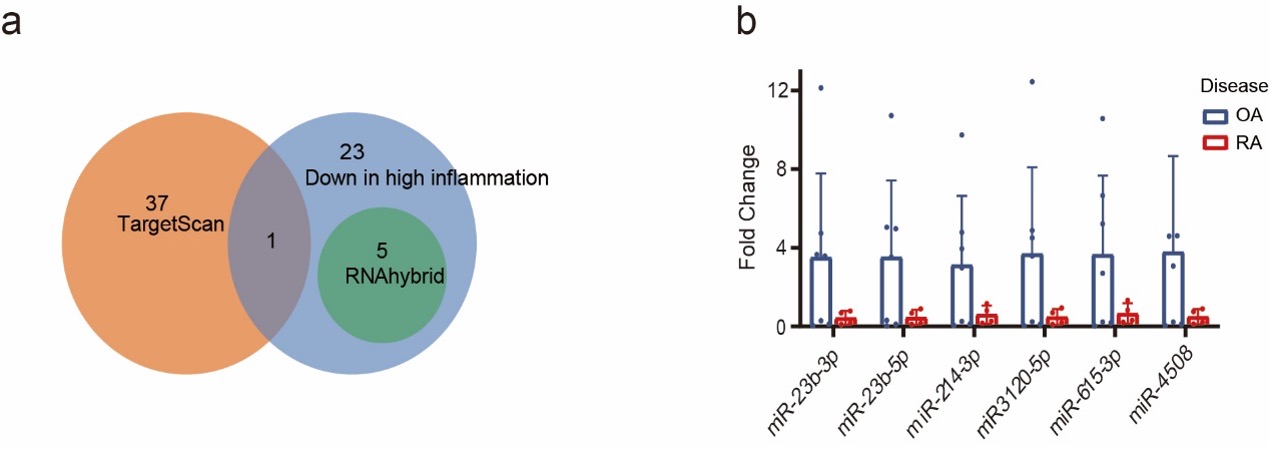
To investigate what could regulate the different HTR2A expression in RA and OA, we examined the content of EVs derived from RA and OA synovial fluid. Integrated with public RNAseq data, TargetScan and RNAhybrid prediction, 6 miRNAs predicted to regulate HTR2A expression, miRNA-23b-3p, miR-23b-5p, miR-214-3p, miR-3120-5P, miR-615-3p, and miR-4508, were significantly lower in RA EVs. A trend of lower expression of these 6 miRNAs was demonstrated by qPCR (Fig.3).
Conclusion: A neurotransmitter receptor of serotonin, HTR2A, was enriched in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fibroblast and positively correlated with inflammation. 6 miRNAs targeting HTR2A were decreased in RA synovial fluid EVs comparing to osteoarthritis. HTR2A may contribute to inflammation and RA pathogenesis, and miRNAs targeting HTR2A might offer new therapeutic strategies to alleviate inflammation in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xiang C, Hong S, Zhao B, Pi H, Du F, Lu X, Tang Y, Shen N, Yang C, Wang R. Fibroblast Expression of Neurotransmitter Receptor HTR2A Associates with Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Joint [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fibroblast-expression-of-neurotransmitter-receptor-htr2a-associates-with-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-joint/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fibroblast-expression-of-neurotransmitter-receptor-htr2a-associates-with-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-joint/