Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Annual screening for pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) has been shown to decrease mortality. The American College of Radiology, European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society, and 6th World Symposium of PH all recommend yearly screening with 1) Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT) with diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), 2) Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE), and 3) B-natriuretic peptide (BNP). Clinician adherence to these screening guidelines is not well established, with one study showing rates as low as 34% (Pauling JD et al.). In our retrospective study, we aim to assess adherence to screening guidelines in our medical center to develop a quality improvement intervention for enhanced timely screening.
Methods: Patient charts were reviewed from Loyola University Medical Center, a quartenary care health system in the Chicagoland area. Patients were selected by meeting the following criteria: 1) patients received a diagnosis of SSc by a rheumatologist (using ICD-10 diagnostic codes), 2) were at least 18 years old at diagnosis, 3) were seen by a rheumatologist in our outpatient clinics from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2022, and 4) did not have a diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension before January 1, 2018.
Charts were reviewed for demographic data, outpatient rheumatology appointments, PFTs, TTEs, and BNPs. Full compliance was defined as an appointment with a completed PFT, TTE, and BNP in the 12 months prior or 6 months after said visit. Ever compliant was defined as a patient having just one of these tests completed. Using these definitions allowed us to not underestimate compliance in situations where a patient did not follow with a rheumatologist all 5 years of the study period (e.g. changed care to an outside provider, established care late, had inconsistent follow-ups).
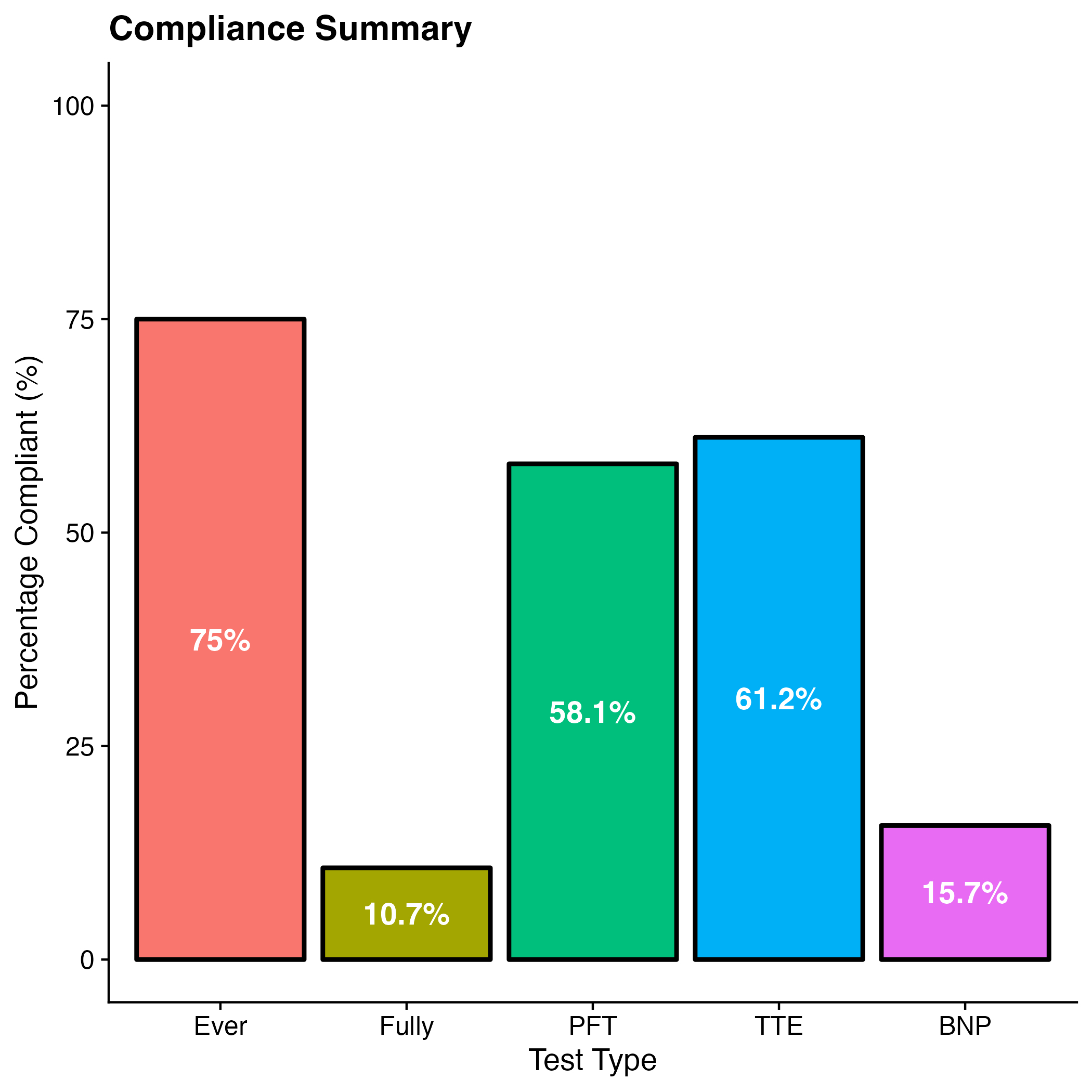
Results: Seventy-nine patients were identified to have met all criteria as above. Demographically, 87% of patients were female, 54% White, 14% Black, 25% Latino, 1% Asian, and 5% other. Over five years, these patients had a total of 484 appointments. Seventy-five percent (363) of all appointments had at least one screening test (PFT, TTE, BNP) completed 12 months prior or 6 months after the visit. However, only 10.7% of all appointments had all three tests completed, as recommended by international guidelines. Analyzing each test separately, only 58.1% (281), 61.2% (296), and 15.7% (76) of appointments had a corresponding PFT, TTE, and BNP, respectively (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Our results show that our medical center is not immune to the internationally reported low rates of guideline-directed screening for PH in SSc patients. These results are the impetus for our quality improvement project currently in progress at our institution. Interventions include an educational session by a PH expert and an order set on our EMR for seamless point-of-care ordering. We hope to share post-intervention results soon, as we all tackle this specialty-wide gap in guideline-care delivery.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hickernell J, Aouhab Z. Evaluating & Improving Adherence to Pulmonary Hypertension Screening in Systemic Sclerosis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-improving-adherence-to-pulmonary-hypertension-screening-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-improving-adherence-to-pulmonary-hypertension-screening-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients/