Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease, affecting multiple organ systems with varying severity among patients. SLE presents a diagnostic challenge due to its protean clinical manifestations. Current standard of care biomarkers such as anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith, and complement proteins C3/C4 have limited discriminatory power characterized by poor sensitivity in incipient cases of SLE. This study aims to compare the clinimetric performance of T-cell bound complement split product C4d (TC4d) and anti-T-cell antibodies IgG (TIgG) and IgM (TIgM) with conventional biomarkers in differentiating Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) from clinically relevant controls (CRCs).
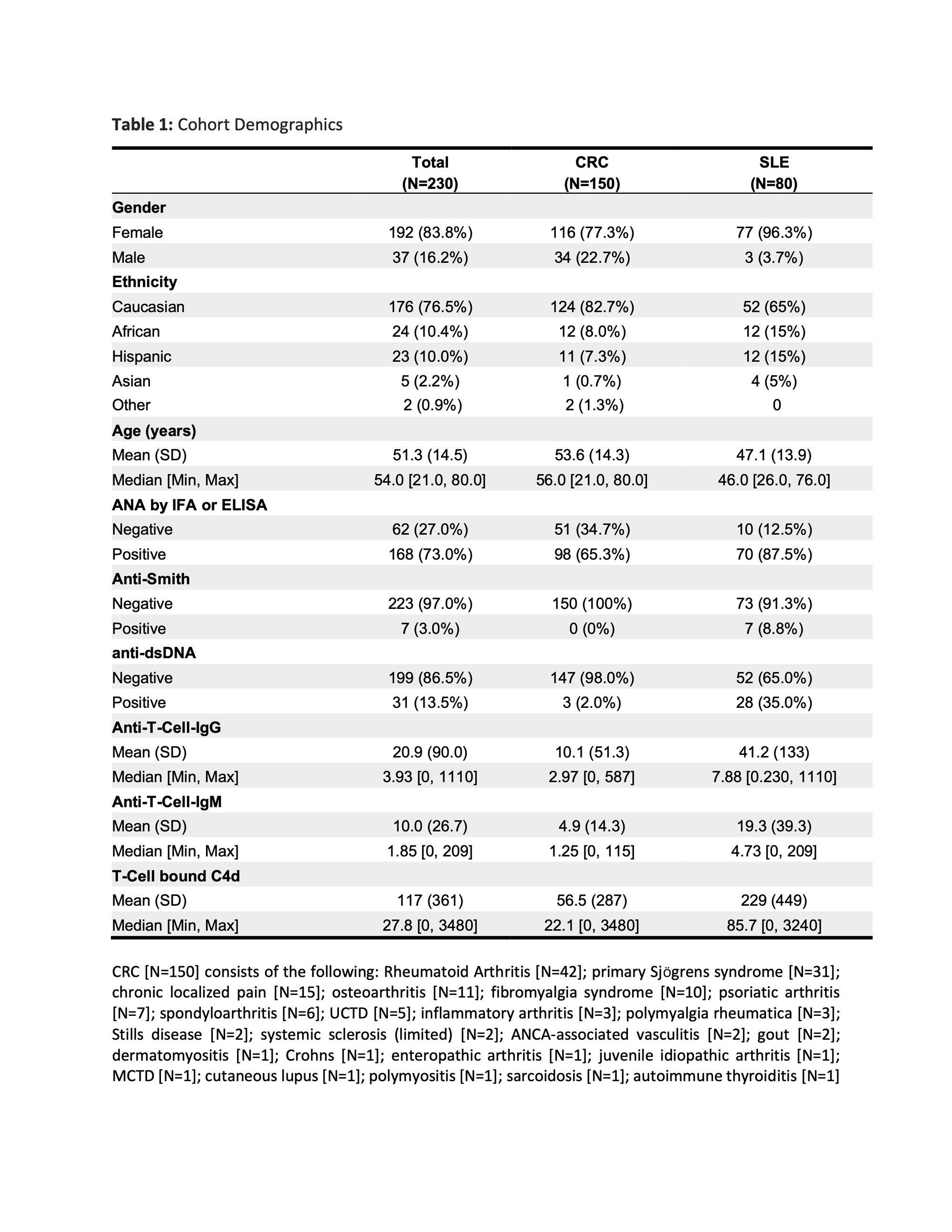
Methods: A total of 230 patients were included in the analysis (SLE = 80; CRC = 150) (Table 1). SLE patients were required to meet either the 1997 ACR, 2012 SLICC, or 2019 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for SLE; CRCs were required to have a clinical diagnosis with an associated ICD-9/ICD-10 code to confirm clinical diagnosis as enumerated in the Table 1 caption. A comprehensive machine learning pipeline integrating feature selection, multiple model architectures training, and cross-validation (CV) techniques was employed to compare the relative diagnostic performances of TIgG, TIgM, and TC4d to conventional SLE biomarkers. The robustness and generalizability of the pipeline were validated through permutational hold-out (HO) predictions, mitigating the risk of overfitting the models developed.
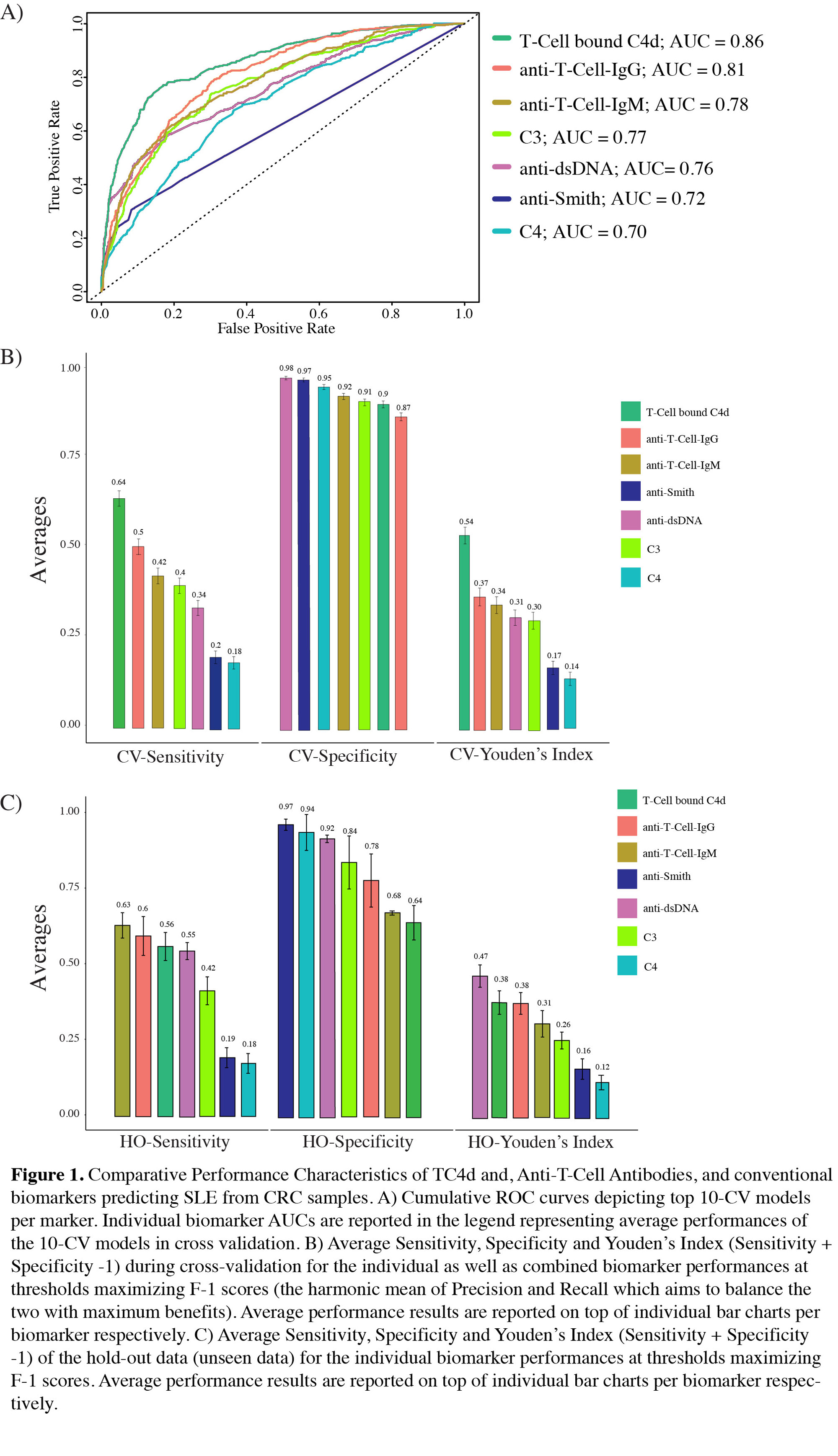
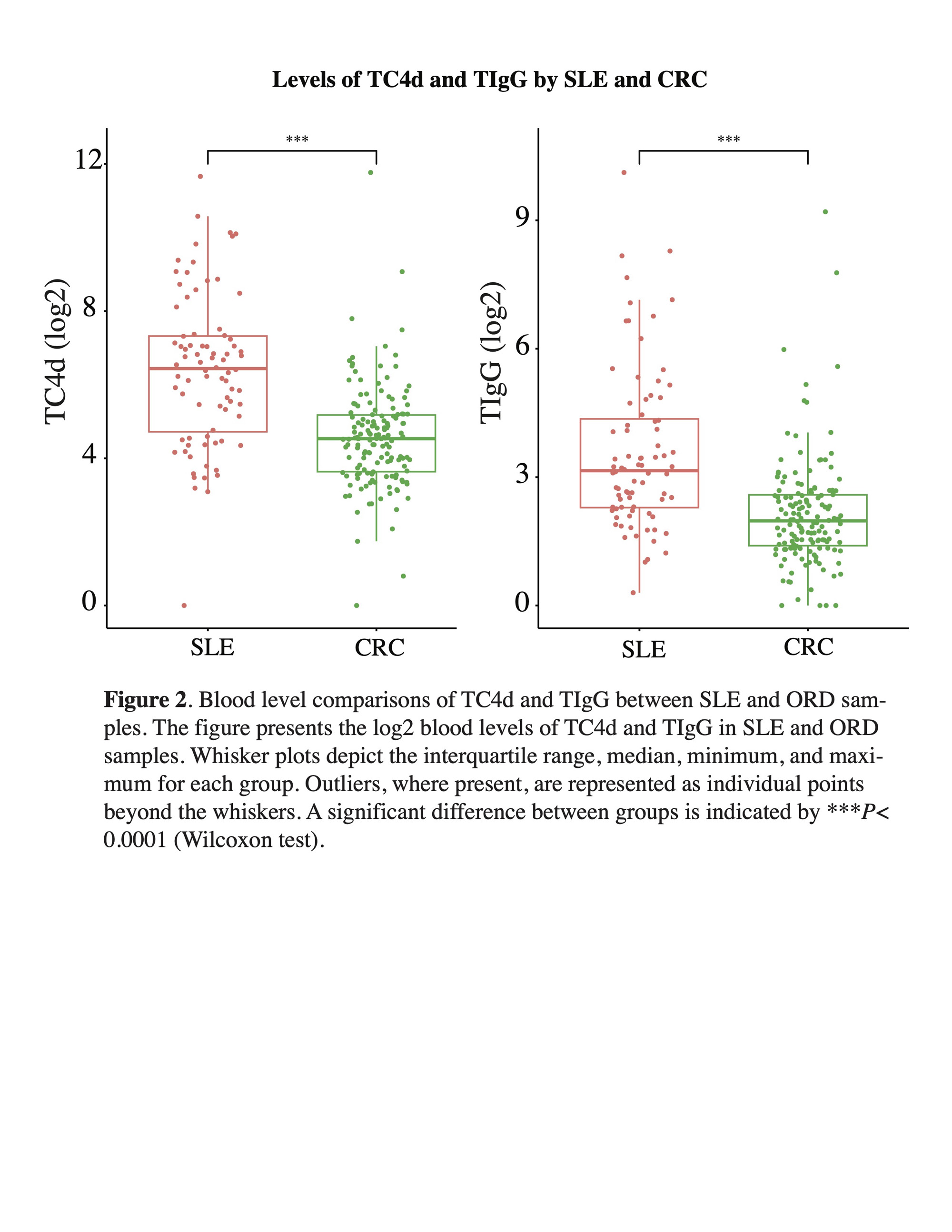
Results: The SLE cohort had a higher proportion of females (96.3% vs. 77.3%), younger age (mean [SD]: 47.1 [13.9] vs. 53.6 [14.3] years), and fewer Caucasians (65.0% vs. 82.7%) as compared to the CRC group (Table 1). Cumulative ROC analysis derived from multiple 10-fold CV models showed the diagnostic performances of TC4d (AUC = 0.86), TIgG (AUC = 0.81), and TIgM (AUC = 0.78) outperformed C3 (AUC = 0.77), anti-dsDNA (AUC = 0.76), anti-Smith (AUC = 0.72), and C4 (AUC = 0.70) (Figure 1, A). While the specificity of TIgG, TIgM, TC4d compared to conventional biomarkers were similar in CV models, the sensitivity for SLE in both 10-CV and HO partitions were significantly higher for TIgG, TIgM, and TC4d compared to conventional biomarkers (Figure 1 B, C). Comparing median blood levels of TC4d and TIgG confirmed a statistically significant difference between SLE and CRC (P< 0.0001) (Figure 2), further highlighting their intrinsic discriminatory power.
Conclusion: The study demonstrates the potential of TIgG, TIgM, and TC4d as sensitive and specific biomarkers for the diagnosis of SLE with improved diagnostic performance relative to conventional biomarkers. These findings suggest an opportunity for improved diagnostic accuracy that could yield timely treatment initiation and improved patient outcomes in SLE. However, further studies are needed to validate the results among larger, more diverse patient cohorts and to determine how T cell antibodies and TC4d biomarkers may improve upon existing integrated diagnostic biomarker solutions. Future efforts will explore the potential of T-Cell biomarkers to predict disease progression and as surrogates of treatment response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Concoff A, Kyttaris V, Sandhu V, O'Malley T, Casaburi G, Kumar S, Liu C, Manzi S, Ahearn J. Enhancing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis: Comparative Performance Characteristics of TC4d and Anti-T-Cell Antibodies with Conventional Biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhancing-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-diagnosis-comparative-performance-characteristics-of-tc4d-and-anti-t-cell-antibodies-with-conventional-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhancing-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-diagnosis-comparative-performance-characteristics-of-tc4d-and-anti-t-cell-antibodies-with-conventional-biomarkers/