Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: We have previously demonstrated that a combination of TNF-a and IL-6 induces mouse osteoclast-like cells with bone resorption activity both in vitro and in vivo [Arthritis & Rheumatology (A&R), 2014]. Recently, we have shown that the combination of TNF-a and IL-6 induces osteoclasts (OCs) derived from human peripheral blood monocytes (PBMs) via RANKL-independent pathways in vitro. In particular, the number of TNF-a and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with RA had a significant positive correlation with the modified total Sharp score. On the other hand, the number of RANKL-induced OCs had a significant negative correlation with whole-body bone mineral density (A&R, 2021). We undertook the present study to clarify the effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor on TNF-a and IL-6-induced OCs and RANKL-induced OCs in PBMs derived from patients with RA or healthy donors (HDs).
Methods: PBMs derived from 5 RA patients and HDs were stimulated by TNF-α and IL-6 or RANKL with or without 100-1000 nM filgotinib, a JAK inhibitor. The number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinucleated cells and bone resorption activity using a pit formation assay were assessed. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of IL-1b and IL-8. Furthermore, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced or RANKL-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs in RA patients before and 6 months after treatment with filgotinib was examined.
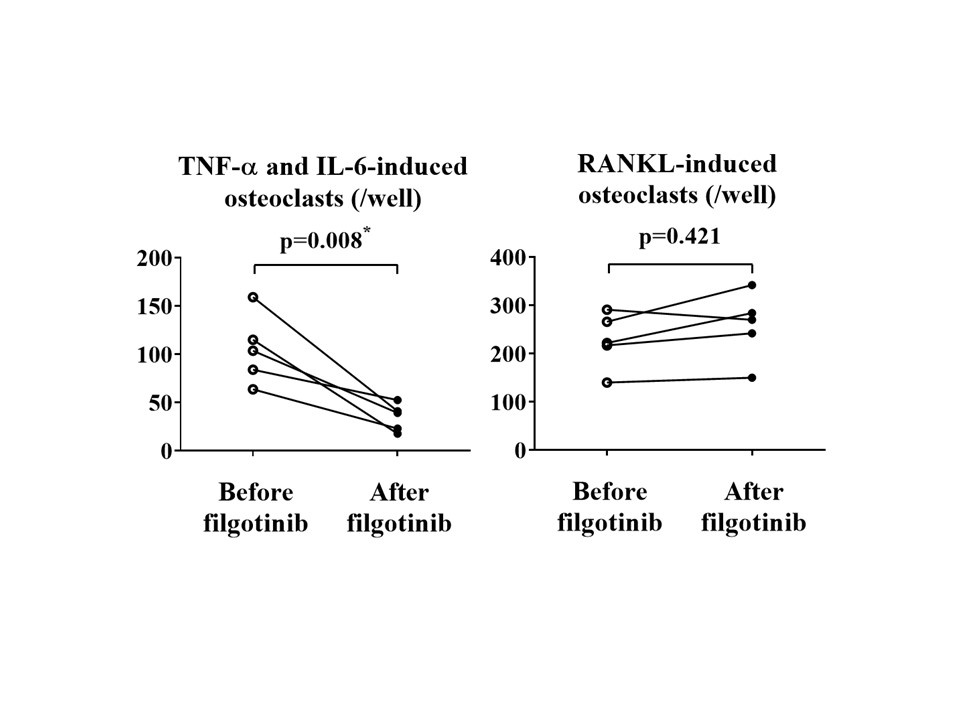
Results: The number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs and RANKL-induced OCs derived from PBMs in RA patients was significantly increased compared to that in HDs (each n=5, p< 0.05). Filgotinib significantly inhibited the differentiation of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs derived from PBMs of RA patients in a dose-dependent manner (n=4, all p< 0.05). On the other hand, the same concentrations of filgotinib did not inhibit osteoclastogenesis induce by RANKL (n=4, all p >0.05). Resorption pits generated by TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs derived from HDs in the presence of filgotinib was reduced comparing with those without filgotinib. In contrast, filgotinib did not inhibit generation of resorption pits by RANKL-induced OCs (n=4). Levels of IL-1b and IL-8 mRNA expressed by TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs from RA patients, but not RANKL-induced OCs, were significantly reduced by filgotinib (each n=3, p< 0.05). Six months after treatment with filgotinib, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs was significantly decreased compared with those of before the treatment (n=5, p=0.008) (Figure). In contrast, no significant change in the number of RANKL-induced OCs by the six-months administration of the JAK inhibitor was observed in the same patients (n = 5, p=0.421).
Conclusion: Filgotinib inhibits TNF-α and IL-6-induced osteoclast differentiation in vitro. Administration of filgotinib reduces differentiation potential of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs in PBMs from RA patients. Our results suggest that the inhibitory mechanism of filgotinib on joint destruction in RA may be related to its inhibition of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs, presumed pathogenic OCs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yokota K, Aizaki Y, Wada T, Kajiyama H, Araki Y, Yazawa H, Akiyama Y, Mimura T. Effects of Janus Kinase Inhibitor on TNF-a and IL-6-Induced Osteoclasts and RANKL-Induced Osteoclasts in Peripheral Blood Monocytes from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-janus-kinase-inhibitor-on-tnf-a-and-il-6-induced-osteoclasts-and-rankl-induced-osteoclasts-in-peripheral-blood-monocytes-from-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-janus-kinase-inhibitor-on-tnf-a-and-il-6-induced-osteoclasts-and-rankl-induced-osteoclasts-in-peripheral-blood-monocytes-from-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/