Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0252–0282) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) constitutes one of the most critical comorbidities in autoimmune diseases (AD), particularly in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic sclerosis (SSc) [1-2]. Therefore, its early diagnosis is pivotal to avoid irreversible lung damage in these patients. However, no definitive serum biomarkers are available to identify ILD in AD patients. In this sense, lung vasculopathy is one of the essential processes to the development of lung fibrosis [3-4]. Accordingly, we sought to determine if E-selectin, ICAM-1, and ET-1, crucial molecules in endothelial damage, could be helpful screening biomarkers for the detection of AD-ILD+.
Methods: The study objective groups involved 21 patients with RA-ILD+ and 21 patients with SSc-ILD+. Furthermore, we included three comparative groups of patients: 25 with RA-ILD–, 20 with SSc-ILD– and 21 with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).Serum levels of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and ET-1 were determined by ELISA.
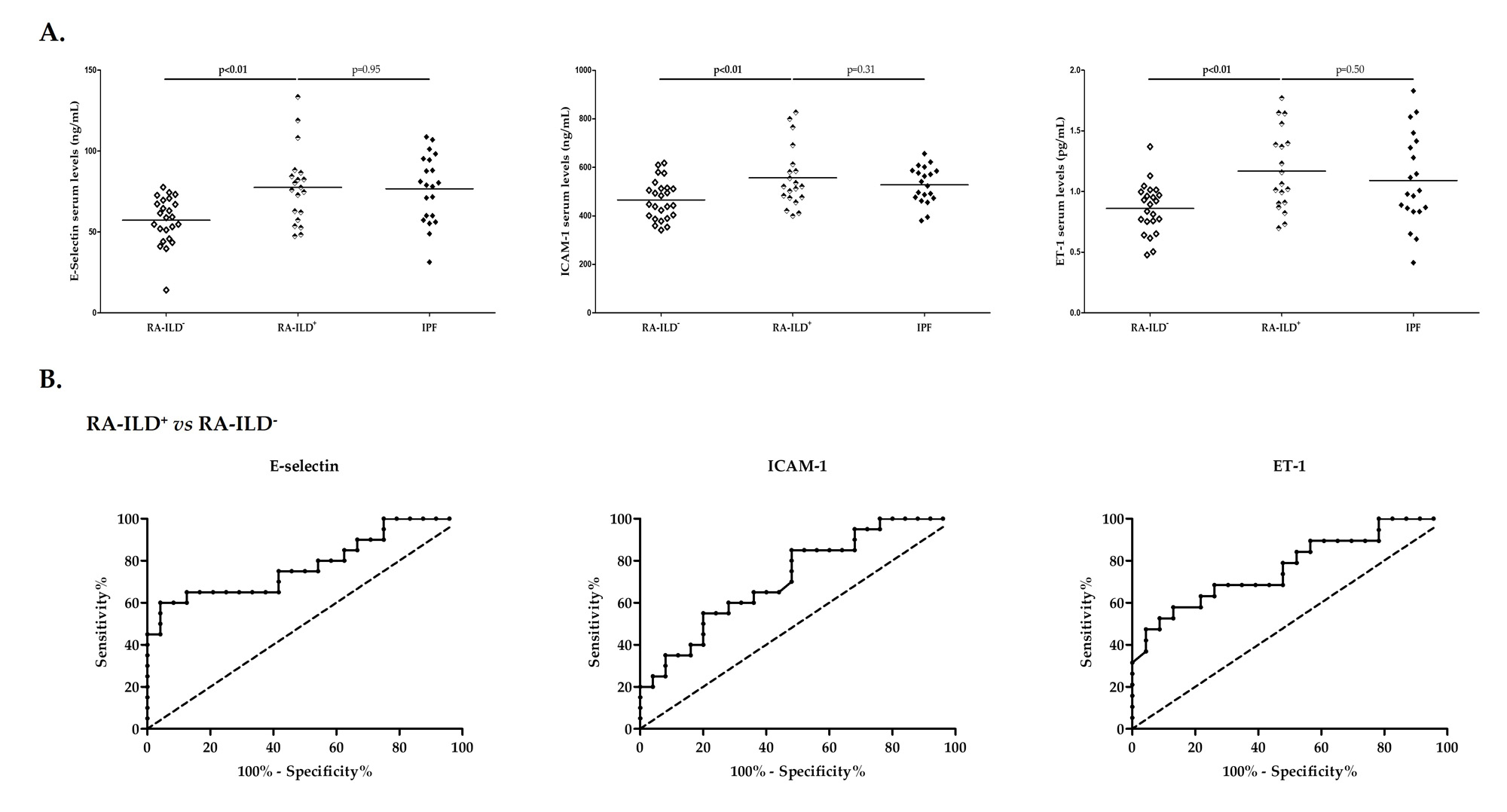
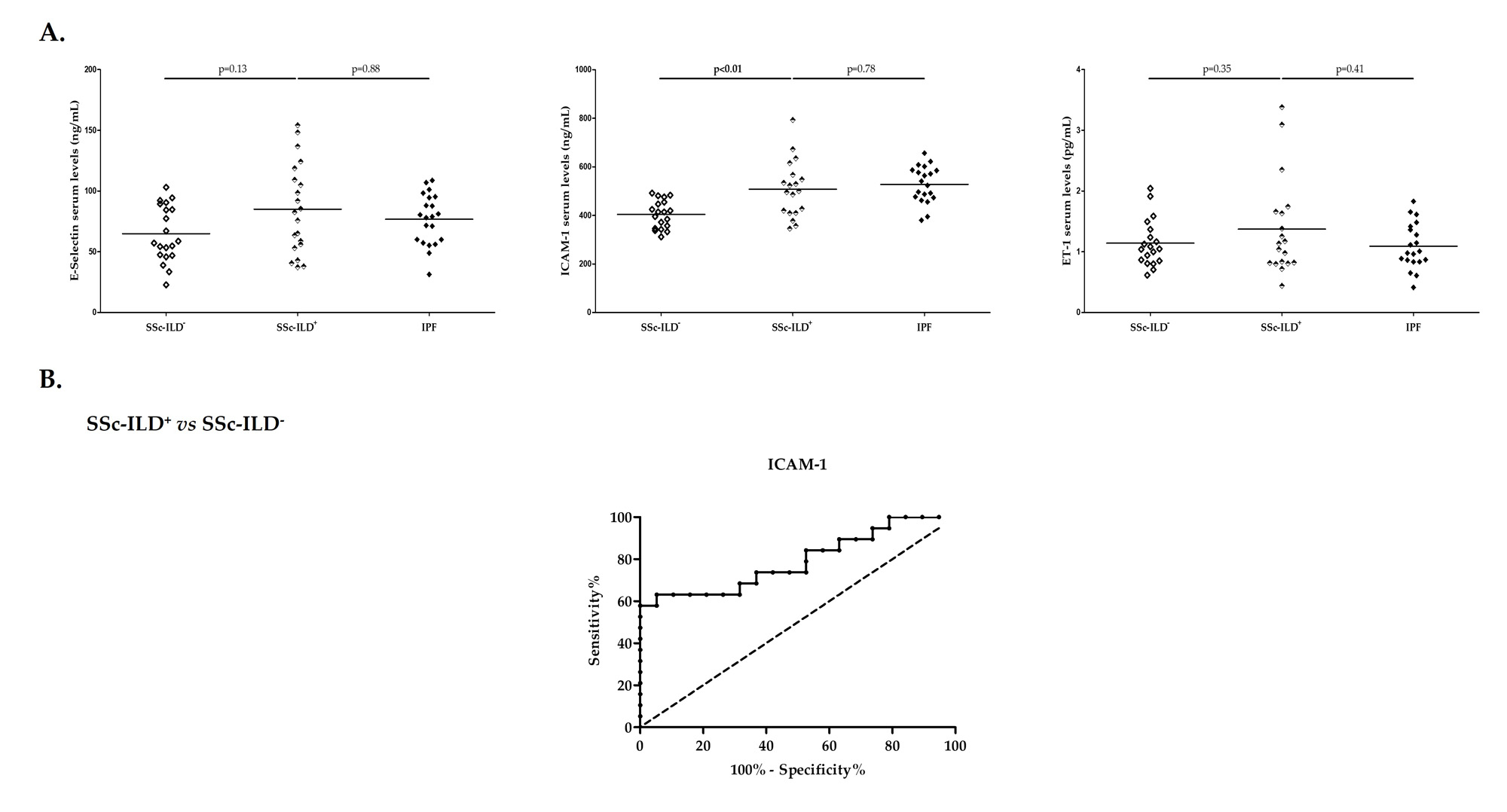
Results: RA-ILD+ patients showed increased levels of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and ET-1 compared to those with RA-ILD– (p< 0.01 in all the cases, Figure 1A). Interestingly, the ability of serum E-selectin, ICAM-1 and ET-1 levels to discriminate patients with RA-ILD+ from those with RA-ILD– were confirmed by performing ROC curves analysis (AUC: 0.78, p< 0.01; AUC: 0.72, p=0.01; AUC: 0.77, p< 0.01, respectively, Figure 1B). The optimal cutoff value for E-selectin, ICAM-1 and ET-1 revealing the best sensitivity and specificity was 74.56 ng/mL, 451.70 ng/mL and 1.02 pg/mL, respectively. Furthermore, higher ICAM-1 serum levels were found in patients with SSc-ILD+ compared to those with SSc-ILD– (p< 0.01, Figure 2A). Of note, the ROC curve supported a utility of ICAM-1 for differentiating patients with SSc-ILD+ from those with SSc-ILD– (Figure 2B). The AUC was 0.79 (p< 0.01) and the optimal cutoff value was 484.70 ng/mL (Figure 2B). Moreover, a negative correlation between ET-1 serum levels and both forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) was observed in patients with RA-ILD+ (r=-0.56, p=0.04 and r=-0.65, p=0.01, respectively). Likely, E-selectin serum levels were negatively correlated with FVC, FEV1 and diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) in patients with SSc-ILD+ (r=-0.64, p< 0.01; r=-0.56, p=0.02; and r=-0.56, p=0.02, respectively).
Conclusion: Our findings support a relevant role of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and ET-1 in RA-ILD+ as well as of ICAM-1 in SSc-ILD+, constituting potential screening blood biomarkers of subclinical ILD in AD. Moreover, this study suggests ET-1 and E-selectin as possible indicators of worsening lung function in RA-ILD+ and SSc-ILD+, respectively.
References: [1] J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 21;8(12):2038; [2] Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Mar 15;201(6):650-660; [3]Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 Feb;80(2):143-150; [4] Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2405.
Personal funds, VP-C:PI18/00042(ISCIII-ERDF); MSM-G:TRANSVAL22/01(IDIVAL); RL-M:CPII21/00004(ISCIII-ESF).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pulito-Cueto V, Remuzgo-Martinez S, Genre Romero F, Atienza-Mateo B, Mora-Cuesta V, Iturbe-Fernández D, Lera-Gómez L, Sebastián-Mora M, Portilla V, Corrales A, Blanco R, Cifrian J, Gonzalez-Gay M, López-Mejías R. E-selectin, ICAM-1 and ET-1 Biomarkers Address the Concern of the Challenging Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/e-selectin-icam-1-and-et-1-biomarkers-address-the-concern-of-the-challenging-diagnosis-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/e-selectin-icam-1-and-et-1-biomarkers-address-the-concern-of-the-challenging-diagnosis-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-autoimmune-diseases/