Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0978–1006) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Autoreactive T cells play a crucial role in the autoimmune pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Activation of inhibitory receptors on T cells is a promising strategy to suppress RA immunopathology. However, the impact of various inhibitory receptors on pathogenic T cell functions in RA remains unclear. This study aimed to define the effects of three inhibitory receptors, PD-1, BTLA, and TIGIT, on activation and function of distinct synovial CD4 T cell populations.
Methods: To evaluate inhibitory receptor effects on cytokine production, we developed an artificial antigen presenting cell (APC)–T cell co-culture system delivering inhibitory signals to T cells. We used a murine fibroblast line engineered to express CD32 (Fc receptor), CD80 (a ligand for CD28) and CD58 (a ligand for CD2). We transduced PD-L2 (ligand for PD-1), HVEM (ligand for BTLA) or CD155 (ligand for TIGIT) into the APCs and assessed their impact on cytokine production by T cells or T cell subsets from RA synovial fluid or blood or tonsil. Additionally, we generated synovial organoids containing engineered fibroblast APCs co-expressing cadherin-11 and each inhibitor receptor ligand to study their functions in a 3D context.
Results: Among T cells from RA synovial tissue, PD-1, BTLA, and TIGIT were highly expressed on Tph and Tfh cells, with intermediate expression on other diverse synovial CD4 T cell populations. To functionally assess CD4+ T cells from RA synovial fluid, we investigated the effects of inhibitory receptors on cytokine production by two populations: Tph cells (PD-1hi CXCR5-) and PD-1int CXCR5- cells. Among B cell helper cytokines produced by Tph cells, IL-21 was suppressed by PD-L2 and HVEM, while CXCL13 was suppressed by PD-L2. Analysis of inhibitory receptor function on PD-1intCXCR5- cells showed that IL-2 production was suppressed by PD-L2, HVEM and CD155, while IFN-γ and TNF production were only significantly suppressed by PD-L2. In contrast, no effect of inhibitory receptors on IL-10 production was observed in PD-1intCXCR5-. In memory CD4+ T cells from blood, PD-L2 reduced the production of TNF, CXCL13, IFN-γ, IL-21 and IL-2. HVEM suppressed TNF, IFN-γ and CXCL13, while CD155 selectively reduced CXCL13 levels. We compared these results to effects on tonsil CD4+ T cell subsets, where PD-1hi CXCR5hi cells were identified as the primary source of CXCL13, PD-1int cells showed a preference for IL-10 production, and PD-1-/low CXCR5- cells primarily secreted IL-2, IFN-γ and TNF. In this context, PD-L2 significantly suppressed the production of IL-2, TNF, IFN-γ and CXCL13 which was consistent with results using blood T cells. In the 3D synovial organoids, PD-L2 suppressed T cell proliferation and decreased the production of IFN-γ and TNF. In organoid containing of memory CD4+ T cells, B cells and cadherin-11+ APCs, PD-L2 reduced the number of T cell-B cell aggregates.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the effects of inhibitory receptors on cytokine production vary across distinct CD4⁺ T cell populations. Activation of PD-1 in particular showed strong suppressive activity in RA synovial T cells, highlighting its potential as a key modulator of pathogenic T cell responses in RA.
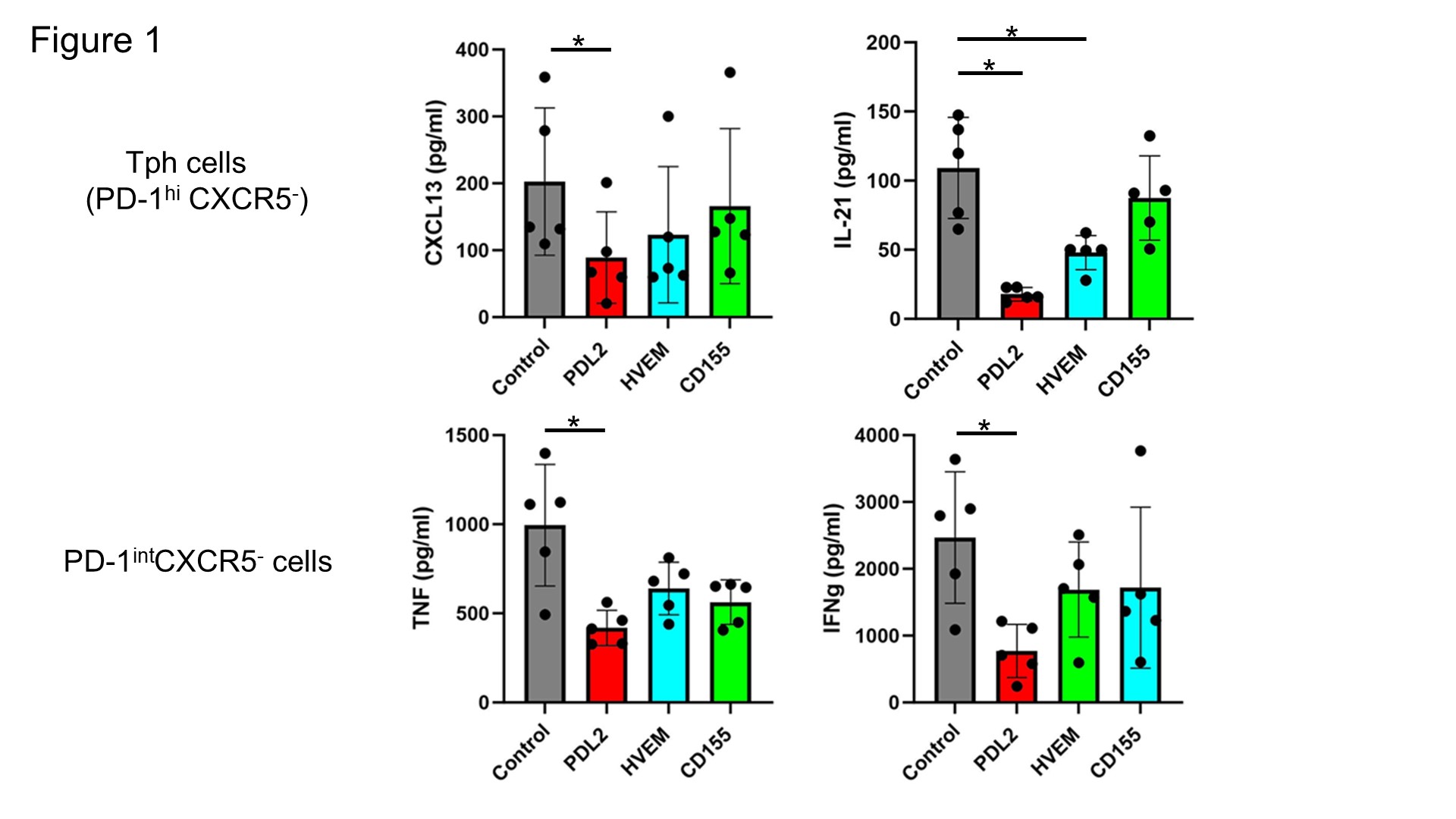 Figure 1. Effects of inhibitory receptor activation on cytokine production by synovial fluid CD4⁺ T cells.
Figure 1. Effects of inhibitory receptor activation on cytokine production by synovial fluid CD4⁺ T cells.
Cytokine production by Tph cells (CXCL13 and IL-21) and PD-1intCXCR5⁻ memory CD4+T cells (TNF and IFN-γ) from RA synovial fluid, co-cultured with APCs expressing PD-L2, HVEM, CD155, or control. Cytokine levels were measured by ELISA (n = 5 RA donors). *=P < 0.05 (Tukey’s multiple comparison test).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Higashioka K, Sowerby J, Marks K, Pena-Nunez D, Chang M, Coblyn J, Massarotti E, Jones B, Hao L, Rao N, Rao D. Distinct Effects of Inhibitory Receptor Agonism on RA Synovial CD4+ T Cell Functions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-effects-of-inhibitory-receptor-agonism-on-ra-synovial-cd4-t-cell-functions/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-effects-of-inhibitory-receptor-agonism-on-ra-synovial-cd4-t-cell-functions/
