Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
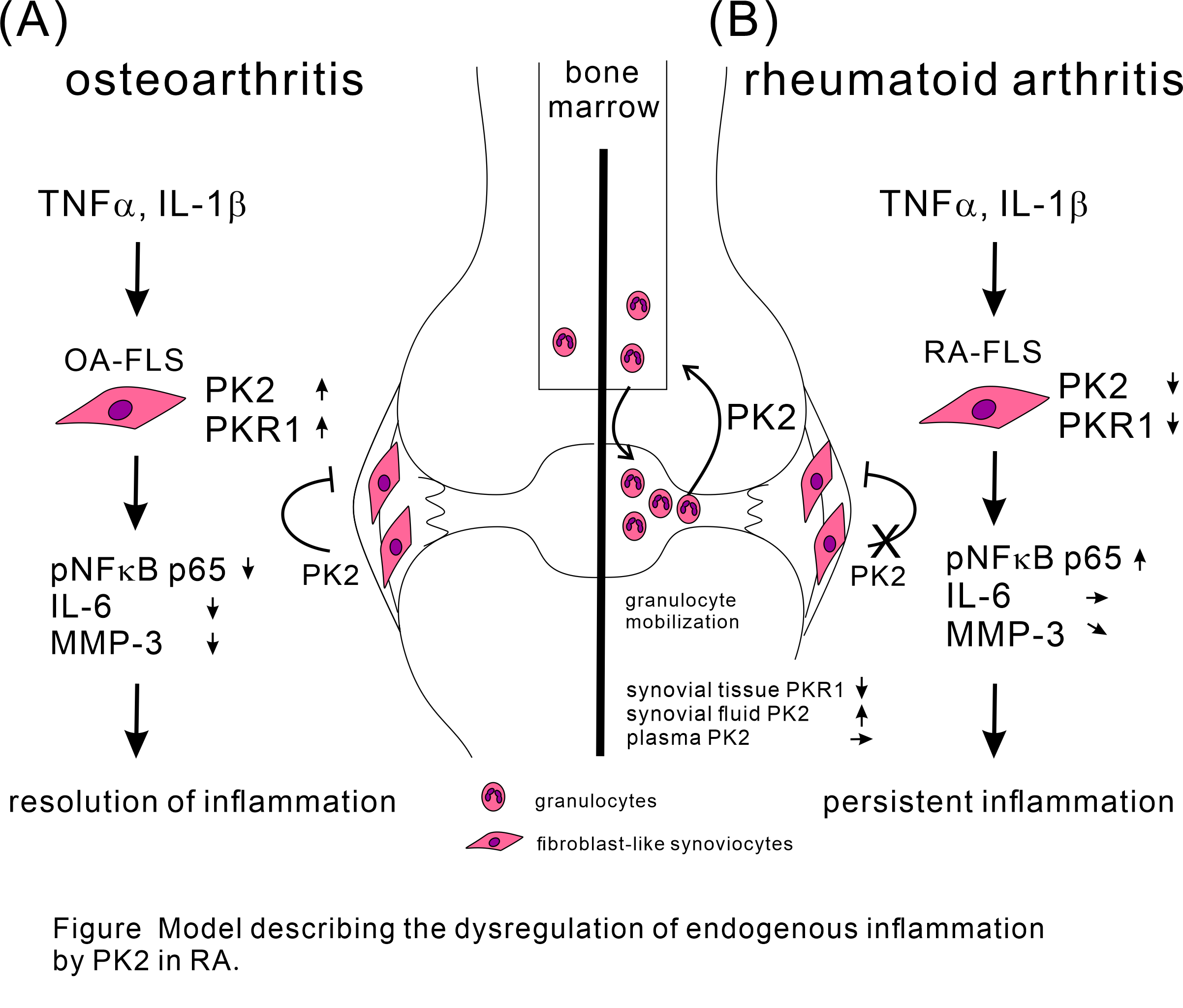
Background/Purpose: Prokineticin 2 (PK2) is a secreted protein involved in several pathological and physiological processes, including the regulation of inflammation, sickness behaviors, and the circadian rhythm. Recently, it was reported that PK2 is associated with the pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. However, whether PK2 influences the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or osteoarthritis (OA) remains unknown.
Methods: We collected synovial tissue, plasma, and synovial fluid from RA and OA patients. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were induced from synovial tissue. We examined the expressions of PK2 and its receptors prokineticin receptor (PKR) 1 and 2 in RA and OA synovial tissues and FLS using immunohistochemistry and measured the concentration of PK2 in plasma and synovial fluid using ELISA. To study the cellular expression of PK2, PKR1, and PKR2 under proinflammatory conditions, we stimulated FLS with TNFa (10 ng/ml), IL-1b (200 pg/ml), and TGFb (10 ng/ml) for 24 and 48 h and examined the expression of PK2, PKR1, and PKR2 using cell-based ELISA. Finally, we analyzed the effect of PK2 on TNFa-pretreated FLS using IL-6 and MMP-3 ELISAs.
Results: PK2, PKR1, and PKR2 were expressed in RA and OA synovial tissues. PKR1 expression in RA synovial tissue was downregulated compared with OA synovial tissue. PK2 and PKR1 were expressed in RA and OA-FLS. However, PKR2 was not expressed in FLS. PK2 expression in RA-FLS was downregulated at 24 h after stimulation with TNFa, IL-1b, and TGFb. PKR1 expression was upregulated at 48 h after stimulation with TNFa and TGFb in OA-FLS and downregulated at 48 h after stimulation with IL-1b in RA-FLS. PKR2 expression in OA- and RA-FLS was upregulated at 24 and 48 h after stimulation with TGFb and at 48 h after stimulation with TNFa in RA-FLS. The PK2 concentration was higher in RA synovial fluid than in OA synovial fluid but similar between RA and OA plasma. PK2 suppressed the production of IL-6 and MMP-3 from TNFa-prestimulated OA-FLS, and this effect was attenuated in TNFa-prestimulated RA-FLS.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that PK2, PKR1, and PKR2 were expressed in synovial tissue. This indicates that PK2 acts locally. Indeed, PK2 had an anti-inflammatory effect on OA-FLS that was likely mediated through the PKR1 pathway, whereas this anti-inflammatory effect was attenuated in RA-FLS because of PKR1 downregulation. This study provides a new model to explain some aspects regarding the chronicity of inflammation in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Noda K, Dufner B, Straub R. Differential Inflammation-mediated Function of Prokineticin 2 in the Synovial Fibroblasts of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared to Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-inflammation-mediated-function-of-prokineticin-2-in-the-synovial-fibroblasts-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-compared-to-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-inflammation-mediated-function-of-prokineticin-2-in-the-synovial-fibroblasts-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-compared-to-osteoarthritis/