Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy is a ground-breaking emerging treatment modality for severe refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and has shown early promise in other diseases.Initial clinical data demonstrate that adoptive transfer of anti-CD19 CAR T cells induce a durable long-term remission in SLE paitents.However, the mechanisms underlying remission are unclear. Our aim was to elucidate the serological factors that are associated with responses in SLE patients following treatment with anti-CD19 CAR T cells.
Methods: Sera were collected from six severe refractory SLE patients prior to and 3 months following anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy.All patients were in remission off-therapy at 3 months following adoptive T cell transfer. Sera were evaluated for 25 cytokines by electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay (MSD). Sera were also evaluated for 17 SLE-associated and 14 infectious disease-associated antibodies using a custom developed Luminex-based immunoassay.
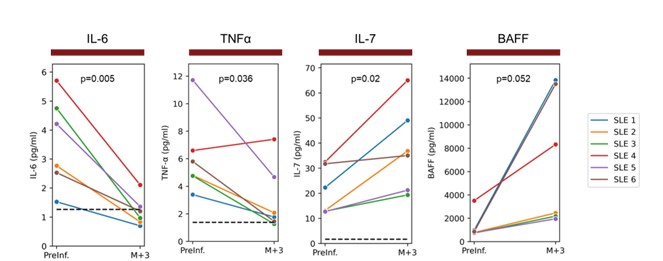
Results: Serum levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNFα were decreased in SLE patients 3 months post-anti-CD19 CAR T cell infusion relative to pre-infusion (Figure 1).Over the same period, the B cell memory and homeostatic cytokines IL-7 and BAFF increased (Figure 1).SLE associated antibodies decreased dramatically in 5 out of 6 patients following anti-CD19 CAR T cell infusion.In 1 out of 6 patients, SLE associated antibodies either remained stable or increased mildly despite resolution of clinical disease. Infectious disease associated antibodies typically remained stable or changed minimally following anti-CD19 CAR T cell infusion. Lastly, circulating CD19+ B cells were detected in all patients 3 months following anti-CD19 CAR T cell infusion.
Conclusion: We report on 6 SLE patients following anti-CD19 CAR T therapy showing sustained remission off-therapy. Serum cytokine data suggest that systemic inflammation is consistently decreased at three months post infusion. An expanded panel of SLE-associated antibodies shows a profound drop in SLE-associated antibodies observed in most patients supports the idea of an immune reset following CAR T therapy. These studies support the continued exploration of anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Basu S, Nunez D, Patel D, Volkov J, Vorndran Z, Wong S, Mackensen A, Schett G. Deep Serological Profiling of SLE Patients Treated with anti-CD19 CAR T Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-serological-profiling-of-sle-patients-treated-with-anti-cd19-car-t-cells/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-serological-profiling-of-sle-patients-treated-with-anti-cd19-car-t-cells/