Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19 may have higher risk of mechanical ventilation than those without rheumatic diseases. We compared COVID-19 lung disease between rheumatic disease patients and general population comparators using a deep learning algorithm that extracts a quantitative measure of radiographic lung disease severity.
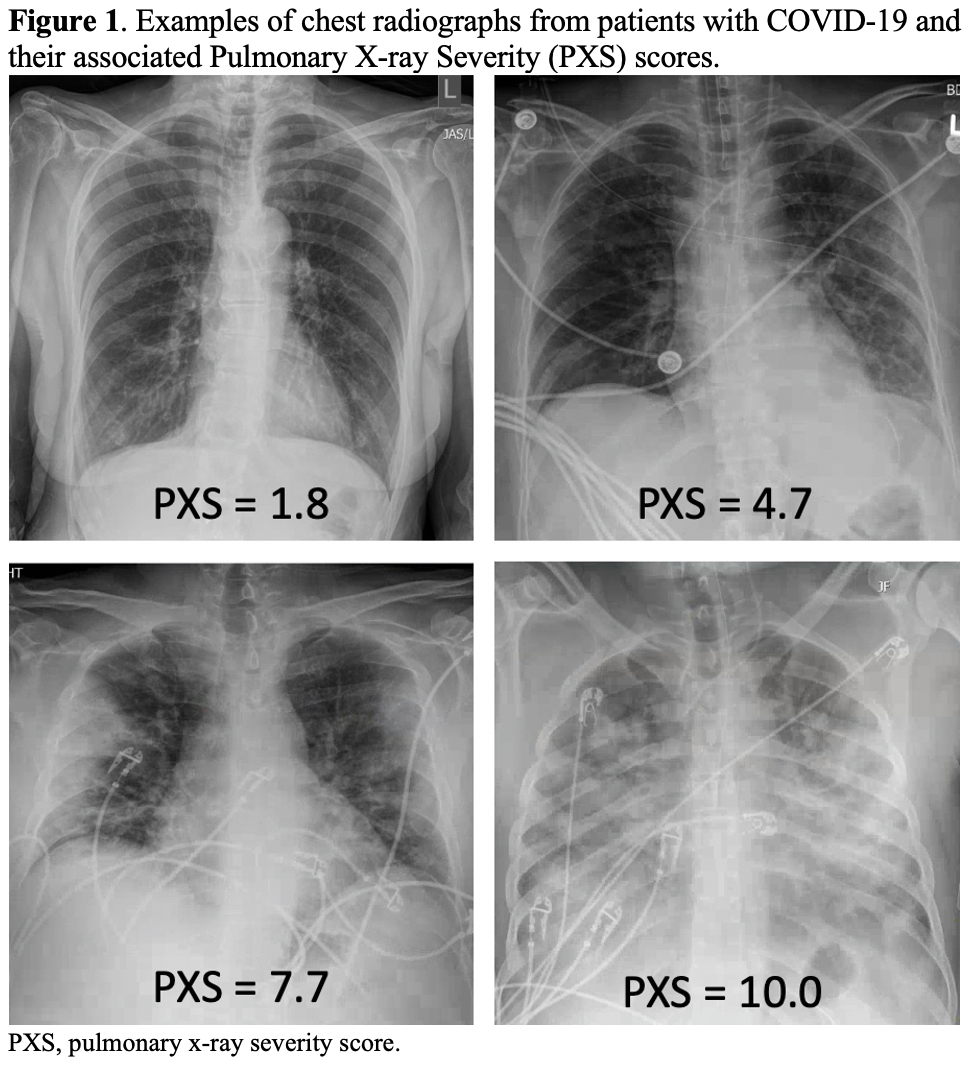
Methods: We performed a comparative cohort study of patients with rheumatic disease who had confirmed COVID-19 and at least one chest radiograph within ±2 weeks of COVID-19 diagnosis between January 31, 2020 and January 31, 2021 in a large healthcare system and comparators (matched up to 10:1 by age, sex, date of diagnosis, and chest radiograph location). Covariates and COVID-19 outcomes (mechanical ventilation and death) were extracted from a centralized data warehouse. A previously validated convolutional Siamese neural network algorithm was used to calculate the Pulmonary X-Ray Severity (PXS) score, a quantitative measure of COVID-19 lung severity. Higher scores indicate more severe pulmonary disease (Figure 1). We compared the PXS scores between rheumatic diseases cases and comparators using quantile regression at the 50th and 85th percentiles. We then evaluated the association of severe PXS score ( >9) with risk of mechanical ventilation and death among patients with rheumatic diseases using logistic regression.
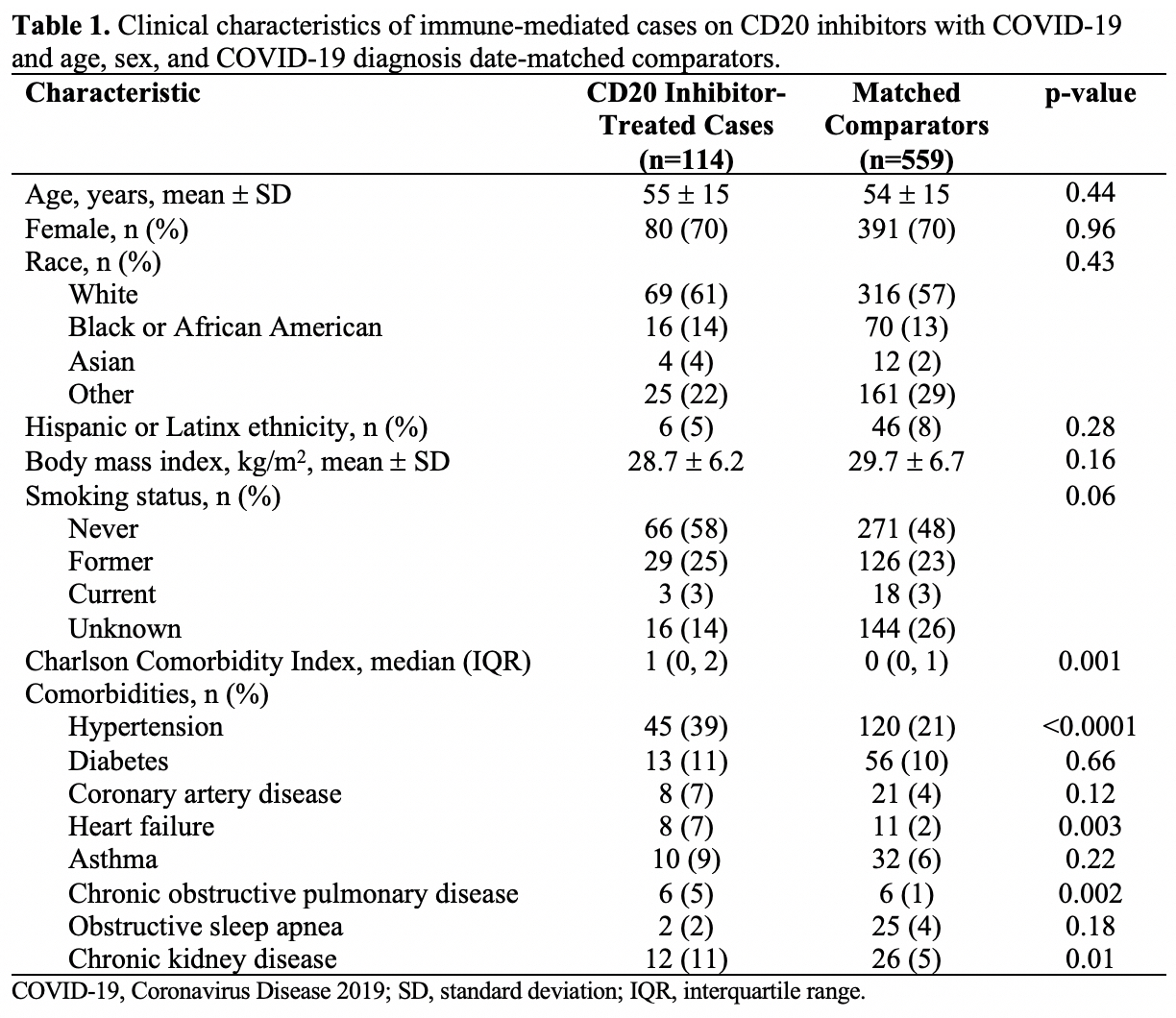
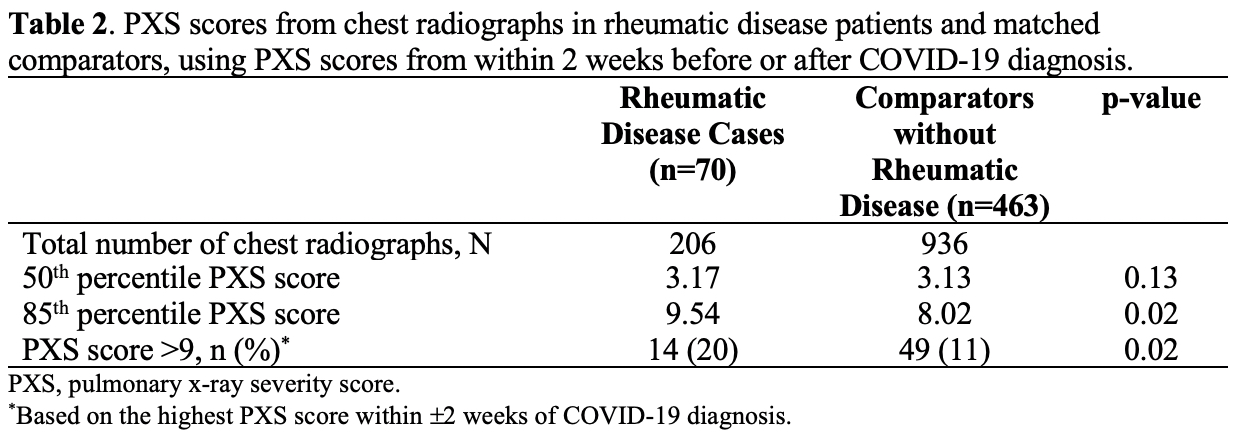
Results: We identified 70 rheumatic disease patients and 463 general population comparators. Rheumatic disease patients had more comorbidities such as hypertension (54% vs. 32%, p< 0.001), diabetes (31% vs. 15%, p< 0.001), and interstitial lung disease (6% vs. 1%, p< 0.01) (Table 1). The most common rheumatic diseases were rheumatoid arthritis (37%), other inflammatory arthritis (17%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (14%). The maximum PXS score within 2 weeks of COVID-19 diagnosis was similar in the rheumatic disease patients and comparators at the 50th percentile (3.17 vs. 3.13, respectively, p=0.10) but significantly higher among rheumatic disease patients at the 85th percentile (9.54 vs. 8.02, p=0.03) (Table 2). Rheumatic disease patients were more likely to have a maximum PXS score >9 (20% vs. 11%, p=0.02), indicating severe pulmonary disease. Among rheumatic disease patients, those with maximum PXS score >9 more frequently required mechanical ventilation (85% vs. 5%, p< 0.0001) and died (14% vs. 2%, p=0.08) compared to those with PXS score ≤9.
Conclusion: Using a previously validated deep learning algorithm, patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19 had more severe radiographic lung disease than matched comparators. Among rheumatic disease patients, more severe radiographic disease was associated with higher risk of mechanical ventilation. Future studies are needed to determine if PXS scores may help to risk-stratify patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel N, D'Silva K, Li M, Hsu T, Di Iorio M, Fu X, Cook C, Prisco L, Martin L, Vanni K, Zaccardelli A, Zhang Y, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Sparks J, Wallace Z. Deep Learning-Derived Chest Radiograph Scores in COVID-19 in Rheumatic Disease Patients versus General Population Comparators [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-learning-derived-chest-radiograph-scores-in-covid-19-in-rheumatic-disease-patients-versus-general-population-comparators/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deep-learning-derived-chest-radiograph-scores-in-covid-19-in-rheumatic-disease-patients-versus-general-population-comparators/