Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science (0807–0812)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-1:15PM
Background/Purpose: Synovitis is a common manifestation of systemic sclerosis (SSc), driving disability and predicting disease progression and mortality. Current immunosuppressive strategies, largely extrapolated from rheumatoid arthritis (RA), offer limited efficacy. A deeper understanding of the pathomechanisms underlying SSc synovitis is therefore needed to enable the development of more effective, targeted therapies.
Methods: Synovial tissue from 11 SSc patients (91% limited cutaneous SSc, excluding overlap syndromes), 7 RA patients (all anti-CCP and RF positive), and 6 non-inflammatory controls (NIC) underwent histological classification. For single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), synovium from 6 SSc, 6 RA, and 6 NIC samples was dissociated, yielding 78,128 cells (SSc: 21,248; RA: 32,062; NIC: 24,818) across nine cell types. Data were analysed using Seurat (v4.3) and integrated using Harmony and STACAS for subpopulation annotation. Bioinformatic analyses included differential expression analysis (MAST), pathway over-representation analysis (ORA), gene module scoring (MSigDB hallmark), and transcription factor activity inference (decoupleR). In vitro qPCR validation was performed on synovial fibroblasts (SF) stimulated with TNF, interferon (IFN)-α, IFN-β, and IFN-γ.
Results: Histology revealed a pauci-immune pathotype in 10/11 SSc synovial biopsies, with significantly lower Krenn scores (p=0.01) and less acute inflammation compared to RA (p< 0.01).Given the stromal predominance in SSc, we focused our analysis on SF (n= 15’502, Fig. 1A) and observed a lower expression of invasion-associated genes in PRG4⁺ lining SF (Fig. 1B), which may explain the lower frequency of radiographic erosions in SSc patients compared to RA (36% vs. 50%).Across all SF, we identified a prominent IFN-α and IFN-γ signature in SSc (both FDR< 0.05, ORA) relative to RA, where TNF response was the dominant signal (FDR< 0.001, ORA). IFN-associated genes (Fig. 1C), JAK/STAT signalling, and IFN-related transcription factors (Fig. 1D) were specifically enriched in FOSB⁺ SF in SSc. Moreover, we observed a complex expression pattern of alternative complement genes and regulators in SSc, particularly in MFAP5⁺/CXCL14⁺ SF (Fig. 1E), which was recapitulated following stimulation of SFs with IFN in vitro (Fig. 1F).Genes specifically overexpressed in SSc SF, including canonical IFN-stimulated genes and complement-related targets, overlapped largely with transcripts previously shown to be downregulated in the skin of SSc patients after Anifrolumab treatment (Fig. 1G), indicating therapeutic potential.Notably, a canonical IFN signature (Fig. 1C), marked by genes such as IRF1, MX1, IFI27, STAT1, and STAT2, was also evident across other synovial cell types in SSc compared to RA and NIC, including endothelial cells and infiltrating MERTK-/SPP1+ macrophages and S100A12+ monocytes.
Conclusion: Our findings provide the first in-depth characterisation of SSc synovitis, revealing a pauci-immune, less-invasive phenotype marked by a dominant IFN signature across SF, macrophages, monocytes and endothelial cells (Fig. 2). This tissue-wide IFN response supports IFN blockade as a promising therapeutic strategy for SSc synovitis.
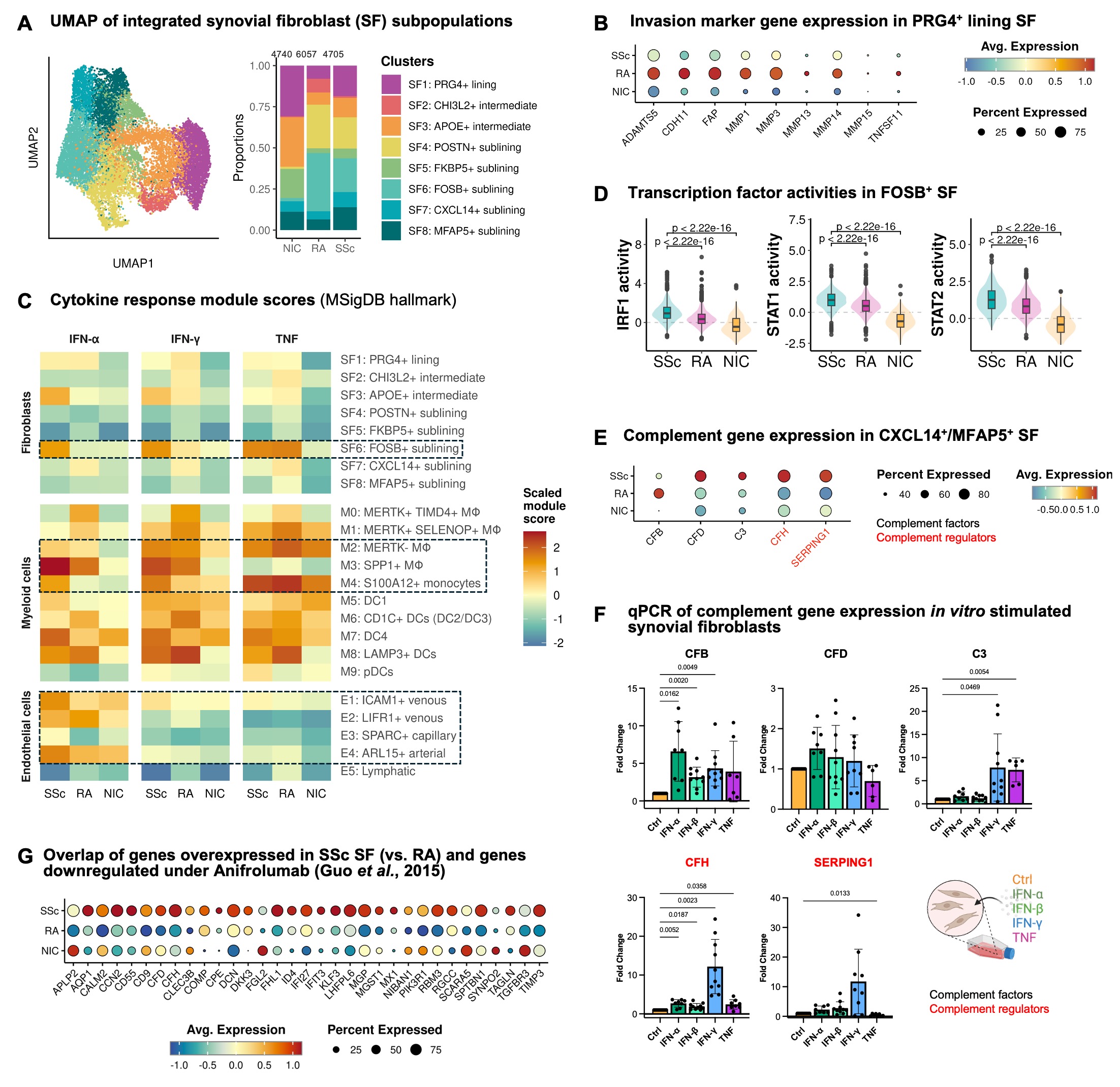 Figure 1. Overview of main results.
Figure 1. Overview of main results.
.jpg) Figure 2. Graphical abstract of proposed mechanism of SSc synovitis and RA compared to non-inflammatory controls (NIC). Created with BioRender.
Figure 2. Graphical abstract of proposed mechanism of SSc synovitis and RA compared to non-inflammatory controls (NIC). Created with BioRender.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Geiss C, Houtman M, Calvo Cebrian C, Micheroli R, Toitou M, Djeffal Y, Khmelevskaya A, Frank-Bertoncelj M, Edalat S, Rauer T, Bürki K, Pauli C, Bonelli M, Karonitsch T, Distler O, Ospelt C, Elhai M. Deciphering Synovitis in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deciphering-synovitis-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deciphering-synovitis-in-systemic-sclerosis/
