Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal domain (BET) family proteins (BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, and BRDT) control the transcription of a wide range of proinflammatory and immunoregulatory genes. BRD4 is implicated in immune-mediated diseases including Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). BRD4 inhibitors have pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects and demonstrated efficacy in animal models of RA (Wang, N., Wu, R., Tang, D. et al. The BET family in immunity and disease. Sig Transduct Target Ther 6, 23, 2021). However, non-specific BRD4 inhibition is limited by toxicity. DC-9476 is a novel selective BRD4(BD2) inhibitor generated through an Artificial Intelligence-driven drug discovery platform. Here we tested the efficacy of DC-9476 on key inflammatory arthritis related disease pathways in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: The biological activities of DC-9476 (1200, 600, 300 and 150 nM) were characterized using the BioMAP® diversity PLUS panel, containing 12 human primary cell-based systems designed to capture different aspects of inflammatory pathways. In vivo efficacy of DC-9476 was tested in the LPS intraperitoneal mouse model. DC-9476 (10, 30 and 100 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously 1 hour prior to LPS followed by analysis of IL-6, TNF-α and IL-17A serum levels by ELISA 2 hours post-LPS. The effects of DC-9476 on chronic inflammatory RA were tested in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. At the onset of arthritis, mice were treated with DC-9476 (p.o., 15, 50 or 150 mg/kg, BD), Etanercept (i.p., 10 mg/kg, QD) or Tofacitinib (p.o., 25 mg/kg, BD). Arthritis score and paw thickness were assessed until day 49. In another CIA study, the effects of DC-9476 (s.c., 100 mg/kg, BD) were compared to those of anti-mouse IL-6 antibody (i.p., 200 μg/mouse, BIW).
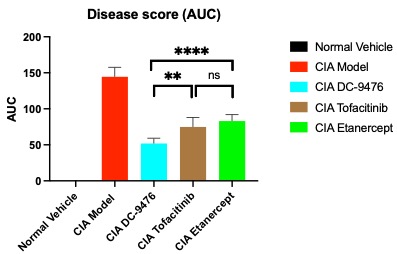
Results: In the BioMAP® Diversity PLUS Panel analysis, DC-9476 reduced levels of proinflammatory factors, particularly IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-6 and secreted IgG in a dose dependent manner, without evidence of cytotoxicity. DC-9476 demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in the LPS mouse model, reducing serum levels of IL-6, TNF-α and IL-17A compared to control (p-values: TNF-α ≤ 0.05 for 10 mg/kg; TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-17A ≤ 0.0001 for 30 and 100 mg/kg). In the CIA model, oral treatment with DC-9476 led to dose-dependent reduction of arthritis score and paw thickness without hematological or other toxicities across a tenfold dose range. Of interest, 150 mg/kg DC-9476 demonstrated significantly better reduction of arthritis scores compared to Etanercept and Tofacitinib (Figure 1). Moreover, DC-9476 was better in reducing arthritis scores than anti-mIL-6 antibody.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that the selectivity for a single BET protein and bromodomain of DC-9476 resulted in favourable anti-inflammatory effects in murine RA models and reduced BET inhibitor-related toxicities. These data indicate that DC-9476 could be a novel class of BET inhibitor for treating RA and warrants the assessment of DC-9476 in ex vivo models derived from active RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Segal Salto M, Ross R, Ferrara S, Chan K, haimov E, Del Galdo F, Mankia K. DC-9476, a Novel Selective BRD4(BD2) Inhibitor, Improves Arthritis Scores in Preclinical Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating Key Inflammatory Pathways [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dc-9476-a-novel-selective-brd4bd2-inhibitor-improves-arthritis-scores-in-preclinical-models-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-by-regulating-key-inflammatory-pathways/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dc-9476-a-novel-selective-brd4bd2-inhibitor-improves-arthritis-scores-in-preclinical-models-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-by-regulating-key-inflammatory-pathways/