Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There has been a surging interest in characterizing subpopulations of osteoarthritis (OA) to facilitate recruitment of the right subgroups for drug development. The APPROACH consortium discovered three biomarker-based endotypes driven by i) structural damage to bone and cartilage, ii) connective tissue inflammation, and iii) low tissue turnover in 295 knee OA (KOA) participants at baseline. There is a need to gain a deeper understanding of the endotypes of OA to unveil the clinically actionable potential of such patient subgroups. The purpose of this study was to further characterize the three endotype subgroups through cytokine-profiling.
Methods: 277 participants from APPROACH fulfilling the ACR criteria for KOA were included. The three endotypes of structural damage, inflammation, and low tissue turnover previously defined by 19 serum and urine biomarkers reflecting bone and cartilage turnover and inflammation were considered at the month six, 12, and 24 visits. 24 cytokines were measured with Luminex Multiplex Immunoassays. Cytokines with ≤ 50% missing values were considered, resulting in 15 included markers. Cytokine levels were log-transformed, trimmed for extreme outliers (Winsor’s and Tukey’s rule), and sex-specific z-score scaling was performed. Cytokine-profiles of each endotype and visit were visualized using min-max normalized median concentrations. Percent changes in geometric mean cytokine concentrations between the endotypes were computed with linear mixed-effects models (LMMs), adjusting for age, sex, and BMI based on non-z-score scaled, log-transformed cytokine levels. P-values were Benjamini-Hochberg-adjusted for multiple testing. Intra-class correlations (ICCs) of the cytokines levels over time were estimated.
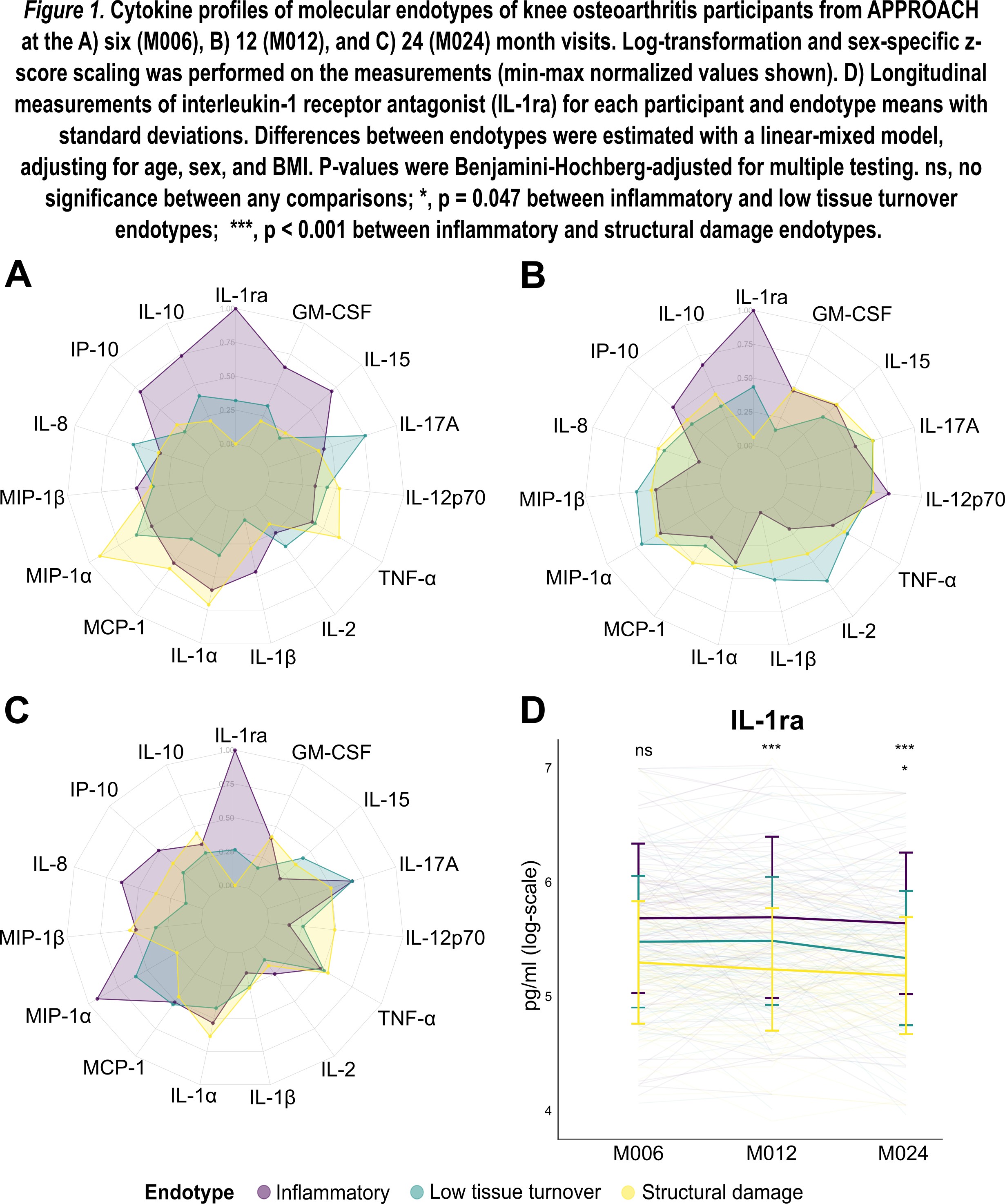
Results: Cytokine-profiling across the visits of the KOA endotypes revealed fluctuating longitudinal cytokine expression patterns (Fig. 1A-C). 8/15 cytokines exhibited good longitudinal stability (ICC > 0.75), with the highest ICCs achieved for MCP-1 of 0.89 (95% CI: 0.87, 0.91) and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) of 0.88 (95% CI: 0.85, 0.90). IL-1ra was the only cytokine with differential levels between the endotypes (Fig. 1D). At month 12, a mean change of IL-1ra of 36% (95% CI: 19%, 54%; p-value < 0.001) was found for the inflammatory endotype relative to structural damage, while it was 40% (95% CI: 22%, 59%; p-value < 0.001) at month 24. At month 24, a mean change of IL-1ra of 21% (95% CI: 10%, 31%; p-value = 0.047) was found for the inflammatory endotype relative to low tissue turnover.
Conclusion: This study further characterized the three KOA by an independent modality from which the endotypes were originally defined. We showed that the cytokine panel was associated with longitudinal fluctuations across the endotype subgroups but found that IL-1ra was persistently and differentially associated with the inflammatory endotype. These results may indicate an intriguing pathobiological involvement of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1ra in OA subgroups driven by an inflammatory molecular endotype.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
T. Hannani M, Bacardit J, Larkin J, Glumoff V, A. Karsdal M, Bay-Jensen A, Mobasheri A, Thudium C. Cytokine Profiling of Molecular Endotypes of Knee Osteoarthritis: Insights from the IMI-APPROACH cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cytokine-profiling-of-molecular-endotypes-of-knee-osteoarthritis-insights-from-the-imi-approach-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cytokine-profiling-of-molecular-endotypes-of-knee-osteoarthritis-insights-from-the-imi-approach-cohort/