Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0897–0915) B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Fc receptors mediate the effector functions of antibodies by linking adaptive and innate immunity. Immunoglobulin G (IgG), the most abundant antibody in circulation and widely used in clinical therapeutics, interacts with a range of Fc gamma (Fcγ) receptors expressed in a cell type–specific manner. However, a systematic understanding of Fcγ receptor and neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) expression across species and immune subsets is incomplete, limiting translational insights from preclinical models. This study aimed to create a comprehensive atlas of Fcγ receptor and FcRn expression across species and identify regulatory factors governing their expression. In parallel, we sought to address species-specific limitations by developing a humanized mouse model for improved antibody evaluation.
Methods: We profiled Fcγ receptor and FcRn expression in humans, cynomolgus macaques, and mice using multimodal approaches including flow cytometry, single-cell RNA sequencing, and integration of chromatin accessibility and transcriptional regulatory data. Gene regulatory networks were inferred using NicheNet, SCENIC+, ChIP-seq, and perturbation experiments to predict transcription factor (TF) influences. To overcome limitations of current preclinical models, we engineered knock-in mice in which five key human Fcγ receptors as well as FcRn are expressed under control of their endogenous human promoters.
Results: Our cross-species comparison revealed marked differences in Fcγ receptor diversity, abundance, and cell type–specific expression, with especially poor conservation in myeloid and granulocyte subsets. Regulatory network analysis uncovered distinct TF programs controlling Fcγ receptor expression across species. The novel humanized FcγR/FcRn mouse model demonstrated physiologic expression of human Fcγ receptors in the appropriate immune and non-immune subsets. Functional validation showed that these receptors mediate canonical Fc-dependent processes, including antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, antigen presentation, anaphylaxis, and antibody pharmacokinetics. Cytokine stimulation further revealed plasticity in receptor expression, mirroring human immune dynamics.
Conclusion: This study provides a reference atlas of Fcγ receptor and FcRn biology across species and introduces a novel, functionally validated humanized mouse model. Together, these resources will aid mechanistic studies and improve the preclinical assessment of antibody-based therapeutics.
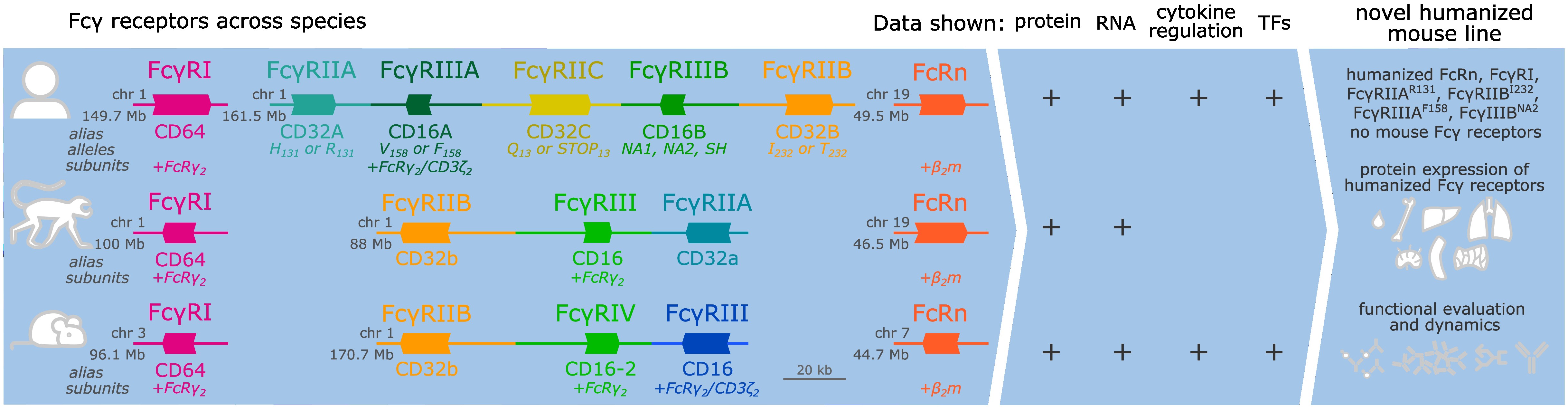 Fcγ receptors across species, their genomic mapping, and the characterization of a novel mouse model with humanized Fcγ receptors.
Fcγ receptors across species, their genomic mapping, and the characterization of a novel mouse model with humanized Fcγ receptors.
.jpg) Protein expression profiles of Fcγ receptors in humans, macaques, mice and humanized mice.
Protein expression profiles of Fcγ receptors in humans, macaques, mice and humanized mice.
.jpg) Fcγ receptors protein and RNA expression, with upstream cytokines and gene regulatory factors across species.
Fcγ receptors protein and RNA expression, with upstream cytokines and gene regulatory factors across species.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Van Damme K, Sichien D, Van der Borght K, Van Gassen S, De Leeuw E, Bosteels V, Jorssen J, De Winter S, Korman A, Benigni F, Corti D, Morel A, Vivier E, Hammad H, Elewaut D, Sonego F, Thiam K, Voet S, Balbino b, Lambrecht B. Cross-Species Cellular Mapping and Humanization of Fcγ Receptors to Advance Antibody Modeling [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cross-species-cellular-mapping-and-humanization-of-fc%ce%b3-receptors-to-advance-antibody-modeling/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cross-species-cellular-mapping-and-humanization-of-fc%ce%b3-receptors-to-advance-antibody-modeling/
