Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by chronic inflammation leading to damage of the vascular endothelium and excessive collagen deposition in several target organs. The interaction of interleukin 2 (IL-2) with the corresponding receptor (IL-2R) is involved in the regulation of autoimmune processes. The shedding product of the IL-2R alpha chain, soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R, CD25), can either reduce or enhance immune responses. Previously, elevated serum levels of sIL-2R were found in the bronchoalveolar lavage of SSc patients with and without interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) as well as serologically in patients with early SSc, and thus suggested to be a biomarker for clinical development in SSc. Furthermore, the presence of idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IMM) seems to play a role since SSc-IMM overlap patients have shown higher markers of inflammation and more frequent organ manifestations.
Methods: To determine if serological levels of sIL-2R could serve as predictor of clinical complications in SSc, sera were analysed [limited cutaneous SSc (lcSSc) n=160; diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc), n=137] using a sandwich ELISA. Clinical data (pulmonary fibrosis, PAH, mRSS, cardiac involvement, therapy) and serological markers (hs-CRP, NT-proBNP, neutrophil counts, creatine kinase, hs-troponin T, beta2-microglobulin) were assessed at the time of serum sampling and up to 48 months after baseline. Clinical progress was defined by the need to change therapies.
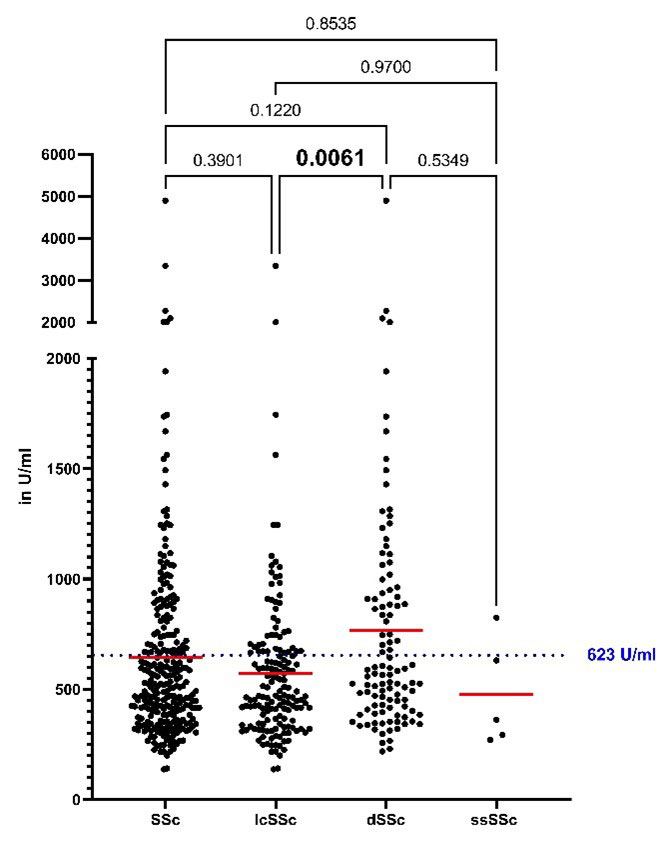
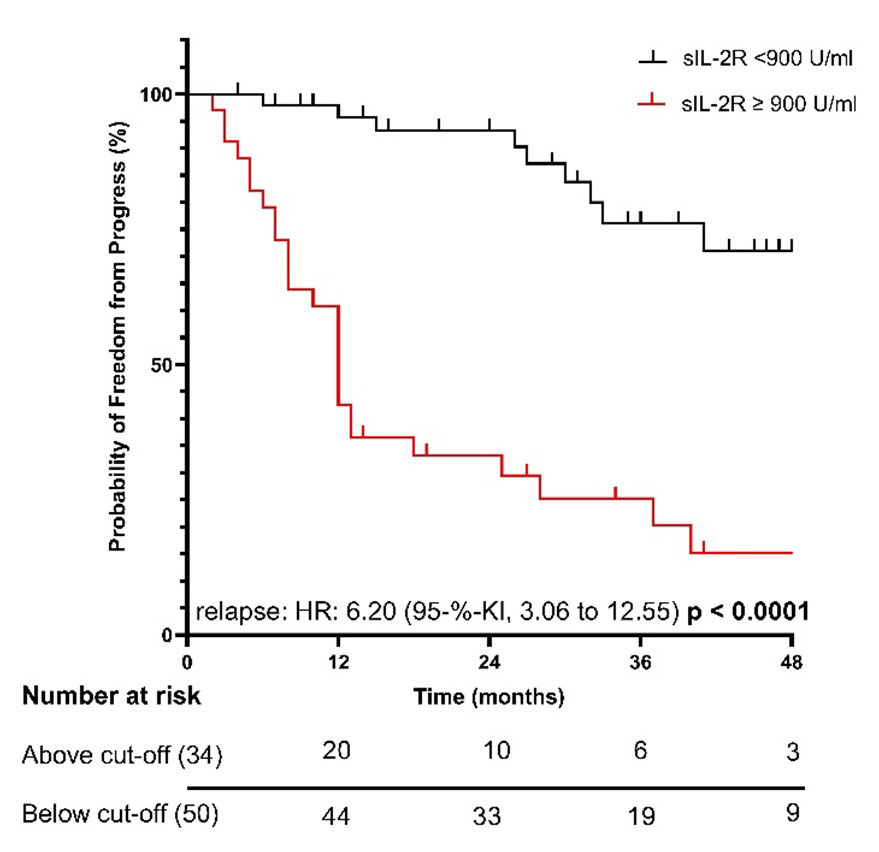
Results: Patients with dcSSc presented elevated levels of sIL-2R compared to all SSc (dcSSc: 765±593 U/ml vs. 646±473 U/ml, p=0.0001; Fig.1). In SSc general, sIL-2R levels correlated with beta2-microglobulin (r=0.6161, p< 0.0001, ROC-AUC:0.8428), hs-CRP (r=0.4091, p< 0.0001, ROC-AUC:0.7110), NT-proBNP (r=0.2610, p< 0.0001, ROC-AUC:0.6793), neutrophiles (r=0.2749, p< 0.0001) and hs-troponin T (r=0.4548, p< 0.0001, ROC-AUC:0.8729). Further, sIL-2R levels discriminated normal from pathological levels of hs-troponin T (sensitivity 80.0%, specificity 80.1%), these results being even more significant in patients without myositis (ROC-AUC: 0.9111; sensitivity 81.82.0%, specificity 87.85%). Using Log-rank test and Mantel-Cox proportional hazard models, we found that sIL-2R levels above 900 U/ml predicted early clinical progress in SSc within 12 months which had led to therapy escalation (HR:6.20, p< 0.0001; Fig. 2).
Conclusion: In SSc, serum levels of sIL-2R could be of diagnostic value by identifying clinical progress. Its role in pathophysiology, especially regarding disease manifestations such as cardiac involvement needs to be further investigated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schumacher L, Klapa S, Mueller A, Riemekasten G. Correlations of Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Serum Levels with Markers of Inflammation and Pathological High-sensitivity Troponin T and Its Possible Role as a Predictor of Early Clinical Progress in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlations-of-soluble-interleukin-2-receptor-serum-levels-with-markers-of-inflammation-and-pathological-high-sensitivity-troponin-t-and-its-possible-role-as-a-predictor-of-early-clinical-progress-in/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlations-of-soluble-interleukin-2-receptor-serum-levels-with-markers-of-inflammation-and-pathological-high-sensitivity-troponin-t-and-its-possible-role-as-a-predictor-of-early-clinical-progress-in/