Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: First-line treatment for cutaneous lupus erythematosus involves the use of antimalarials. Treatment response is highly variable with some patients responding well to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), some necessitating the addition of quinacrine (QC) and others refractory to treatment from both (NR). Here we compared the immune infiltrate composition of CLE skin between 3 different treatment response groups with imaging mass cytometry. We then used correlation matrices to highlight the differences in pathway heterogeneity between each of the groups. We also employed unsupervised learning to visualize the distinct cell-dominant subtypes in each of the groups.
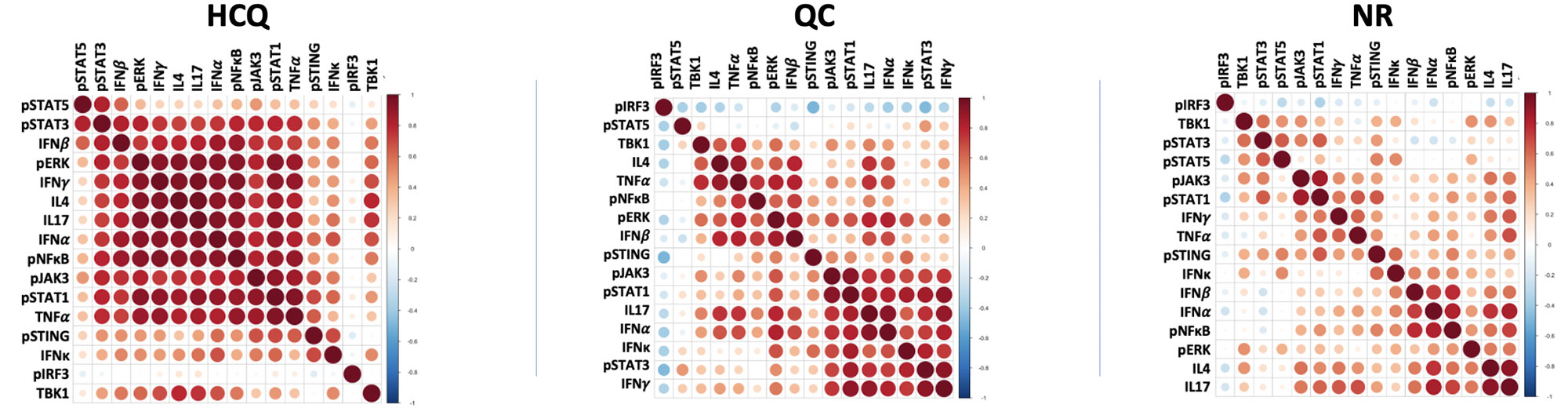
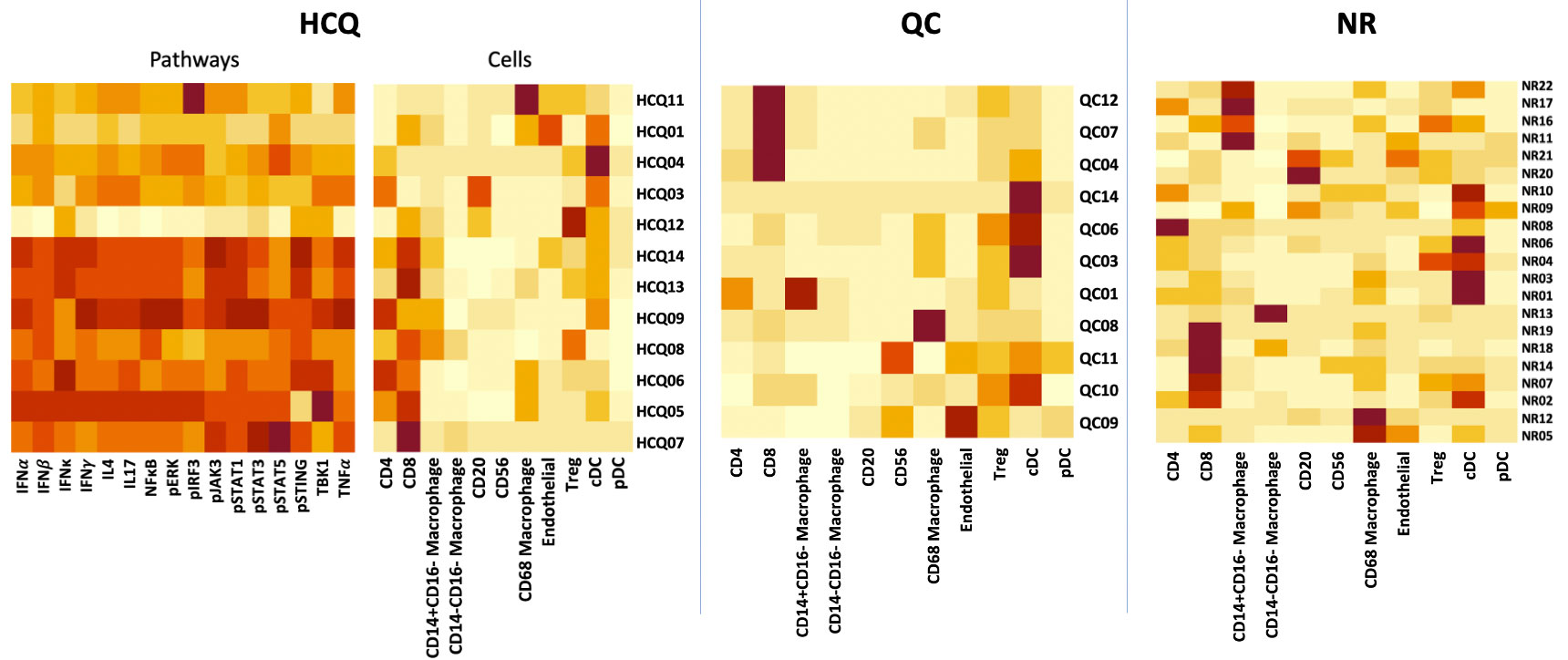
Methods: Infiltrate composition of CLE skin biopsies were characterized using imaging mass cytometry, where we stained biopsies (12 HCQ, 11 QC, 20 NR) with two separate panels of 37-metal conjugated antibodies, which enabled the measurement of different cell types, cytokines and pathway proteins within the tissue sample. Correlation matrices of cytokines/pathways with superimposed hierarchical clustering were constructed for each of the three treatment groups to visualize correlation strength for all markers simultaneously. Cell measurements were scaled within each cell type and then subjected to K-means clustering. Results of cell clustering were visualized using horizontally scaled heat maps, which demonstrated cellular predominance within each patient’s biopsy.
Results: Correlation matrices revealed a single large correlation cluster in HCQ, two medium clusters in QC and many clusters in NR. This indicates relatively homogenous cytokine/pathway activity in HCQ, two separate mechanisms in QC and significant heterogeneity in NR. Cell clustering heatmaps demonstrated heavy CD4/CD8 dominance in HCQ, two noteworthy QC subgroups, one being dominated by CD8 cells (61% vs. 7%, p=0.1) and the other by cDC (62% vs. 15%, p=0.1), and three noteworthy NR subgroups being CD8-dominant (48% vs. 9%, p< 0.00001), cDC-dominant (38% vs. 10%, p< 0.001) and CD14+CD16+ dominant (45% vs. 4%, p< 0.00001). Furthermore, CD4/CD8 dominance in HCQ appeared to be positively associated with general increased levels of pathways.
Conclusion:
HCQ responsive patients may share a common origin for pathway activity whereas QC patients potentially possess 2 separate mechanisms responsive to quinacrine therapy. NR patients showed substantial heterogeneity, which implies multiple possible origins of pathway activity thus supporting the need for personalized therapy. In terms of cells, tandem CD4/CD8 presence could potentially be used as a predictor for hydroxychloroquine-responsiveness. In QC and NR subgroups, most patients displayed single cell type predominance, most notably cDC and CD8, which suggests potential utility for personalized medicine in targeting single cell types.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chin F, Vazquez T, Dan J, Diaz D, Sprow G, Patel J, Kodali N, Feng R, Werth V. Correlation Matrices Visualize Differential Degree of Cell and Pathway Heterogeneity in Skin of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Treatment Subgroups [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-matrices-visualize-differential-degree-of-cell-and-pathway-heterogeneity-in-skin-of-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-treatment-subgroups/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-matrices-visualize-differential-degree-of-cell-and-pathway-heterogeneity-in-skin-of-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-treatment-subgroups/