Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II (1364–1390)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe vascular complication of systemic sclerosis (SSc) and a major cause of mortality. Despite significant advances in the treatment of PAH, the pathogenesis of SSc-PAH is not well understood. Our previous work has shown that serum levels of complement factor D (fD, adipsin), a critical regulator of complement alternative pathway (AP) activation and amplification loop engagement, is associated with limited cutaneous SSc and SSc-PAH. Here we assessed the levels of complement cascade proteins utilizing a well-characterized cohort of SSc-PAH to investigate the possible role of complement components as biomarkers for disease development and progression.
Methods: We evaluated 156 SSc-PAH patients from the PAH Biobank (www.pahbiobank.org), 33 SSc without PAH, 27 patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and 40 healthy controls. Patients with interstitial lung disease were excluded from the SSc-PAH group. Plasma levels of complement components (C1q, C2, C3, C4, C5, fB, fD, fI, fH, Properdin and Mannose binding lectin) were assessed by Luminex at Exsera Biolabs, a CAP/CLIA certified laboratory. Associations between complement levels and clinical data in SSc-PAH (including NYHA functional status, 6-minute walk test, and hemodynamic data) were assessed and were corrected for age, sex, race, disease duration, obesity, smoking and scleroderma subtype. ANOVA was used to determine differences between serum complement levels across groups. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to characterize associations.
Results: Four out of 11 complement components (fD, C1q, C3, C5) were significantly dysregulated in SSc-PAH patients compared to healthy controls (p< 0.0001). Logistic regression analysis using these eleven markers revealed that C3, C5, fB and fH were able to distinguish SSc-PAH from all of the control groups. When comparing SSc-PAH to SSc without PAH, we found that fD, C2, C3, C4 and C5 were markedly and specifically elevated in SSc-PAH. Within the SSc-PAH cohort, a number of complement factors were significantly associated with markers of disease severity including VO2 (fH OR=1.03, p=0.02 and C3 OR=0.982, p=0.01), NYHA functional status (fB OR=1.063 p< 0.001, fH OR=0.964 p=0.03, fI OR=0.699 p=0.001, C2 OR=0.786 p=0.001), right atrial pressure (fD OR=0.320, p=0.001 and MBL OR=3.593, p=0.01), cardiac index (fH OR=1.048, p=0.008), cardiac output (fH OR=0.028, p< 0.0001) and mortality at follow-up (fH OR=0.975, p=0.014).
Conclusion: Factor D and other complement components are significantly altered in patients with SSc-PAH compared to controls. Factor H demonstrates potential utility as a marker of severity across multiple outcomes. These findings suggest that the alternative complement cascade plays a critical role in SSc-PAH pathogenesis and can potentially serve as a biomarker to inform diagnosis and prognosis.
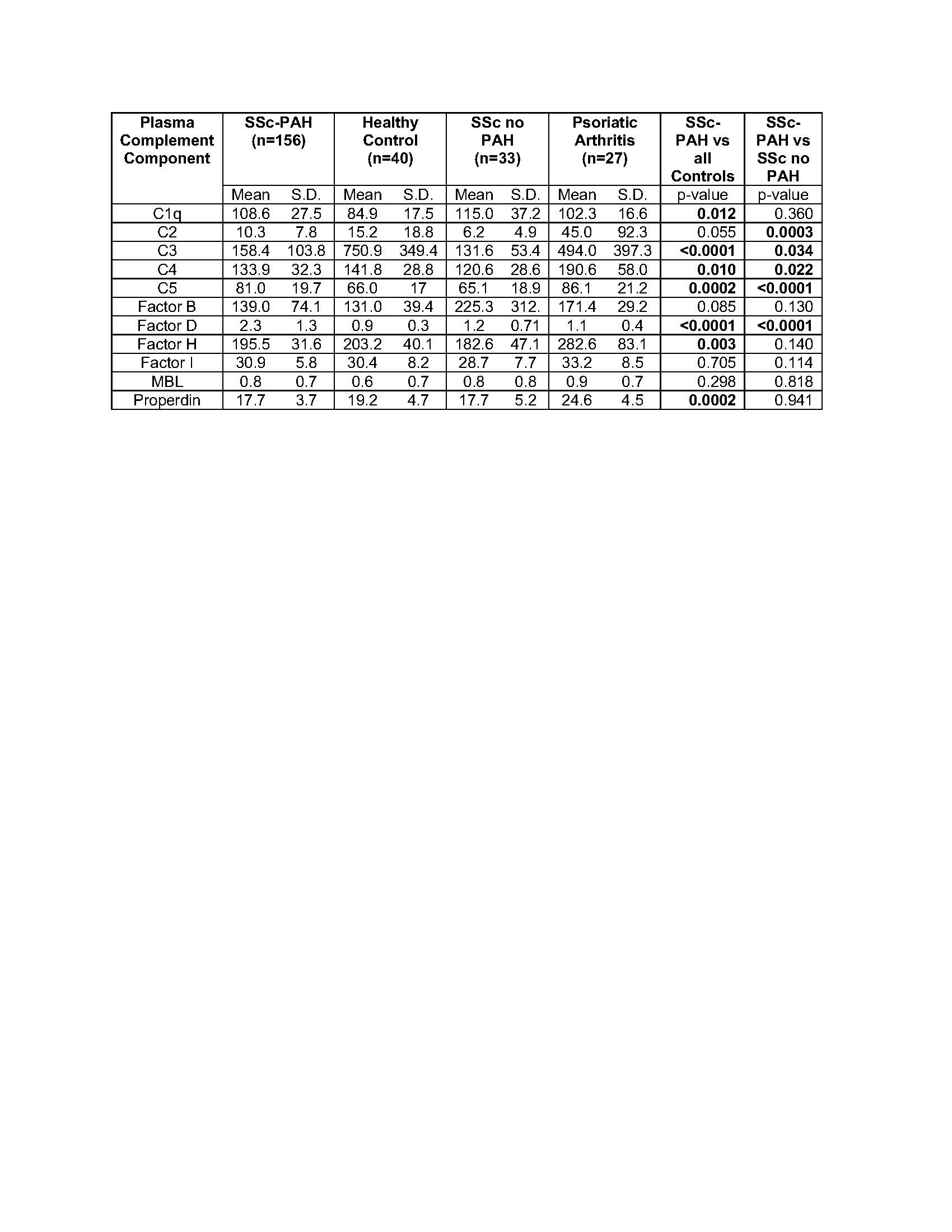 Table 1. Plasma levels of 11 complement components in SSc-PAH, SSc patients without PAH, healthy controls and patients with psoriatic arthritis are represented as mean and standard deviation (S.D.). Comparisons of all SSc-PAH (n= 156) vs all controls (n=100) and SSc-PAH vs SSc without PAH are shown with corresponding ANOVA p-value.
Table 1. Plasma levels of 11 complement components in SSc-PAH, SSc patients without PAH, healthy controls and patients with psoriatic arthritis are represented as mean and standard deviation (S.D.). Comparisons of all SSc-PAH (n= 156) vs all controls (n=100) and SSc-PAH vs SSc without PAH are shown with corresponding ANOVA p-value.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marangoni R, Feng C, Frazer-Abel A, Tomlinson S, Wielgosz A, Lutz K, Pauciulo M, Nichols W, Holers V, Ritchlin C, White III R, Korman B. Complement Factor D and Factor H Represent Disease and Severity Biomarkers for Systemic Sclerosis Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (SSc-PAH) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-factor-d-and-factor-h-represent-disease-and-severity-biomarkers-for-systemic-sclerosis-associated-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-ssc-pah/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-factor-d-and-factor-h-represent-disease-and-severity-biomarkers-for-systemic-sclerosis-associated-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-ssc-pah/
