Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II (1565–1583)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The diagnostic gold standard for gout remains aspiration and identification of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals under polarised light microscopy. Joint aspiration is invasive and in certain patients may not be possible. The 2015 gout classification criteria include imaging evidence of urate deposition in the diagnostic criteria. The imaging modalities with sufficient published data and investigator experience to support their utility in identifying urate deposition accurately were ultrasound (US) and dual energy computed tomography (DECT). Despite the fact that US and DECT are both candidates to quantify urate deposition and monitor urate depletion, it is still unknown whether these techniques provide similar quantification of the extent of urate deposition in a given patient.
The aim of the study was to compare the quantification of urate deposition by US and DECT in a group of patients with gout and asymptomatic hyperuricaemia (AH).
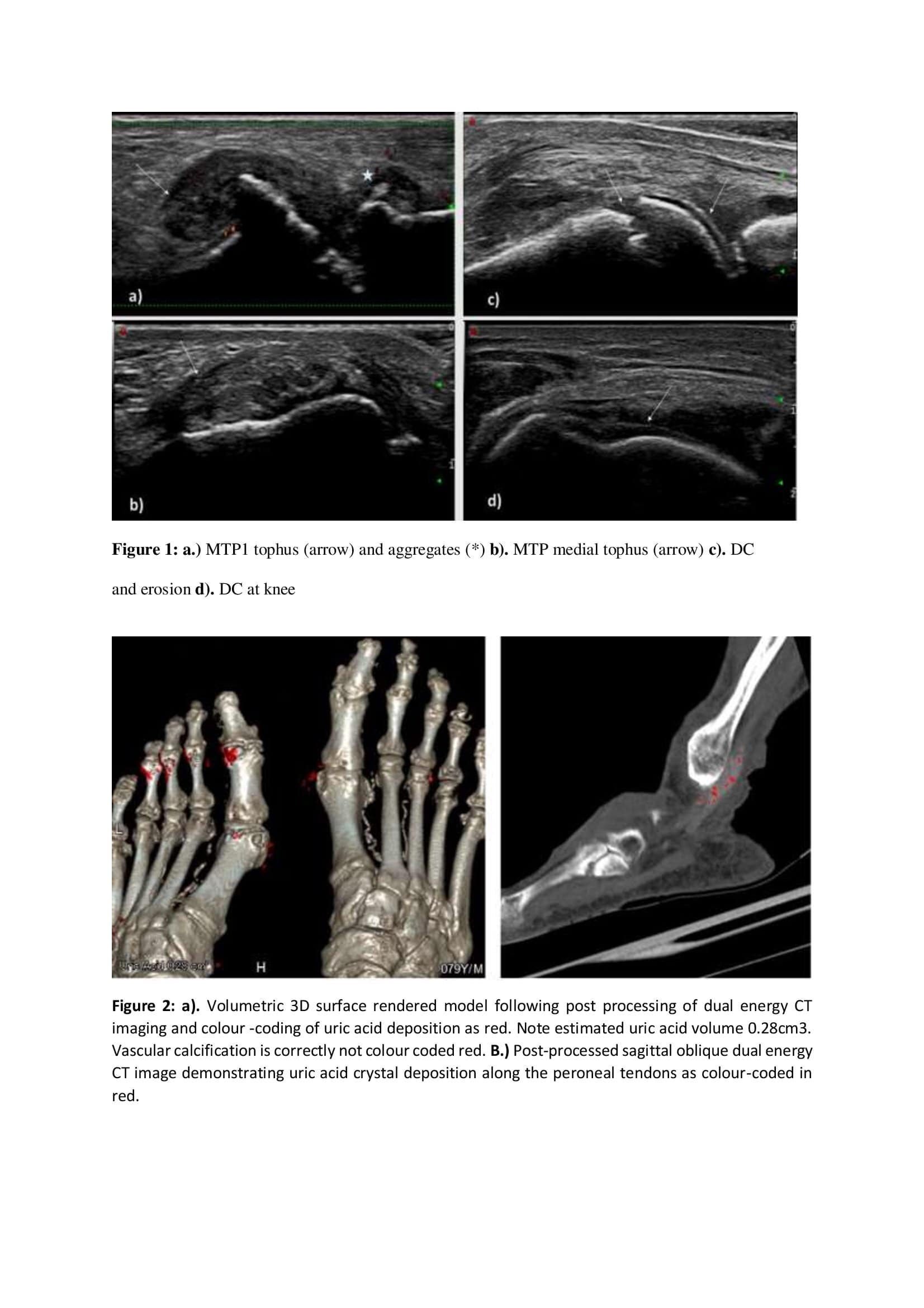
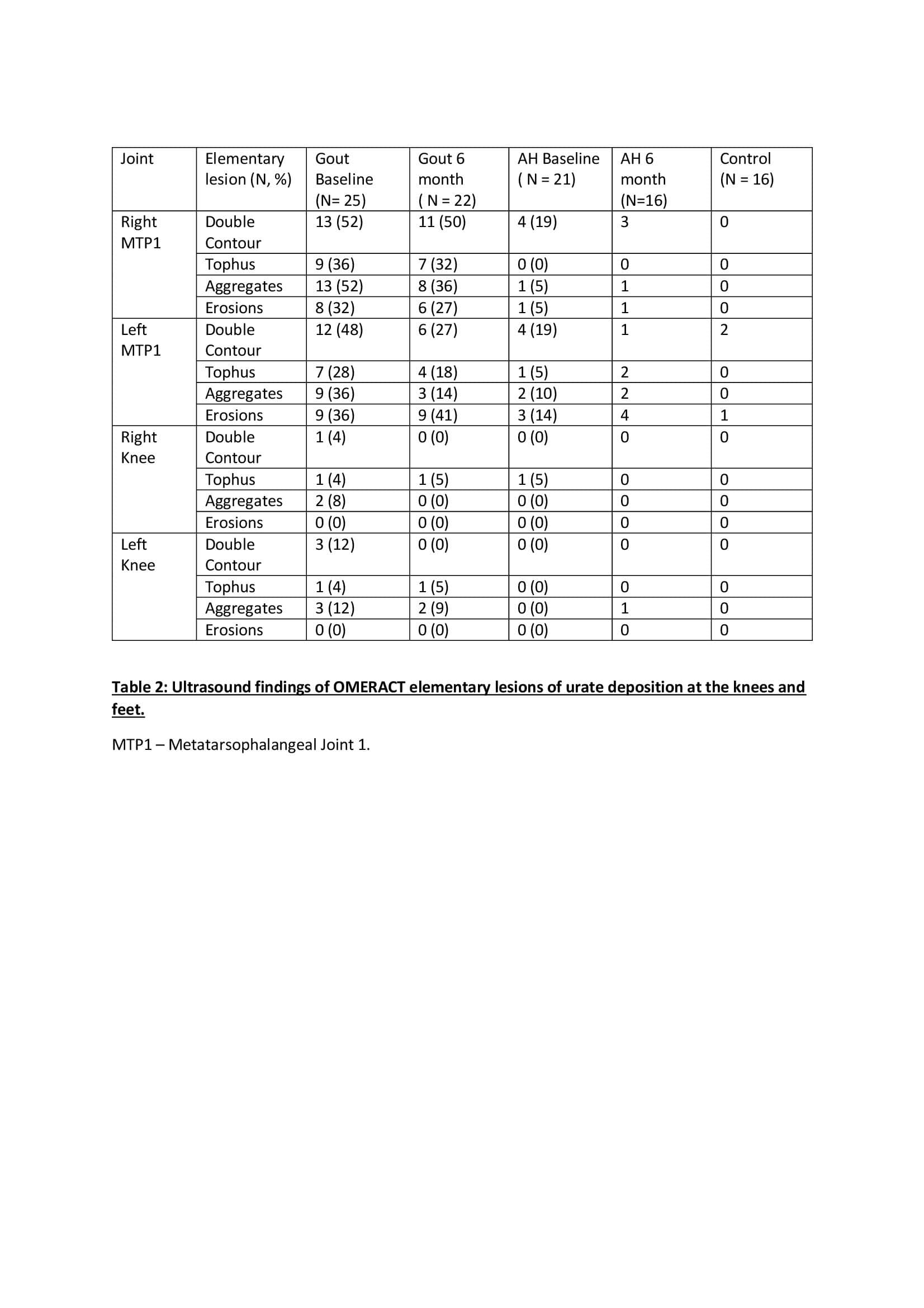
Methods: Patients with either AH or gout according to 2015 diagnostic criteria were prospectively recruited to undergo quantification of MSU deposition in the knees and feet using US and DECT. A urate quantification score for each imaging modality was calculated, for US images a semiquantitative composite scoring system ( 1= present, 0 = absent) was used to obtain a sum score for total elementary lesions of urate deposition (double contour, tophi, aggregate or erosion) across all four joints. Exact quantification of urate deposition was calculated using specific quantification software and recorded as a deposition urate score during DECT. Gout patients underwent 6 months of treatment with urate lowering therapy (ULT) in a treat to target approach and follow up US and DECT after six months of treatment.
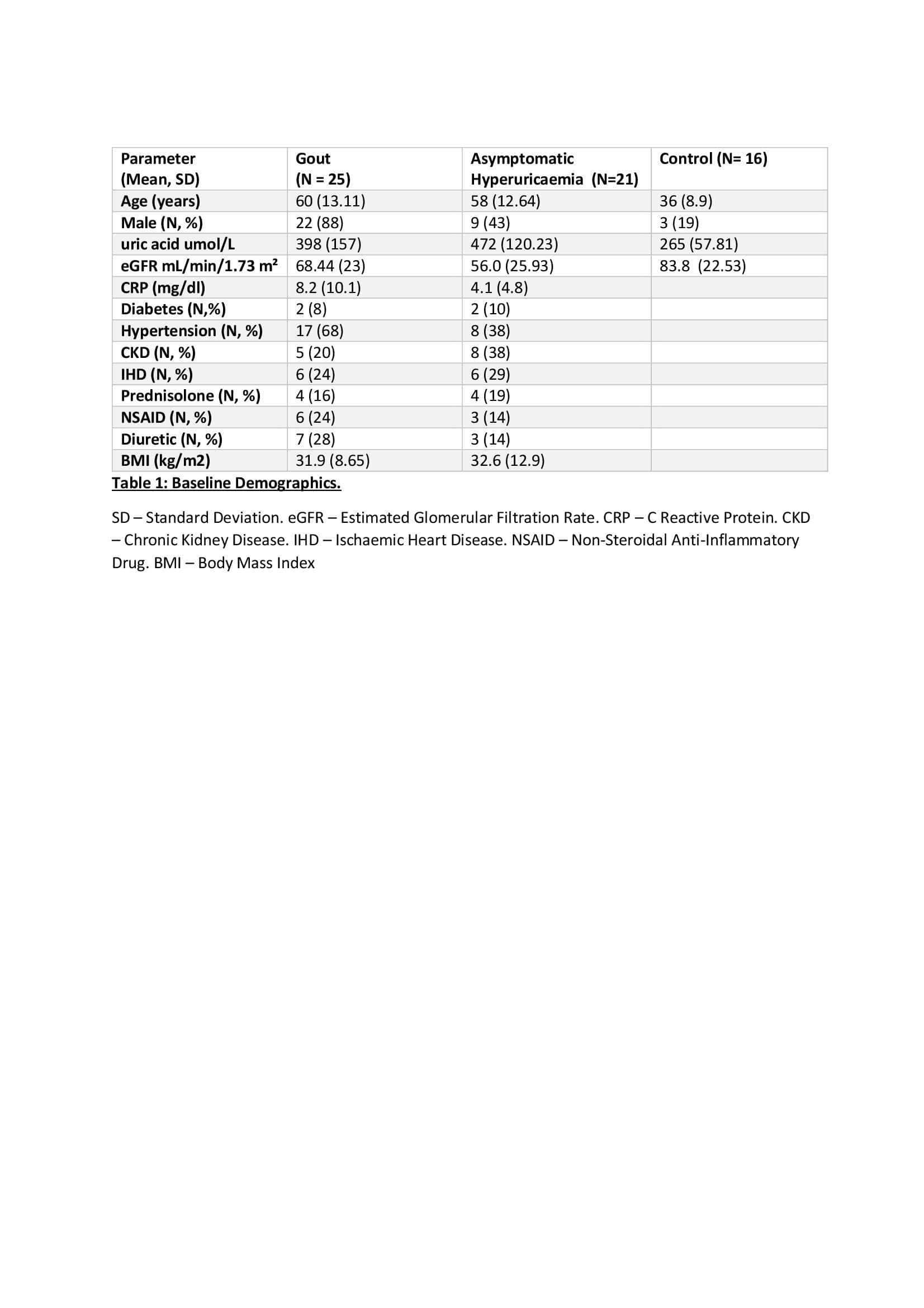
Results: A total of 62 patients (gout=25, AH=21, Control=16) were recruited. Mean (SD) age was 60 (13.11) years in gout, 58 (12.64) years in AH and 36 (8.9) years in control groups. Mean sUA umol/L levels at baseline in gout, AH and control were (398, 472 and 265) respectively.
For the gout cohort the mean (SD) US score at baseline was 3.64 (2.52) and on repeat US following 6 months of ULT this reduced to 2.68 (2.01). In the AH group the mean (SD) US score at baseline was 0.81 (0.98). There is a significant difference (P< 0.01) between the mean baseline US score in Gout and AH patients.
22 and 18 patients underwent baseline DECT imaging of the feet from the Gout and AH groups respectively. The Mean (SD) deposition urate score in the gout cohort at baseline was 0.104 (0.306.) Following 6 months of ULT the mean (SD) urate deposition score was 0.069 (0.246). The mean (SD) deposition urate score in the AH group was 0.782 (0.155).
In the gout cohort of patients there is a significant correlation between the sum US Score and the DECT deposition urate score ( Spearman correlation coefficient .544).
Conclusion: US and DECT imaging modalities demonstrate correlation in urate quantification in patients with gout.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Flood R, Saeed A, Harrington K, Shortt C, Mullan R, Kane D. Comparison of Urate Quantification in Gout and Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia by Ultrasound and Dual Energy Computed Tomography [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-urate-quantification-in-gout-and-asymptomatic-hyperuricemia-by-ultrasound-and-dual-energy-computed-tomography/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-urate-quantification-in-gout-and-asymptomatic-hyperuricemia-by-ultrasound-and-dual-energy-computed-tomography/